|
Law Of 22 Prairial
The Law of 22 Prairial, also known as the ''loi de la Grande Terreur'', the law of the Great Terror, was enacted on 10 June 1794 (22 Prairial of the Year II under the French Revolutionary Calendar). It was proposed by Georges Auguste Couthon but seems to have been written by Maximilien Robespierre according to Laurent Lecointre. Using this law, the Committee of Public Safety simplified the judicial process to one of indictment and prosecution. Background The immediate background to the introduction of the Prairial Law was the attempted assassinations of Jean-Marie Collot d'Herbois on 23 May and of Maximilien Robespierre on 25 May. Introducing the decree at the Convention, Georges Couthon, who had drafted it, argued that political crimes were far worse than common crimes because in the latter "only individuals are wounded" whereas in the former "the existence of free society is threatened". Under these circumstances, "indulgence is an atrocity... clemency is parricide". The la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robespierre Exécutant Le Bourreau
Maximilien François Marie Isidore de Robespierre (; ; 6 May 1758 – 28 July 1794) was a French lawyer and statesman, widely recognised as one of the most influential and controversial figures of the French Revolution. Robespierre fervently campaigned for the voting rights of universal manhood suffrage, all men and their unimpeded admission to the National Guard (France), National Guard. Additionally, he advocated the right to petition, the right to bear arms in self-defence, and the abolition of the Atlantic slave trade. A radical Jacobin leader, Robespierre was elected as a deputy to the National Convention in September 1792, and in July 1793, he was appointed a member of the Committee of Public Safety. Robespierre faced growing disillusionment due in part to the politically motivated violence associated with him. Increasingly, members of the Convention turned against him, and accusations came to a head on 9 Thermidor. Robespierre was arrested and with around 90 othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prairial
Prairial () was the ninth month A month is a unit of time, used with calendars, that is approximately as long as a natural phase cycle of the Moon; the words ''month'' and ''Moon'' are cognates. The traditional concept of months arose with the cycle of Moon phases; such lunar mo ... in the French Republican calendar. This month was named after the French word ''prairie'' 'meadow'. It was the name given to several ships. Prairial was the third month of the spring quarter (). It started May 20 or May 21. It ended June 18 or June 19. It follows Floréal and precedes Messidor. Day name table Like all FRC months, Prairial lasted 30 days and was divided into three 10-day weeks called ''décades'' (decades). Every day had the name of an agricultural plant, except the 5th (Quintidi) and 10th day (Decadi) of every decade, which had the name of a domestic animal (Quintidi) or an agricultural tool (Decadi). Conversion table See also * Revolt of 1 Prairial Year III Exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law In French Revolution
Law is a set of rules that are created and are law enforcement, enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a Social science#Law, science and as the art of justice. State-enforced laws can be made by a legislature, resulting in statutes; by the executive through decrees and regulations; or by judges' decisions, which form precedent in common law jurisdictions. An autocrat may exercise those functions within their realm. The creation of laws themselves may be influenced by a constitution, written or tacit, and the rights encoded therein. The law shapes politics, economics, history and society in various ways and also serves as a mediator of relations between people. Legal systems vary between Jurisdiction (area), jurisdictions, with their differences analysed in comparative law. In Civil law (legal system), civil law jurisdictions, a legislature or othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1794 Events Of The French Revolution
Events January–March * January 1 – The Stibo Group is founded by Niels Lund as a printing company in Aarhus (Denmark). * January 13 – The U.S. Congress enacts a law providing for, effective May 1, 1795, a Flag of the United States#Later flag acts, United States flag of 15 stars and 15 stripes, in recognition of the recent admission of Vermont and Kentucky as the 14th and 15th states. A subsequent act restores the number of stripes to 13, but provides for additional stars upon the admission of each additional state. * January 21 – King George III of Great Britain delivers the speech opening Parliament and recommends a continuation of Britain's war with France. * February 4 – French Revolution: The National Convention of the French First Republic abolishes slavery. * February 8 – Wreck of the Ten Sail on Grand Cayman. * February 11 – The first session of the United States Senate is open to the public. * March 4 – The Eleventh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1794 In Law
Events January–March * January 1 – The Stibo Group is founded by Niels Lund as a printing company in Aarhus (Denmark). * January 13 – The U.S. Congress enacts a law providing for, effective May 1, 1795, a United States flag of 15 stars and 15 stripes, in recognition of the recent admission of Vermont and Kentucky as the 14th and 15th states. A subsequent act restores the number of stripes to 13, but provides for additional stars upon the admission of each additional state. * January 21 – King George III of Great Britain delivers the speech opening Parliament and recommends a continuation of Britain's war with France. * February 4 – French Revolution: The National Convention of the French First Republic abolishes slavery. * February 8 – Wreck of the Ten Sail on Grand Cayman. * February 11 – The first session of the United States Senate is open to the public. * March 4 – The Eleventh Amendment to the United States Consti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Suspects
:''Note: This decree should not be confused with the Law of General Security (), also known as the "Law of Suspects," adopted by Napoleon III in 1858 that allowed punishment for any prison action, and permitted the arrest and deportation, without judgment, of anyone convicted of political offenses after 1848.'' The Law of Suspects () was a decree passed by the French National Convention on 17 September 1793, during the French Revolution. Some historians consider this decree the start of the Reign of Terror; they argue that the decree marked a significant weakening of individual freedoms that led to "revolutionary paranoia" that swept the nation.Jean Tulard, Jean-François Fayard, & Alfred Fierro, ''Histoire et Dictionnaire de la Révolution française,'' Éd. Bouquins-Robert Laffont, 1997, The law ordered the arrest of all avowed enemies and suspected enemies of the Revolution, and specifically aimed at unsubmissive former nobles, émigrés, officials removed or suspended from o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine Quentin Fouquier-Tinville
Antoine Quentin Fouquier de Tinville (, 10 June 17467 May 1795), also called Fouquier-Tinville and nicknamed posthumously the Provider of the Guillotine was a French lawyer and accusateur public of the Revolutionary Tribunal during the French Revolution and Reign of Terror. From March 1793 he served as the "public prosecutor" in Paris, demanding the execution of numerous accused individuals, including famous ones, like Marie-Antoinette, Danton or Robespierre and overseeing the sentencing of over two thousand of them to the guillotine. In April 1794, it was decreed to centralise the investigation of court records and to bring all the political suspects in France to the Revolutionary Tribunal to Paris. Following the events of the 10th Thermidor, he was arrested early August. He was tried by the Revolutionary Tribunal as one of the major figures responsible for the excesses and injustices that marked the period of the Reign of Terror. During his trial, he defended himself by sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermidorian Reaction
In the historiography of the French Revolution, the Thermidorian Reaction ( or ''Convention thermidorienne'', "Thermidorian Convention") is the common term for the period between the ousting of Maximilien Robespierre on 9 Thermidor II, or 27 July 1794, and the inauguration of the French Directory on 2 November 1795. The Thermidorian Reaction was named after the month in which the coup took place and was the latter part of the National Convention's rule of France. It was marked by the end of the Reign of Terror, decentralization of executive powers from the Committee of Public Safety, and a turn from the radical Jacobin policies of the Montagnard Convention to more moderate positions. Economic and general populism, dechristianization, and harsh wartime measures were largely abandoned, as the members of the convention, disillusioned and frightened of the centralized government of the Terror, preferred a more stable political order that would have the approval of the plurality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
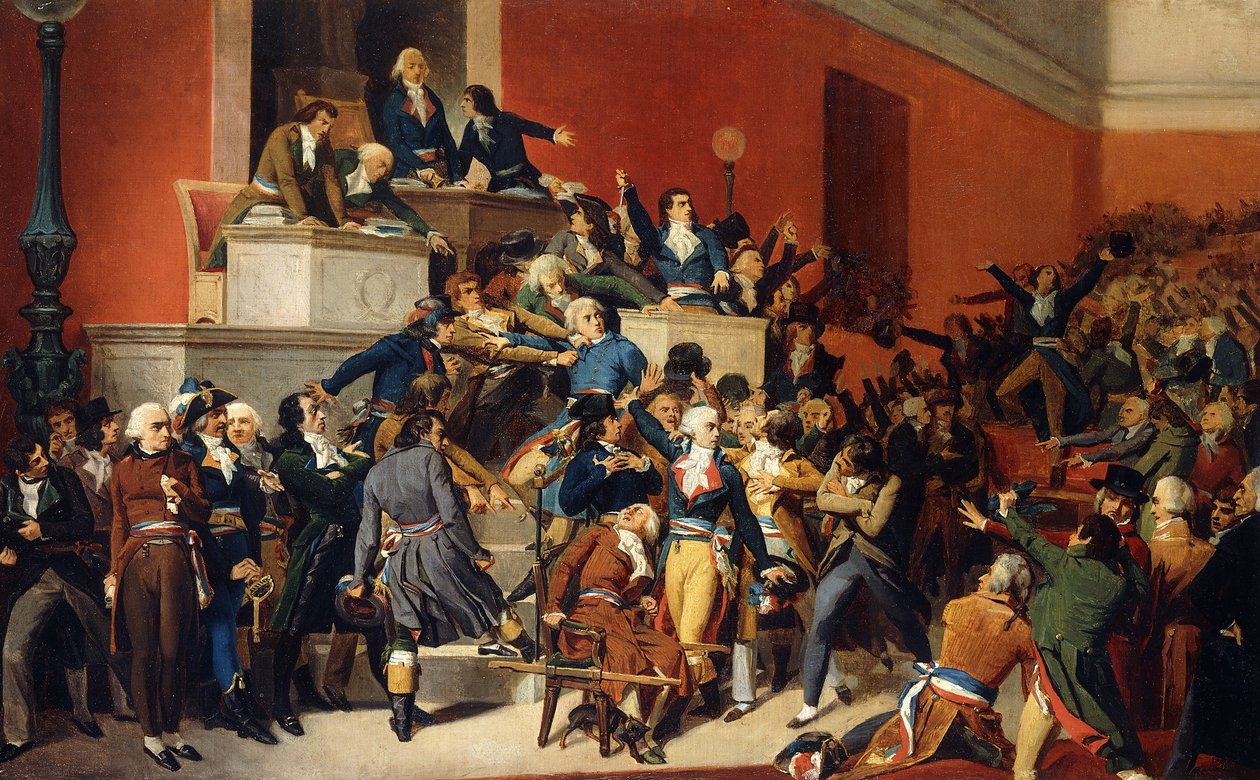
Fall Of Maximilien Robespierre
Maximilien Robespierre addressed the National Convention on 26 July 1794, was arrested the next day, and executed on 28 July. In his speech on 26 July, Robespierre spoke of the existence of internal enemies, conspirators, and calumniators, within the Convention and the governing Committees. He refused to name them, which alarmed the deputies who feared Robespierre was preparing another purge of the Convention, similar to previous ones during the Reign of Terror. On the following day, this tension in the Convention allowed Jean-Lambert Tallien, one of the conspirators whom Robespierre had in mind in his denunciation, to turn the Convention against Robespierre and decree his arrest. By the end of 28 July Robespierre was executed by guillotine in the Place de la Révolution. Robespierre's fall led to more moderate policies being implemented during the subsequent Thermidorian Reaction. Background Purge of the Hébertists and Dantonists On 27 July 1793, Robespierre was elected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Lambert Tallien
Jean-Lambert Tallien (, 23 January 1767 – 16 November 1820) was a French politician of the revolutionary period. Though initially an active agent of the Reign of Terror, he eventually clashed with its leader, Maximilien Robespierre, and is best known as one of the key figures of the Thermidorian Reaction that led to the fall of Robespierre and the end of the Terror. Early life and journalism Tallien was born in Paris to Lambert Tallien, the ''maître d'hôtel'' of the Marquis de Bercy, and Jeanne Lambert. The marquis, noticing his ability, had him educated, and got him a place as a lawyer's clerk. Supportive of the Revolution, he gave up his desk to enter a printer's office, and by 1791 was overseer of the printing department of the Comte de Provence. During his employment, he conceived the idea of the '' journal-affiche'', and after the arrest of the king at Varennes in June 1791 he placarded a large printed sheet on all the walls of Paris twice a week, under the title of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merlin De Douai
Philippe-Antoine Merlin, known as Merlin de Douai (, 30 October 1754 – 26 December 1838), was a French politician and lawyer. Early life Merlin de Douai was born at Arleux, Nord, and was called to the Flemish bar association in 1775. He collaborated in the ''Répertoire de jurisprudence'', the later editions of which appeared under Merlin's superintendence, and contributed to other important legal compilations. In 1782 he purchased a position as royal secretary at the chancellery of the Flanders parlement. His reputation spread to Paris and he was consulted by leading magistrates. The Duke of Orléans selected him to be a member of his privy council. As an elected member of the States-General for the Third Estate in Douai, he was one of the chief of those who applied the principles of liberty and equality embodied in the National Constituent Assembly's ''Tennis Court Oath'' of 20 June 1789. Career On behalf of the committee, appointed to deal with the ''Ancien Régime''� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bourdon De L'Oise
Bourdon derives from the French for bumblebee, and may refer to: * Bourdon (bell), the lowest bell in a set * Bourdon (organ pipe), a stopped organ pipe of a construction favored for low pitches * Bourdon (surname) * Drone (music): The lowest course of a lute, or the lowest drone pipe of a bagpipe, sometimes called a bourdon * Faux bourdon, fauxbourdon, faburden or falsobordone, terms applied (without perfect consistency) to a variety of music compositional techniques * Bourdon, Somme, a small town in France * Bourdon (grape), another name for the French wine grape Douce noir See also * Bourdon gauge or Bourdon tube, named after Eugène Bourdon * Boudon **Boudon noir, an alternative name for the Italian wine grape Dolcetto * Boudin (other) *Burden (other) Burden or burthen may refer to: People * Burden (surname), people with the surname Burden Places * Burden, Kansas, United States * Burden, Luxembourg Arts, entertainment, and media Films * Burden (2018 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |