|
Lazy Learning
(Not to be confused with the lazy learning regime, see Neural tangent kernel). In machine learning, lazy learning is a learning method in which generalization of the training data is, in theory, delayed until a query is made to the system, as opposed to eager learning, where the system tries to generalize the training data before receiving queries. The primary motivation for employing lazy learning, as in the K-nearest neighbors algorithm, used by online recommendation systems ("people who viewed/purchased/listened to this movie/item/tune also ...") is that the data set is continuously updated with new entries (e.g., new items for sale at Amazon, new movies to view at Netflix, new clips at YouTube, new music at Spotify or Pandora). Because of the continuous update, the "training data" would be rendered obsolete in a relatively short time especially in areas like books and movies, where new best-sellers or hit movies/music are published/released continuously. Therefore, one cannot r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Neural Tangent Kernel
In the study of Artificial neural network, artificial neural networks (ANNs), the neural tangent kernel (NTK) is a Kernel method, kernel that describes the evolution of Deep learning, deep artificial neural networks during their training by gradient descent. It allows ANNs to be studied using theoretical tools from kernel methods. In general, a kernel is a Positive-definite kernel, positive-semidefinite Symmetric function, symmetric function of two inputs which represents some notion of similarity between the two inputs. The NTK is a specific kernel derived from a given neural network; in general, when the neural network parameters change during training, the NTK evolves as well. However, in the limit of large layer width the NTK becomes constant, revealing a duality between training the wide neural network and kernel methods: gradient descent in the Large width limits of neural networks, infinite-width limit is fully equivalent to kernel gradient descent with the NTK. As a result, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task (computing), tasks without explicit Machine code, instructions. Within a subdiscipline in machine learning, advances in the field of deep learning have allowed Neural network (machine learning), neural networks, a class of statistical algorithms, to surpass many previous machine learning approaches in performance. ML finds application in many fields, including natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, email filtering, agriculture, and medicine. The application of ML to business problems is known as predictive analytics. Statistics and mathematical optimisation (mathematical programming) methods comprise the foundations of machine learning. Data mining is a related field of study, focusing on exploratory data analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Training Data
In machine learning, a common task is the study and construction of algorithms that can learn from and make predictions on data. Such algorithms function by making data-driven predictions or decisions, through building a mathematical model from input data. These input data used to build the model are usually divided into multiple data sets. In particular, three data sets are commonly used in different stages of the creation of the model: training, validation, and test sets. The model is initially fit on a training data set, which is a set of examples used to fit the parameters (e.g. weights of connections between neurons in artificial neural networks) of the model. The model (e.g. a naive Bayes classifier) is trained on the training data set using a supervised learning method, for example using optimization methods such as gradient descent or stochastic gradient descent. In practice, the training data set often consists of pairs of an input vector (or scalar) and the correspondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Eager Learning
In artificial intelligence Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ..., eager learning is a learning method in which the system tries to construct a general, input-independent target function during training of the system, as opposed to lazy learning, where generalization beyond the training data is delayed until a query is made to the system. The main advantage gained in employing an eager learning method, such as an artificial neural network, is that the target function will be approximated globally during training, thus requiring much less space than using a lazy learning system. Eager learning systems also deal much better with noise in the training data. Eager learning is an example of offline learning, in which post-training queries to the system have no effect on the sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
K-nearest Neighbors Algorithm
In statistics, the ''k''-nearest neighbors algorithm (''k''-NN) is a Non-parametric statistics, non-parametric supervised learning method. It was first developed by Evelyn Fix and Joseph Lawson Hodges Jr., Joseph Hodges in 1951, and later expanded by Thomas M. Cover, Thomas Cover. Most often, it is used for statistical classification, classification, as a ''k''-NN classifier, the output of which is a class membership. An object is classified by a plurality vote of its neighbors, with the object being assigned to the class most common among its ''k'' nearest neighbors (''k'' is a positive integer, typically small). If ''k'' = 1, then the object is simply assigned to the class of that single nearest neighbor. The ''k''-NN algorithm can also be generalized for regression analysis, regression. In ''-NN regression'', also known as ''nearest neighbor smoothing'', the output is the property value for the object. This value is the average of the values of ''k'' nearest neighbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Recommendation System
Recommendation may refer to: * European Union recommendation, in international law * Letter of recommendation, in employment or academia * W3C recommendation, in Internet contexts * A computer-generated recommendation created by a recommender system A recommender system (RecSys), or a recommendation system (sometimes replacing ''system'' with terms such as ''platform'', ''engine'', or ''algorithm'') and sometimes only called "the algorithm" or "algorithm", is a subclass of information fi ... See also * * * * * * * * Commendation (other) * Commend {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
K-nearest Neighbor Algorithm
In statistics, the ''k''-nearest neighbors algorithm (''k''-NN) is a non-parametric supervised learning method. It was first developed by Evelyn Fix and Joseph Hodges in 1951, and later expanded by Thomas Cover. Most often, it is used for classification, as a ''k''-NN classifier, the output of which is a class membership. An object is classified by a plurality vote of its neighbors, with the object being assigned to the class most common among its ''k'' nearest neighbors (''k'' is a positive integer, typically small). If ''k'' = 1, then the object is simply assigned to the class of that single nearest neighbor. The ''k''-NN algorithm can also be generalized for regression. In ''-NN regression'', also known as '' nearest neighbor smoothing'', the output is the property value for the object. This value is the average of the values of ''k'' nearest neighbors. If ''k'' = 1, then the output is simply assigned to the value of that single nearest neighbor, also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
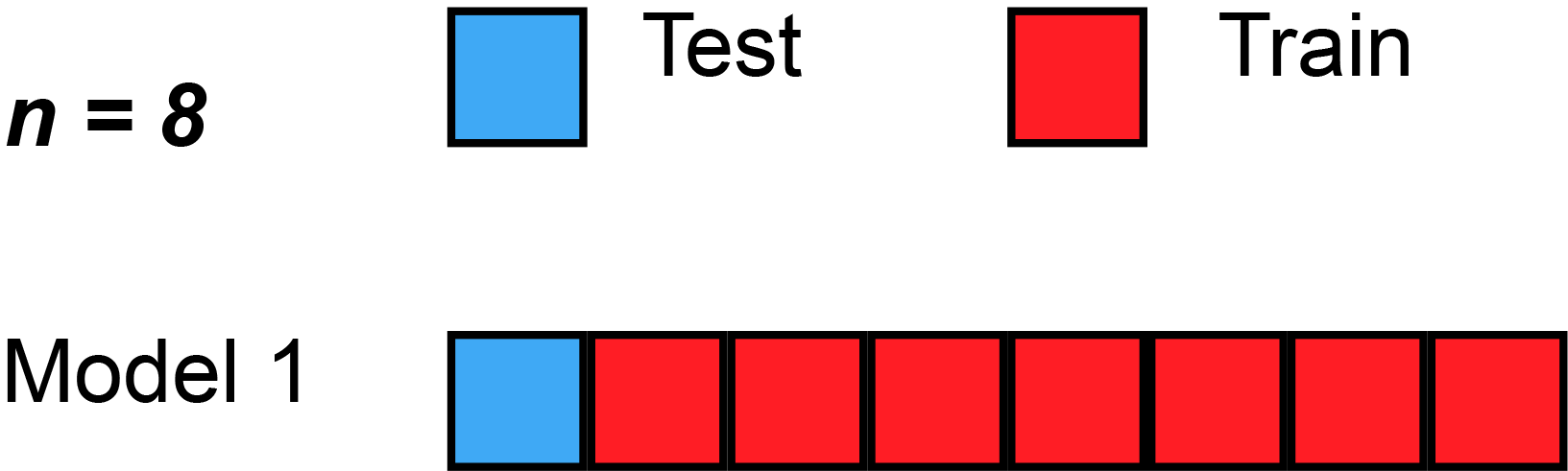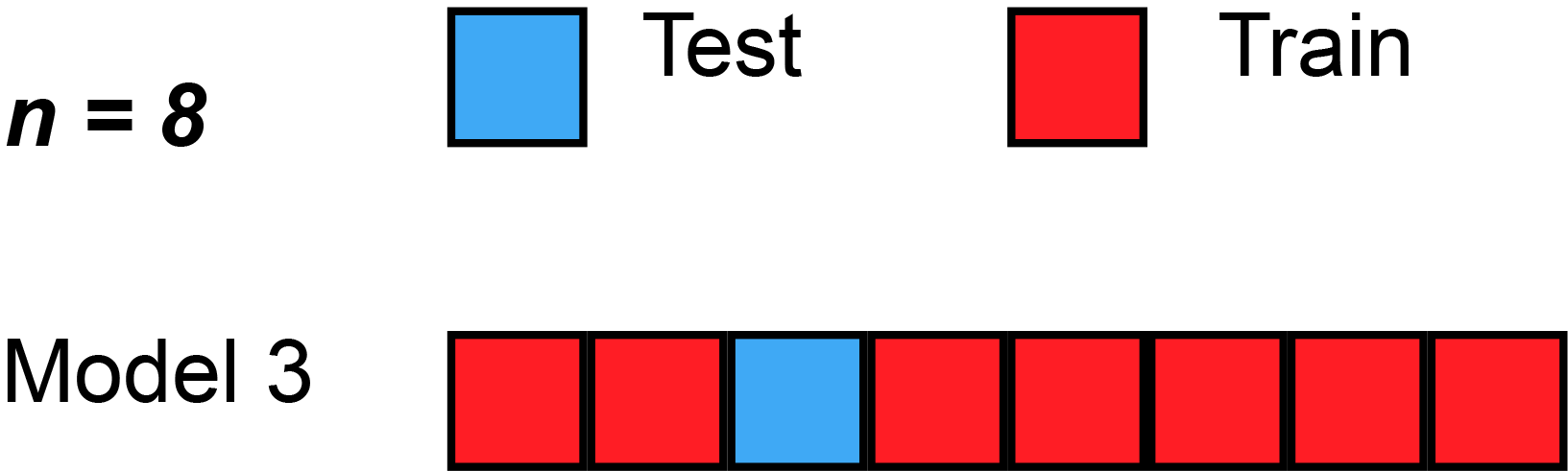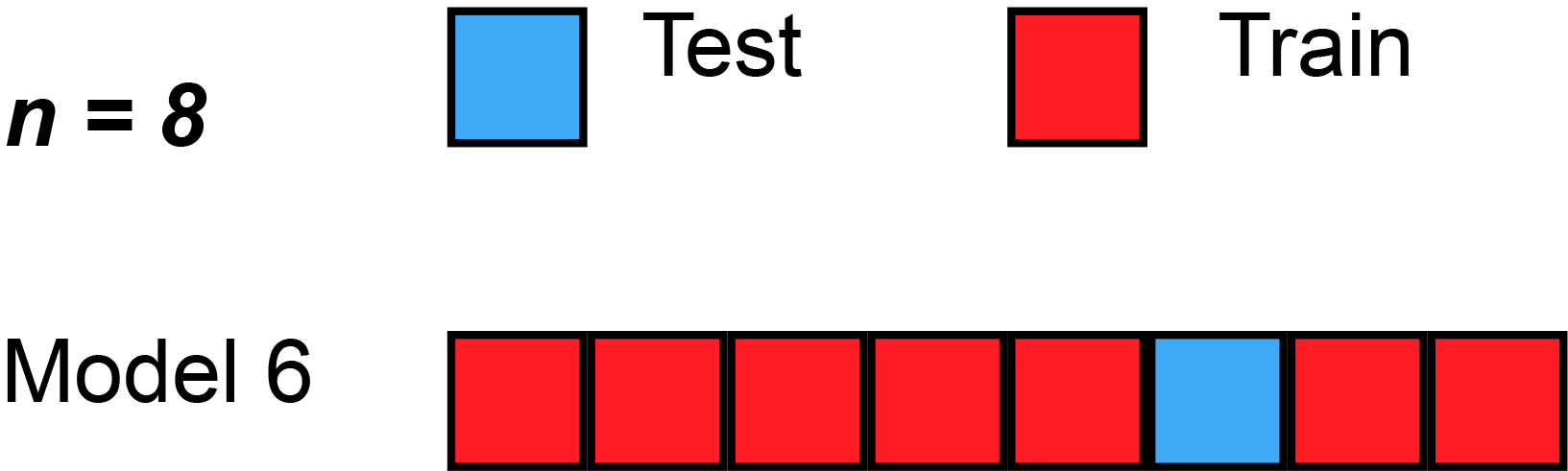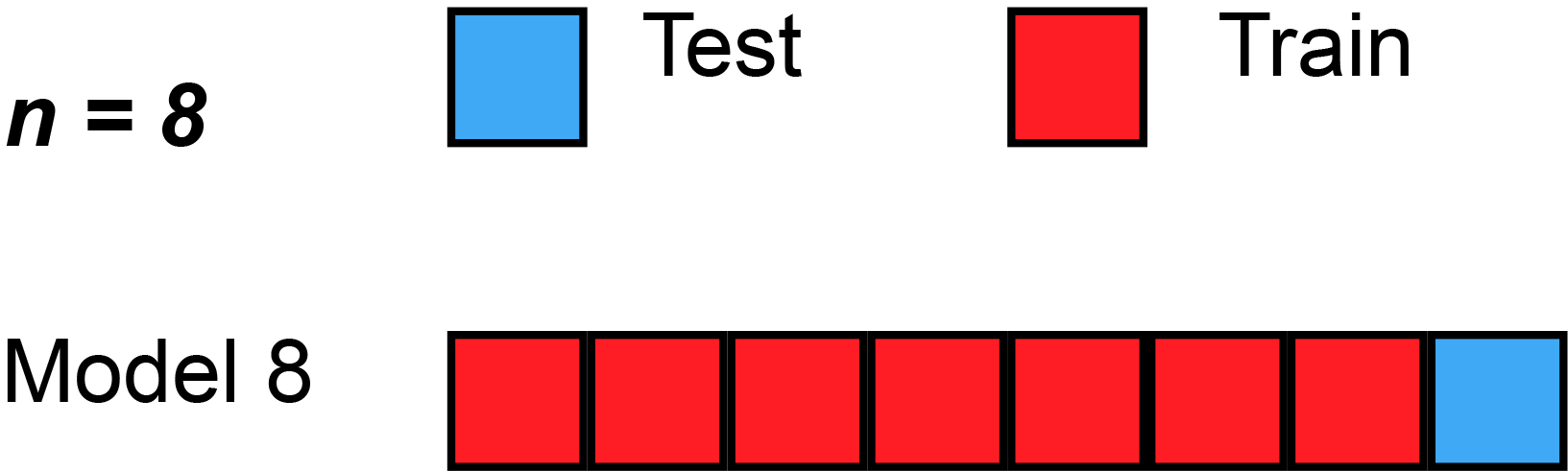 |
PRESS Statistic
In statistics, the predicted residual error sum of squares (PRESS) is a form of cross-validation used in regression analysis to provide a summary measure of the fit of a model to a sample of observations that were not themselves used to estimate the model. It is calculated as the sum of squares of the prediction residuals for those observations. Specifically, the PRESS statistic is an exhaustive form of cross-validation, as it tests all the possible ways that the original data can be divided into a training and a validation set. Procedure Instead of ''fitting'' only one model on all data, leave-one-out cross-validation is used to fit N models (on N observations) where for each model one data point is left out from the training set. The out-of-sample predicted value is calculated for the omitted observation in each case, and the PRESS statistic is calculated as the sum of the squares of all the resulting prediction errors: : \operatorname =\sum_^n (y_i - \hat_)^2 Usage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Entrez
The Entrez () Global Query Cross-Database Search System is a federated search engine, or web portal that allows users to search many discrete health sciences databases at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) website. The NCBI is a part of the National Library of Medicine (NLM), which is itself a department of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which in turn is a part of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The name "Entrez" (a greeting meaning "Come in" in French) was chosen to reflect the spirit of welcoming the public to search the content available from the NLM. Entrez Global Query is an integrated search and retrieval system that provides access to all databases simultaneously with a single query string and user interface. Entrez can efficiently retrieve related sequences, structures, and references. The Entrez system can provide views of gene and protein sequences and chromosome maps. Some textbooks are also available onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
National Center For Biotechnology Information
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is part of the National Library of Medicine (NLM), a branch of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is approved and funded by the government of the United States. The NCBI is located in Bethesda, Maryland, and was founded in 1988 through legislation sponsored by US Congressman Claude Pepper. The NCBI houses a series of databases relevant to biotechnology and biomedicine and is an important resource for bioinformatics tools and services. Major databases include GenBank for DNA sequences and PubMed, a bibliographic database for biomedical literature. Other databases include the NCBI Epigenomics database. All these databases are available online through the Entrez search engine. NCBI was directed by David Lipman, one of the original authors of the BLAST sequence alignment program and a widely respected figure in bioinformatics. GenBank NCBI had responsibility for making available the GenBank DNA seque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
K-nearest Neighbors
In statistics, the ''k''-nearest neighbors algorithm (''k''-NN) is a non-parametric supervised learning method. It was first developed by Evelyn Fix and Joseph Hodges in 1951, and later expanded by Thomas Cover. Most often, it is used for classification, as a ''k''-NN classifier, the output of which is a class membership. An object is classified by a plurality vote of its neighbors, with the object being assigned to the class most common among its ''k'' nearest neighbors (''k'' is a positive integer, typically small). If ''k'' = 1, then the object is simply assigned to the class of that single nearest neighbor. The ''k''-NN algorithm can also be generalized for regression. In ''-NN regression'', also known as '' nearest neighbor smoothing'', the output is the property value for the object. This value is the average of the values of ''k'' nearest neighbors. If ''k'' = 1, then the output is simply assigned to the value of that single nearest neighbor, also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Local Regression
Local regression or local polynomial regression, also known as moving regression, is a generalization of the moving average and polynomial regression. Its most common methods, initially developed for scatterplot smoothing, are LOESS (locally estimated scatterplot smoothing) and LOWESS (locally weighted scatterplot smoothing), both pronounced . They are two strongly related non-parametric regression methods that combine multiple regression models in a ''k''-nearest-neighbor-based meta-model. In some fields, LOESS is known and commonly referred to as Savitzky–Golay filter (proposed 15 years before LOESS). LOESS and LOWESS thus build on "classical" methods, such as linear and nonlinear least squares regression. They address situations in which the classical procedures do not perform well or cannot be effectively applied without undue labor. LOESS combines much of the simplicity of linear least squares regression with the flexibility of nonlinear regression. It does this b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |