|
Latin Rights
Latin rights or Latin citizenship ( or ) were a set of legal rights that were originally granted to the Latins and therefore in their colonies ( Latium adiectum). ''Latinitas'' was commonly used by Roman jurists to denote this status. With the Roman expansion in Italy, many settlements and coloniae outside of Latium had Latin rights. All the ''Latini'' of Italy obtained Roman citizenship as a result of three laws which were introduced during the Social War between the Romans and their allies among the Italic peoples (''socii'') which rebelled against Rome. The '' Lex Iulia de Civitate Latinis (et sociis) Danda'' of 90 BC conferred Roman citizenship on all citizens of the Latin towns and the Italic towns who had not rebelled. The ''Lex Plautia Papiria de Civitate Sociis Danda'' of 89 BC granted Roman citizenship to all federated towns in Italy south of the River Po (in northern Italy). The ''Lex Pompeia de Transpadanis'' of 89 BC granted the ''ius Latii'' to the communities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vespasian
Vespasian (; ; 17 November AD 9 – 23 June 79) was Roman emperor from 69 to 79. The last emperor to reign in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty, which ruled the Empire for 27 years. His fiscal reforms and consolidation of the empire brought political stability and a vast building program. Vespasian was the first emperor from an Equestrian (Roman), equestrian family who rose only later in his lifetime into the Roman Senate, senatorial rank as the first of his family to do so. He rose to prominence through military achievement: he served as legatus, legate of Legio II Augusta during the Roman invasion of Britain in 43, and later led the suppression of the First Jewish–Roman War, Jewish rebellion of 66–70. While he was engaged in the campaign in Judaea (Roman province), Judaea, Emperor Nero died by suicide in June 68, plunging Rome into a year of civil war known as the Year of the Four Emperors. After Galba and Otho perished in quick succession, V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. The reign of Augustus initiated an Roman imperial cult, imperial cult and an era of regional hegemony, imperial peace (the or ) in which the Roman world was largely free of armed conflict. The Principate system of government was established during his reign and lasted until the Crisis of the Third Century. Octavian was born into an equites, equestrian branch of the plebeian Octavia gens, Octavia. Following his maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar's assassination of Julius Caesar, assassination in 44 BC, Octavian was named in Caesar's will as his Adoption in ancient Rome, adopted son and heir, and inherited Caesar's name, estate, and the loyalty of his legions. He, Mark Antony, and Marcus Lepidus formed the Second Triumvirat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil war, a civil war. He subsequently became Roman dictator, dictator from 49 BC until Assassination of Julius Caesar, his assassination in 44 BC. Caesar played a critical role in Crisis of the Roman Republic, the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Marcus Licinius Crassus, Crassus, and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass political power were opposed by many in the Roman Senate, Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the private support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrician (ancient Rome)
The patricians (from ) were originally a group of ruling class families in ancient Rome. The distinction was highly significant in the Roman Kingdom and the early Roman Republic, Republic, but its relevance waned after the Conflict of the Orders (494 BC to 287 BC). By the time of the late Republic and Roman Empire, Empire, membership in the patriciate was of only nominal significance. The social structure of ancient Rome revolved around the distinction between the patricians and the plebeians. The status of patricians gave them more political power than the plebeians, but the relationship between the groups eventually caused the Conflict of the Orders. This time period resulted in changing of the social structure of ancient Rome. After the Western Roman Empire, Western Empire fell, the term "patrician" continued as a high Byzantine aristocracy and bureaucracy, honorary title in the Eastern Empire. In many Italian city-states, medieval Italian republics, especially in Republic of V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Roque, Cádiz
San Roque is a municipality of Spain belonging to the province of Cádiz, which in turn is part of the autonomous community of Andalusia. It is also part of the of Campo de Gibraltar. Located in the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula, San Roque is a short way inland of the north side of the Bay of Gibraltar, to the north of the Gibraltar peninsula. The municipality has a total surface of 145 km2 with a population of approximately 25,500 people, as of 2005. The foundation of San Roque as a city owes to the creation of a sort of Gibraltar-in-exile by refugees fleeing from the Rock in the wake of its seizure by Anglo-Dutch forces in 1704. In addition of the main nucleus of San Roque, the municipality also includes settlements such as Puente Mayorga, , Sotogrande, Campamento, or Guadiaro. Placename San Roque is Spanish for Saint Roch, a Christian saint who was revered in a shrine dating back to 1508 that predates the foundation of the town. Geography San Roque lies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
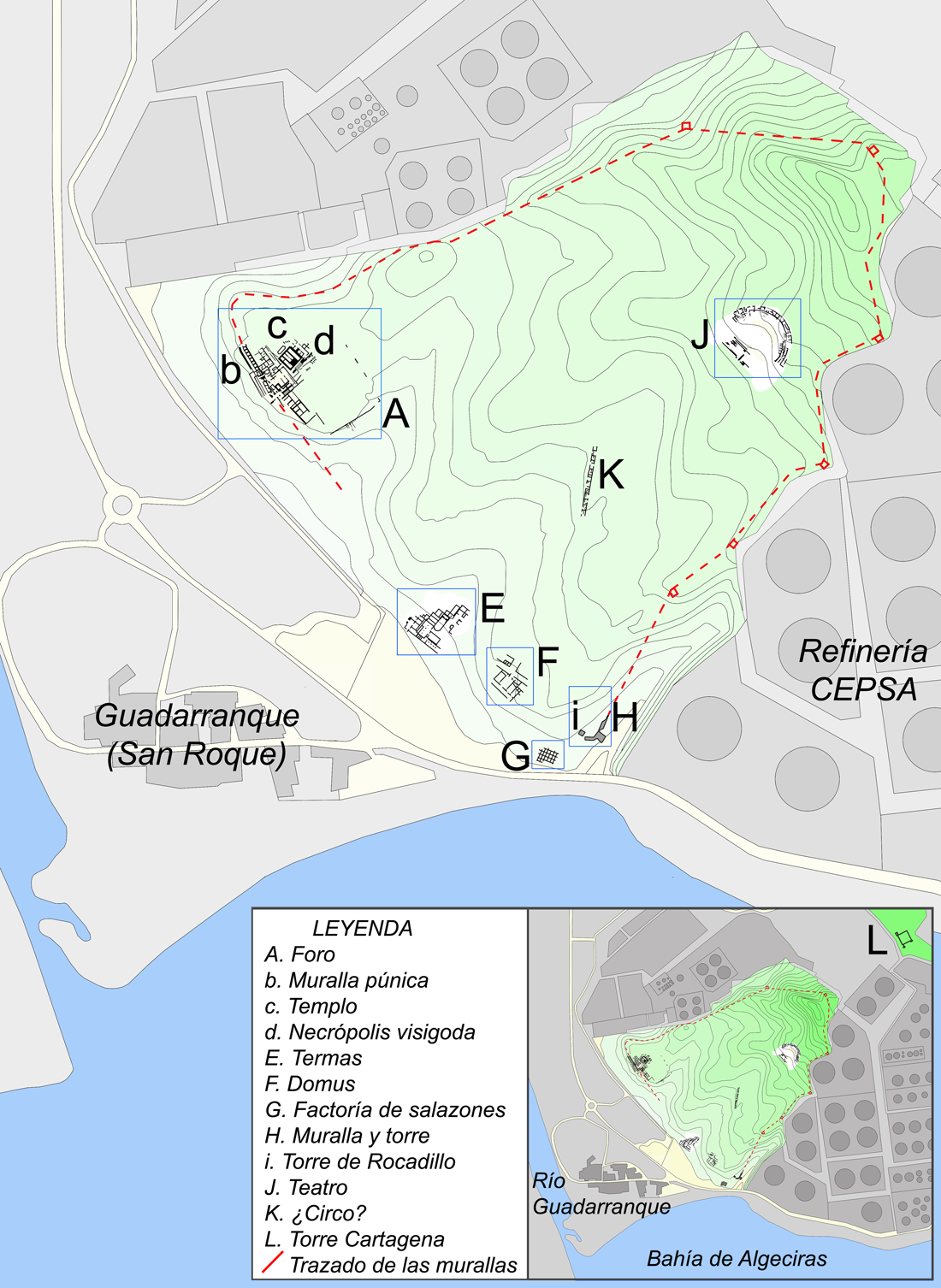
Carteia
Carteia () was a Phoenician and Ancient Rome, Roman town at the head of the Bay of Gibraltar in Spain. It was established at the most northerly point of the bay, next to the town of San Roque, Cádiz, San Roque, about halfway between the modern cities of Algeciras and Gibraltar, overlooking the sea on elevated ground at the confluence of two rivers, nowadays called Guadarranque and Cachon. According to Strabo, it was founded around 940 BC as the trading settlement of ''Kʿrt'' (meaning "city" in the Phoenician language; compare Carthage and Cartagena, Spain, Cartagena). The area had much to offer a trader; the hinterland behind Carteia, in the modern south of Andalusia, was rich in wood, cereals, oranges, lemons, lead, iron, copper and silver. Dyes were another much sought-after commodity, especially those from the murex shellfish, used to make the prized Tyrian purple. Strabo and Pomponius Mela, mention that some believe that Carteia used to be the Tartessos. Pliny the Elder w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Colonies
Colonies in antiquity were post-Iron Age city-states founded from a mother-city or metropolis rather than from a territory-at-large. Bonds between a colony and its metropolis often remained close, and took specific forms during the period of classical antiquity. Generally, colonies founded by the ancient Phoenicians, Carthage, Rome, Alexander the Great and his successors remained tied to their metropolis, though Greek colonies of the Archaic and Classical eras were sovereign and self-governing from their inception. While earlier Greek colonies were often founded to solve social unrest in the mother-city by expelling a part of the population, Hellenistic, Roman, Carthaginian, and Han Chinese colonies served as centres for trade (entrepôts), expansion and empire-building. Sabean Colonization of Africa One of the oldest colonisation process in history occurred around 1000 BC, the Sabeans of southern Arabia, with a civilization based on agriculture, began to colonize the hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin War
The (Second) Latin War of 340–338 BCThe Romans customarily dated events by noting the consuls who held office that year. The Latin War broke out in the year that Titus Manlius Imperiosus Torquatus and Publius Decius Mus were consuls and ended in the year that Lucius Furius Camillus and Gaius Maenius were consuls. When converted to the western calendar using the traditional Varronian chronology, those years become 340 and 338 BC. However, modern historians have shown that the Varronian chronology dates the Latin War four years too early because of inclusion of unhistorical "dictator years". Despite that known inaccuracy, the Varronian chronology remains in use by convention also in academic literature and so is also the chronology used in this article. Forsythe(2005), pp. 369-370 was a conflict between the Roman Republic and its neighbors, the Latin peoples of ancient Italy. It ended in the dissolution of the Latin League and incorporation of its territory into the Roman sphere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin League
The Latin League ( – 338 BC)Stearns, Peter N. (2001). ''The Encyclopedia of World History''. Houghton Mifflin. pp. 76–78. . was an ancient confederation of about 30 villages and tribes in the region of Latium near the ancient city of Rome, organized for mutual defense. The term "Latin League" is one coined by modern historians with no precise Latin equivalent. Creation The Latin League was originally created for protection against enemies from surrounding areas (the Etruscans) under the leadership of the city of Alba Longa. An incomplete fragment of an inscription recorded by Cato the Elder claims that at one time the league included Tusculum, Aricia, Lanuvium, Lavinium, Cora, Tibur, Pometia and Ardea. Roman leadership of the League During the reign of Tarquinius Superbus, the Latins were persuaded to acknowledge the leadership of Rome. The treaty with Rome was renewed, and it was agreed that the troops of the Latins would attend on an appointed day to form a united mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2,746,984 residents in , Rome is the list of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, third most populous city in the European Union by population within city limits. The Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, with a population of 4,223,885 residents, is the most populous metropolitan cities of Italy, metropolitan city in Italy. Rome metropolitan area, Its metropolitan area is the third-most populous within Italy. Rome is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, within Lazio (Latium), along the shores of the Tiber Valley. Vatican City (the smallest country in the world and headquarters of the worldwide Catholic Church under the governance of the Holy See) is an independent country inside the city boun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |