|
Lead Polonide
Lead polonide is the polonide of lead, with the chemical formula of . It occurs naturally, as lead is produced in the alpha decay of polonium. Preparation Lead polonide can be formed by reacting polonium vapour and lead under a vacuum. Properties Lead polonide has a sodium chloride structure, which is the same as lead telluride. It has a cubic crystal structure, with the space group Fmm (No. 225), with lattice constant A lattice constant or lattice parameter is one of the physical dimensions and angles that determine the geometry of the unit cells in a crystal lattice, and is proportional to the distance between atoms in the crystal. A simple cubic crystal has ... ''a'' = 6.59 Å.Link) References {{Polonium compounds Lead(II) compounds Polonides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Monoxide
Lead(II) oxide, also called lead monoxide, is the inorganic compound with the molecular formula Pb O. It occurs in two polymorphs: litharge having a tetragonal crystal structure, and massicot having an orthorhombic crystal structure. Modern applications for PbO are mostly in lead-based industrial glass and industrial ceramics, including computer components. Types Lead oxide exists in two polymorphs: * Red tetragonal (α-PbO), obtained at temperatures below * Yellow orthorhombic (β-PbO), obtained at temperatures above Synthesis PbO may be prepared by heating lead metal in air at approximately . At this temperature it is also the end product of decomposition of other oxides of lead in air: :PbO2->[] Pb12O19 ->[] Pb12O17 ->[] Pb3O4 ->[] PbO Thermal decomposition of lead(II) nitrate or lead carbonate, lead(II) carbonate also results in the formation of PbO: :2 → 2 PbO + 4 + : → PbO + PbO is produced on a large scale as an intermediate product in r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Formula
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name since it does not contain any words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called '' empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of atoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice Constant
A lattice constant or lattice parameter is one of the physical dimensions and angles that determine the geometry of the unit cells in a crystal lattice, and is proportional to the distance between atoms in the crystal. A simple cubic crystal has only one lattice constant, the distance between atoms, but, in general, lattices in three dimensions have six lattice constants: the lengths ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' of the three cell edges meeting at a vertex, and the angles ''α'', ''β'', and ''γ'' between those edges. The crystal lattice parameters ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' have the dimension of length. The three numbers represent the size of the unit cell, that is, the distance from a given atom to an identical atom in the same position and orientation in a neighboring cell (except for very simple crystal structures, this will not necessarily be distance to the nearest neighbor). Their SI unit is the meter, and they are traditionally specified in angstroms (Å); an angstrom being 0.1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of a repeating pattern in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of the pattern that leave it unchanged. In three dimensions, space groups are classified into 219 distinct types, or 230 types if chiral copies are considered distinct. Space groups are discrete cocompact groups of isometries of an oriented Euclidean space in any number of dimensions. In dimensions other than 3, they are sometimes called Bieberbach groups. In crystallography, space groups are also called the crystallographic or Fedorov groups, and represent a description of the symmetry of the crystal. A definitive source regarding 3-dimensional space groups is the ''International Tables for Crystallography'' . History Space groups in 2 dimensions are the 17 wallpaper groups which have been known for several centuries, though the proof that the list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Crystal Structure
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals. There are three main varieties of these crystals: *Primitive cubic (abbreviated ''cP'' and alternatively called simple cubic) *Body-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cI'' or bcc) *Face-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cF'' or fcc) Note: the term fcc is often used in synonym for the ''cubic close-packed'' or ccp structure occurring in metals. However, fcc stands for a face-centered cubic Bravais lattice, which is not necessarily close-packed when a motif is set onto the lattice points. E.g. the diamond and the zincblende lattices are fcc but not close-packed. Each is subdivided into other variants listed below. Although the ''unit cells'' in these crystals are conventionally taken to be cubes, the primitive unit cells often are not. Bravais lattices The three Bravais latices in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
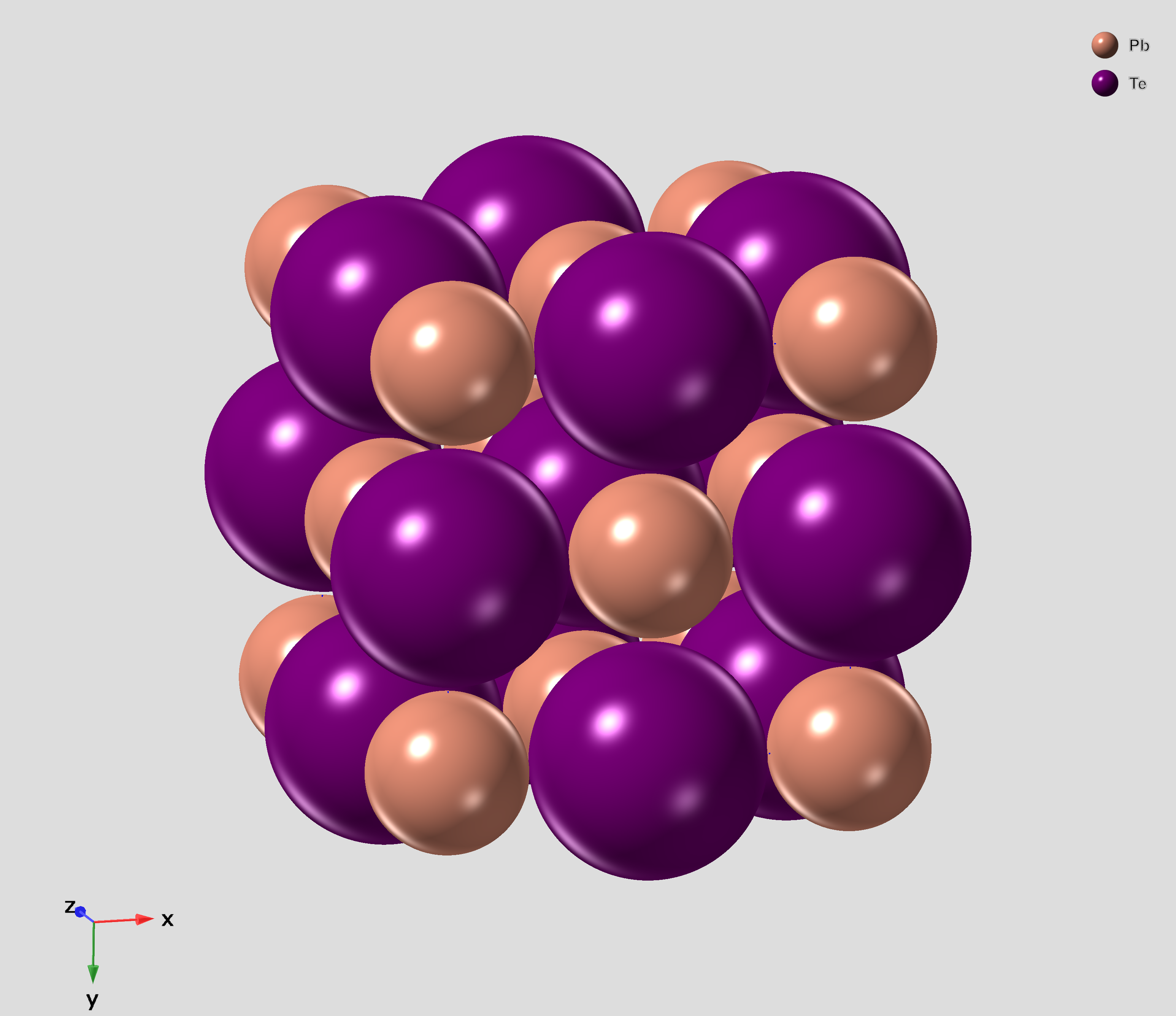
Lead Telluride
Lead telluride is a compound of lead (element), lead and tellurium (PbTe). It crystallizes in the NaCl crystal structure with Pb atoms occupying the cation and Te forming the anionic lattice. It is a narrow gap semiconductor with a band gap of 0.32 eV. It occurs naturally as the mineral altaite. Properties * Dielectric constant ~1000. * Electron Effective mass (solid-state physics), Effective mass ~ 0.01Electron rest mass, ''m''e * Hole mobility, μp = 600 cm2 V−1 s−1 (0 K); 4000 cm2 V−1 s−1 (300 K) * Seebeck coefficient: ~326 μV/K (undoped, at 300K), ~200 μV/K (Ag-doped) Applications PbTe has proven to be a very important intermediate Thermoelectric materials, thermoelectric material. The performance of thermoelectric materials can be evaluated by the figure of merit, ZT=S^2\sigma T/\kappa, in which S is the Seebeck coefficient, \sigma is the Electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conducti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as Salt#Edible salt, edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs as the mineral halite. In its edible form, it is commonly used as a condiment and curing (food preservation), food preservative. Large quantities of sodium chloride are used in many industrial processes, and it is a major source of sodium and chlorine compounds used as feedstocks for further Chemical synthesis, chemical syntheses. Another major application of sodium chloride is deicing of roadways in sub-freezing weather. Uses In addition to the many familiar domestic uses of salt, more dominant applications of the approximately 250 million tonnes per year production (2008 data) include chemicals and de-icing.Westphal, Gisbert ''et al.'' (2002) "Sodium Chloride" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim . Chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polonium
Polonium is a chemical element; it has symbol Po and atomic number 84. A rare and highly radioactive metal (although sometimes classified as a metalloid) with no stable isotopes, polonium is a chalcogen and chemically similar to selenium and tellurium, though its metallic character resembles that of its horizontal neighbors in the periodic table: thallium, lead, and bismuth. Due to the short half-life of all its isotopes, its natural occurrence is limited to tiny traces of the fleeting polonium-210 (with a half-life of 138 days) in uranium ores, as it is the penultimate daughter of natural uranium-238. Though two longer-lived isotopes exist (polonium-209 with a half-life of 124 years and polonium-208 with a half-life of 2.898 years), they are much more difficult to produce. Today, polonium is usually produced in milligram quantities by the neutron irradiation of bismuth. Due to its intense radioactivity, which results in the radiolysis of chemical bonds and radioactive self-he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angewandte Chemie
''Angewandte Chemie'' (, meaning "Applied Chemistry") is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that is published by Wiley-VCH on behalf of the German Chemical Society (Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker). Publishing formats include feature-length reviews, short highlights, research communications, minireviews, essays, book reviews, meeting reviews, correspondences, corrections, and obituaries. This journal contains review articles covering all aspects of chemistry. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal had a 2023 impact factor of 16.1. Editions The journal appears in two editions with separate volume and page numbering: a German edition, ''Angewandte Chemie'', and a fully English-language edition, ''Angewandte Chemie International Edition''. The editions are identical in content with the exception of occasional reviews of German-language books or German translations of IUPAC recommendations. Publication history In 1887, Ferdinand Fischer established the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Decay
Alpha decay or α-decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus). The parent nucleus transforms or "decays" into a daughter product, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an atomic number that is reduced by two. An alpha particle is identical to the nucleus of a helium-4 atom, which consists of two protons and two neutrons. It has a charge of and a mass of , and is represented as ^_\alpha. For example, uranium-238 undergoes alpha decay to form thorium-234. While alpha particles have a charge , this is not usually shown because a nuclear equation describes a nuclear reaction without considering the electrons – a convention that does not imply that the nuclei necessarily occur in neutral atoms. Alpha decay typically occurs in the heaviest nuclides. Theoretically, it can occur only in nuclei somewhat heavier than nickel (element 28), where the overall binding energy per nucleon is no longer a maximum a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable nuclide, stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its Amphoterism, amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and base (chemistry), bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Lead compounds, Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Sulfide
Lead sulfide refers to two compounds containing lead and sulfur: *Lead(II) sulfide Lead(II) sulfide (also spelled '' sulphide'') is an inorganic compound with the formula Pb S. Galena is the principal ore and the most important compound of lead. It is a semiconducting material with niche uses. Formation, basic properties, rel ..., PbS, containing lead in the +2 oxidation state, naturally occurring as the mineral galena * Lead(IV) sulfide, PbS2, containing lead in the +4 oxidation state {{Chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |