|
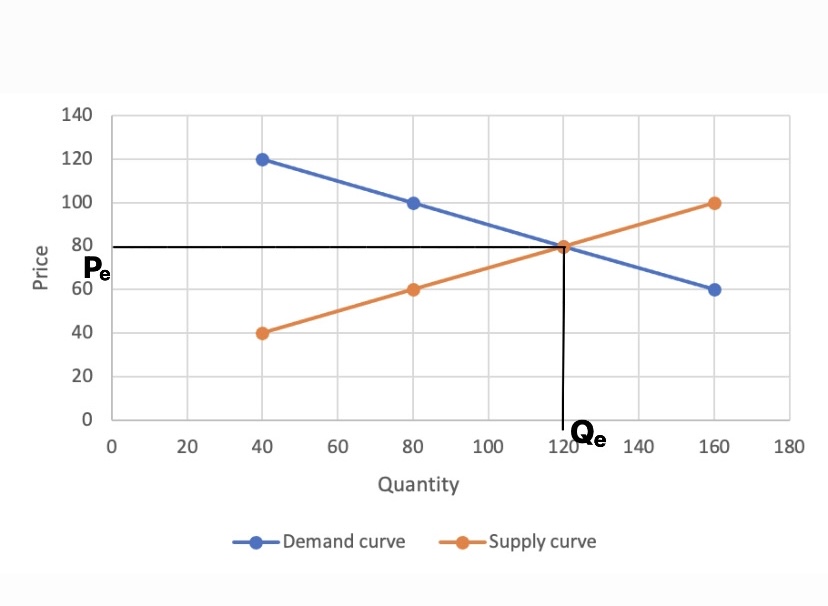
Law Of Demand
In microeconomics, the law of demand is a fundamental principle which states that there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. In other words, "conditional on ceteris paribus, all else being equal, as the price of a Goods, good increases (↑), quantity demanded will decrease (↓); conversely, as the price of a good decreases (↓), quantity demanded will increase (↑)". Alfred Marshall worded this as: "When we say that a person's demand for anything increases, we mean that he will buy more of it than he would before at the same price, and that he will buy as much of it as before at a higher price". The law of demand, however, only makes a qualitative statement in the sense that it describes the direction of change in the amount of quantity demanded but not the magnitude of change. The law of demand is represented by a graph called the demand curve, with quantity demanded on the x-axis and price on the y-axis. Demand curves are downward sloping by defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illustration Of Law Of Demand
An illustration is a decoration, interpretation, or visual explanation of a text, concept, or process, designed for integration in print and digitally published media, such as posters, flyers, magazines, books, teaching materials, animations, video games and films. An illustration is typically created by an illustrator. Digital illustrations are often used to make websites and apps more user-friendly, such as the use of emojis to accompany digital type. Illustration also means providing an example; either in writing or in picture form. The origin of the word "illustration" is late Middle English (in the sense ‘illumination; spiritual or intellectual enlightenment’): via Old French from Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... from Latin ''illustratio''(n-), from the verb ''illustrare''. Illustration styles Contemporary illustration uses a wide range of styles and techniqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price Elasticity Of Demand
A good's price elasticity of demand (E_d, PED) is a measure of how sensitive the quantity demanded is to its price. When the price rises, quantity demanded falls for almost any good ( law of demand), but it falls more for some than for others. The price elasticity gives the percentage change in quantity demanded when there is a one percent increase in price, holding everything else constant. If the elasticity is −2, that means a one percent price rise leads to a two percent decline in quantity demanded. Other elasticities measure how the quantity demanded changes with other variables (e.g. the income elasticity of demand for consumer income changes). Price elasticities are negative except in special cases. If a good is said to have an elasticity of 2, it almost always means that the good has an elasticity of −2 according to the formal definition. The phrase "more elastic" means that a good's elasticity has greater magnitude, ignoring the sign. Veblen and Giffen goods are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxury Good
In economics, a luxury good (or upmarket good) is a good for which demand increases more than what is proportional as income rises, so that expenditures on the good become a more significant proportion of overall spending. Luxury goods are in contrast to necessity goods, where demand increases proportionally less than income. ''Luxury goods'' is often used synonymously with superior goods. Definition and etymology The word "luxury" derives from the Latin verb ''luxor'' meaning to overextend or strain. From this, the noun ''luxuria'' and verb ''luxurio'' developed, "indicating immoderate growth, swelling, ... in persons and animals, willful or unruly behavior, disregard for moral restraints, and licensciousness", and the term has had negative connotations for most of its long history. One definition in the OED is a "thing desirable but not necessary". A luxury good can be identified by comparing the demand for the good at one point in time against the demand for the good at a di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Famine (Ireland)
The Great Famine, also known as the Great Hunger ( ), the Famine and the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of mass starvation and disease in Ireland lasting from 1845 to 1852 that constituted a historical social crisis and had a major impact on Irish society and history as a whole. The most severely affected areas were in the western and southern parts of Ireland—where the Irish language was dominant—hence the period was contemporaneously known in Irish as , which literally translates to "the bad life" and loosely translates to "the hard times". The worst year of the famine was 1847, which became known as "Black '47".Éamon Ó Cuív – the impact and legacy of the Great Irish Famine The population of Ireland on the eve of the famine was about 8.5 million; by 1901, it was just 4.4 million. During the Great Hunger, roughly 1 million people died and more than 1 million more Irish diaspora, fled the country, causing the country's population to fall by 20–25% between 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Robert Giffen
Sir Robert Giffen (22 July 1837 – 12 April 1910) was a Scottish statistician and economist. Life Giffen was born at Strathaven, Lanarkshire. He entered a solicitor's office in Glasgow, and while in that city attended courses at the university. He drifted into journalism, and after working for the ''Stirling Journal'' he went to London in 1862 and joined the staff of the Globe. He also assisted John Morley, when the latter edited the ''Fortnightly Review''. In 1868 he became Walter Bagehot's assistant-editor on ''The Economist''; and his services were also secured in 1873 as city editor of the ''Daily News'', and later of ''The Times''. His reputation as a financial journalist and statistician, gained in these years, led to his appointment in 1876 as head of the statistical department in the Board of Trade, and subsequently he became assistant secretary (1882) and finally controller-general (1892), retiring in 1897. As chief statistical adviser to the government, he drew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veblen Good
A Veblen good is a type of luxury good, named after American economist Thorstein Veblen, for which the demand increases as the price increases, in apparent contradiction of the law of demand, resulting in an upward-sloping demand curve. The higher prices of Veblen goods may make them desirable as a status symbol in the practices of conspicuous consumption and conspicuous leisure. A product may be a Veblen good because it is a positional good, something few others can own. Background Veblen goods are named after American economist Thorstein Veblen, who first identified conspicuous consumption as a mode of status-seeking (i.e., keeping up with the Joneses) in ''The Theory of the Leisure Class'' (1899). The testability of this theory was questioned by Colin Campbell due to the lack of complete honesty from research participants. However, research in 2007 studying the effect of social comparison on human brains can be used as an evidence supporting Veblen. The idea that seeking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giffen Goods
In microeconomics and consumer theory, a Giffen good is a product that people consume more of as the price rises and vice versa, violating the law of demand. For ordinary goods, as the price of the good rises, the substitution effect makes consumers purchase less of it, and more of substitute goods; the income effect can either reinforce or weaken this decline in demand, but for an ordinary good never outweighs it. By contrast, a Giffen good is so strongly an inferior good (in higher demand at lower incomes) that the contrary income effect more than offsets the substitution effect, and the net effect of the good's price rise is to increase demand for it. This phenomenon is known as the Giffen paradox. Background Giffen goods are named after Scottish economist Sir Robert Giffen, to whom Alfred Marshall attributed this idea in his book '' Principles of Economics'', first published in 1890. Giffen first proposed the paradox from his observations of the purchasing habits of the V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer Behaviour
Consumer behaviour is the study of individuals, groups, or organisations and all activities associated with the Purchasing, purchase, Utility, use and disposal of goods and services. It encompasses how the consumer's emotions, Attitude (psychology), attitudes, and Preference (economics), preferences affect Buyer decision process, buying behaviour, and how external cues—such as visual prompts, auditory signals, or tactile (haptic) feedback—can shape those responses. Consumer behaviour emerged in the 1940–1950s as a distinct sub-discipline of marketing, but has become an Interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary social science that blends elements from psychology, sociology, Social Anthropology, social anthropology, anthropology, ethnography, ethnology, marketing, and economics (especially behavioural economics). The study of consumer behaviour formally investigates individual qualities such as demographics, personality lifestyles, and behavioural variables (like usage rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advertising Elasticity Of Demand
Advertising elasticity of demand (or simply advertising elasticity, often shortened to AED) is an elasticity measuring the effect of an increase or decrease in advertising on a market.Pindyck; Rubinfeld (2001). pp.405-407. Traditionally, it is considered as being positively related, demand for the good that is subject of the advertising campaign can be inversely related to the amount spent if the advertising is negative. Definition Good advertising will result in a positive shift in demand for a good. AED is used to measure the effectiveness of this strategy in increasing demand versus its cost. Mathematically, then, AED measures the percentage change in the quantity of a good demanded induced by a given percentage often change in spending on advertising in that sector:Curran (1999). pp.182-183. :AED = \frac = \frac In other words, the percentage by which sales will increase after a 1% increase in advertising expenditure, assuming all other factors remain equal (''ceteris parib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Good
In economics, inferior goods are those goods the demand for which falls with increase in income of the consumer. So, there is an inverse relationship between income of the consumer and the demand for inferior goods. There are many examples of inferior goods, including cheap cars, public transit options, payday lending, and inexpensive food. The shift in consumer demand for an inferior good can be explained by two natural economic phenomena: the substitution effect and the income effect. Description In economics, inferior goods are goods whose demand decreases when consumer income rises (or demand increases when consumer income decreases). This behaviour is unlike the supply and demand behaviour of normal goods, for which the opposite is observed; normal goods are those goods for which the demand rises as consumer income rises. Inferiority, in this sense, is an observable fact relating to affordability rather than a statement about the quality of the good. As a rule, these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Good
In economics, a normal good is a type of a Good (economics), good which experiences an increase in demand due to an increase in income, unlike inferior goods, for which the opposite is observed. When there is an increase in a person's income, for example due to a wage rise, a good for which the demand rises due to the wage increase, is referred as a normal good. Conversely, the demand for normal goods declines when the income decreases, for example due to a wage decrease or layoffs. Analysis There is a positive correlation between the income and demand for normal goods, that is, the changes income and demand for normal goods moves in the same direction. That is to say, that normal goods have an elastic relationship for the demand of a good with the income of the person consuming the good. In economics, the concept of elasticity, and specifically income elasticity of demand is key to explain the concept of normal goods. Income elasticity of demand measures the magnitude of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Income Elasticity Of Demand
In economics, the income elasticity of demand (YED) is the responsivenesses of the quantity demanded for a good to a change in consumer income. It is measured as the ratio of the percentage change in quantity demanded to the percentage change in income. For example, if in response to a 10% increase in income, quantity demanded for a good or service were to increase by 20%, the income elasticity of demand would be 20%/10% = 2.0. Mathematical definition :\epsilon_d = \frac The point elasticity version, which defines it as an instantaneous rate of change of quantity demanded as income changes, is as follows. For a given Marshallian demand function Q(I,\vec) , with arguments income and a vector of prices of various goods, :\epsilon_d = \frac\frac This can be rewritten in the form :\epsilon_d = \frac For discrete changes the elasticity is (using the arc elasticity) :\epsilon_d= \times =\times , where subscripts 1 and 2 refer to values before and after the change. Interpr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |