|
Leader Of The Opposition (Thailand)
The Leader of the Opposition in the House of Representatives (; ), more commonly described as the Leader of the Opposition, is the politician in the politics of Thailand who leads the main minority party in the House of Representatives. The Leader of the Opposition is the leader of the largest political party in the House of Representatives that is not in government and the member of the party do not hold the position of speaker or deputy speaker of the House of Representatives. Following the Westminster-style parliamentary system, Thailand has had an official Leader of the Opposition since 1975. Under the 2017 Constitution the Leader of the Opposition was given an official role within the Thai political system. The constitution stipulates that the Leader of the Opposition must be selected after the Prime Minister and the Cabinet has taken office. To be nominated as candidate one must be the leader of the largest political party with no member holding any ministerial positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leader Of The Opposition
The Leader of the Opposition is a title traditionally held by the leader of the Opposition (parliamentary), largest political party not in government, typical in countries utilizing the parliamentary system form of government. The leader of the opposition is typically seen as an alternative prime minister, premier, first minister, or chief minister to the incumbent; in the Westminster system, they head a rival alternative government known as the shadow cabinet or opposition frontbencher, front bench. The same term is also used to refer to the leader of the largest political party that is not in Executive (government), government in subnational state, provincial, and other regional and local legislatures. The full title for the Leader of the Opposition is the ''Leader of His Majesty's Most Loyal Opposition'' in the United Kingdom and in many Commonwealth realms. Current leaders of the opposition Parliamentary systems * Leader of the Opposition (Albania) (unofficial position) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2017 Constitution Of Thailand
The Constitution of the Kingdom of Thailand (; ) provides the basis for the rule of law in Thailand. Since the abolition of the absolute monarchy in 1932, Thailand has had 20 charters or constitutions. Many changes followed military coups, reflecting the high degree of political instability in the country. After each successful coup, military regimes abrogated the existing constitution, generally without public consultation. The 1997 constitution of Thailand, often called the "people's constitution", was considered a landmark in terms of the degree of public participation involved in its drafting as well as the democratic nature of its articles. It stipulated an elected bicameral legislature, and many human rights were explicitly acknowledged for the first time. Many of these reforms disappeared in the military coup of 2006. The current constitution was adopted in 2017. The 105-page, 279-article proposed constitution was approved by 61.4 percent of Thai voters with 59. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
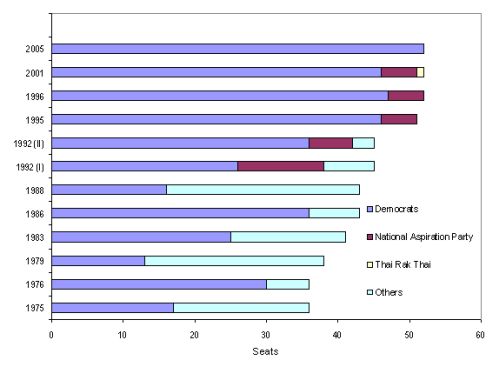
Democrat Party (Thailand)
The Democrat Party () is a conservative List of political parties in Thailand, Thai political party. The party is the oldest active political party in Thailand, it was founded in 1946 as a royalist party; it now upholds a Conservatism, liberal-conservative and Market economy, pro-market position. The Democrat Party made its best showings in parliament in 1948, 1976, and 1996. It has never won an outright parliamentary majority. The party's electoral support bases are southern Thailand and Bangkok, although the party's strength in Bangkok has declined rapidly since the 2019 Thai general election, 2019 general election. Since 2004 Bangkok gubernatorial election, 2004, Democrat candidates won three elections for the governorship of Bangkok. From 2005 to 2019, the Democrat Party was led by Abhisit Vejjajiva, former Prime Minister of Thailand, prime minister. Names The Thai name of the party, ''Prachathipat'' (ประชาธิปัตย์), is derived from the word ''prach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mom Rajawongse
The precedence of Thai royalty follows a system of ranks known as ''thanandon'' (), which are accompanied by royal titles. The Sovereign There are two styles which can be used for a king in ordinary speech, depending on whether he has been crowned: *Crowned kings: ''Phra Bat Somdet Phra Chao Yu Hua'' (wikt:เจ้า, เจ้า; ) is the style used in ordinary speech when referring to the kings of Thailand after their coronation. This style may be used in two ways: **Preceding the name of the king; e.g., ''Phra Bat Somdet Phra Chao Yu Hua Phumiphon Adunyadet'' (; His Majesty King Bhumibol Adulyadej). **More formally it can be split across the name, possibly with the omission (or modification) of the words ''"Phra Chao Yu Hua"''; e.g., ''Phra Bat Somdet Phra Paramintara Maha Phumiphon Adunyadet'' () and ''Phra Bat Somdet Phra Paramindara Maha Prajadhipok Phra Pokklao Chao Yu Hua'' (). *Uncrowned kings: ''Somdet Phra Chao Yu Hua'' (), normally preceding the king's name, is res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seni Pramoj In 1945 (cropped)
Seni was an ancient Egyptian official with the titles ''king's son of Kush'' (''Viceroy of Kush''), ''overseer of the southern countries'' and ''mayor of the southern city'' ( Thebes). He was in office under the kings Thutmosis I and Thutmosis II. As ''king's son of Kush'' he was the main official in charge of the Nubian provinces. Seni is mainly known from the inscription on two doorjambs found at the Nubian fortress of Kumma, where his titles are listed including ''overseer of the double granary of Amun''.Kurt Sethe: ''Urkunden der 18. Dynastie, vol. 1: Historisch-biographische Urkunden'', Leipzig 1906, p. 142 (online The inscription is not dated, but there was found a biographical inscription at Semna (Nubia) , Semna where there is reported that an official was promoted by Thutmosis I to a ''king's son''. The name of the person in the inscription is lost, but there also appears the title ''overseer of the double granary of Amun'', indicating that this inscription might belong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Audit Commission
State most commonly refers to: * State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory **Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country **Nation state, a state where the majority identify with a single nation (with shared culture or ethnic group) ** Constituent state, a political subdivision of a state ** Federated state, constituent states part of a federation *** U.S. state * State of nature, a concept within philosophy that describes the way humans acted before forming societies or civilizations State may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Literature * ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State * ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States * '' Our State'', a monthly magazine published in North Carolina and formerly called ''The State'' * The State (Larry Niven), a fictional future government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Anti-Corruption Commission (Thailand)
The National Anti-Corruption Commission ( Abrv: NACC; , ) is a constitutional organization of Thailand. It is sometimes confused with the Anti-Corruption Organization of Thailand (ACT), a private foundation. History The Constitution of the Kingdom of Thailand B.E. 2517 (1974) Section 66 stated "The State should organize government service works and other works efficiently and should take all steps to prevent and suppress the quest for benefits by corruption means." The Counter Corruption Act was promulgated in 1975 and allowed the establishment of Office of the Commission of Counter Corruption (OCCC), but OCCC was granted little power to combat corruption. The Constitution of the Kingdom of Thailand B.E. 2540 (1997) added checks and balances to assure integrity and transparency in government. New independent government agencies like the National Counter Corruption Commission, the Constitutional Court, the Administrative Court, the Office of the Auditor-General, the Nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ombudsmen
An ombudsman ( , also ) is a government employee who investigates and tries to resolve complaints, usually through recommendations (binding or not) or mediation. They are usually appointed by the government or by parliament (often with a significant degree of independence). Ombudsmen also aim to identify systemic issues leading to poor service or breaches of people's rights. At the national level, most ombudsmen have a wide mandate to deal with the entire public sector, and sometimes also elements of the private sector (for example, contracted service providers). In some cases, there is a more restricted mandate to a certain sector of society. More recent developments have included the creation of specialized children's ombudsmen. In some countries, an inspector general, citizen advocate or other official may have duties similar to those of a national ombudsman and may also be appointed by a legislature. Below the national level, an ombudsman may be appointed by a state, lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Election Commission (Thailand)
The Election Commission (, ) is an Independent Government Agencies of Thailand, independent government agency and the sole election management body of Thailand. It oversees government elections (parliamentary elections and local elections) as well as referendums throughout the Thailand, Kingdom of Thailand. Established by the 1997 constitution, the Election Commission (EC) has extensive powers to manage, oversee, and regulate the electoral process. The EC has reacted to irregularities in the 2000 Thai Senate election, 2000 Senate elections, the April 2006 Thai general election, 2006 House elections, and the 2007 Thai general election, 2007 House elections, forcing re-elections and disqualifying many candidates. Election Commission is heavily criticized for untrustworthy and unprofessional practice during 2023 election, some critics are expected that the commission itself is under the influence of the military and orchestrated election fraud itself. Roles and responsibilities The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Court Of Thailand
The Constitutional Court (, , ), officially the Constitutional Court of the Kingdom of Thailand, is a Thai court created by the 1997 constitution with jurisdiction over the constitutionality of parliamentary acts, royal decrees, draft legislation, as well as the appointment and removal of public officials and issues regarding political parties. The current court is part of the judicial branch of the Thai national government. The court, along with the 1997 constitution, was dissolved and replaced by a Constitutional Tribunal in 2006 following the 2006 Thai coup d'état. While the Constitutional Court had 15 members, seven from the judiciary and eight selected by a special panel, the Constitution Tribunal had nine members, all from the judiciary. A similar institution, consisting of nine members, was again established by the 2007 Constitution. The Constitutional Court has provoked much public debate, both regarding the court's jurisdiction and composition as well as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ex-officio
An ''ex officio'' member is a member of a body (notably a board, committee, or council) who is part of it by virtue of holding another office. The term ''List of Latin phrases (E)#ex officio, ex officio'' is Latin, meaning literally 'from the office', and the sense intended is 'by right of office'; its use dates back to the Roman Republic. According to ''Robert's Rules of Order'', the term denotes only how one becomes a member of a body. Accordingly, the rights of an ''ex officio'' member are exactly the same as other members unless otherwise stated in regulations or bylaws. It relates to the notion that the position refers to the position the ex officio holds, rather than the individual that holds the position. In some groups, ''ex officio'' members may frequently abstain from voting. Opposite notions are dual mandate, when the same person happens to hold two offices or more, although these offices are not in themselves associated; and personal union, when two states share the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cabinet Ministries Of Thailand
The Government Ministries of Thailand (: ''Krasuang'') are the government agencies that compose the executive branch of the Government of Thailand. Each ministry is headed by a minister of state (, ) and, depending on the prime minister, several deputy ministers ( . The combined heads of these agencies form the Cabinet of Thailand. There are 19 ministries. The combined employees of these departments make up the civil service of Thailand. Ministries History During the Rattanakosin Period, the kingdom's administration was similar to that of the Ayutthaya Period. There were two chief ministers (: the first running military affairs or ''samuhakalahom'' (, and the second ''Samuhanayok'' ( for civilian affairs. The civilian ministry was divided further into four ''kroms'' (, headed by a ''senabodi'' ( or 'minister'. This type of administration was called the '' Chatusadom'' ( : Rama V reforms King Chulalongkorn (Rama V), who had received a European education and traveled widel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |