|
Lateral Pectoral Nerve
The lateral pectoral nerve (also known as the lateral anterior thoracic nerve) arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, and through it from the C5-7. It passes across the axillary artery and vein, pierces the clavipectoral (coracoclavicular) fascia, and enters the deep surface of the pectoralis major to innervate it. Function The lateral pectoral nerve provides motor innervation to the pectoralis major muscle. Although this nerve is described as mostly motor, it also has been considered to carry proprioceptive and nociceptive fibers. It arises either from the lateral cord or directly from the anterior divisions of the upper and middle trunks of the brachial plexus. This is unlike the medial pectoral nerve, which derives from the medial cord (or directly from the anterior division of the lower trunk). It splits into four to seven branches that pierce the clavipectoral fascia to innervate the entire pectoralis major or its superior portion. The medial and latera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Block
Nerve block or regional nerve blockade is any deliberate interruption of signals traveling along a nerve, often for the purpose of pain relief. #Local anesthetic nerve block, Local anesthetic nerve block (sometimes referred to as simply "nerve block") is a short-term block, usually lasting hours or days, involving the injection of an anesthetic, a corticosteroid, and other agents onto or near a nerve. Neurolytic block, the deliberate temporary degeneration of nerve fibers through the application of chemicals, heat, or freezing, produces a block that may persist for weeks, months, or indefinitely. Neurectomy, the cutting through or removal of a nerve or a section of a nerve, usually produces a permanent block. Because neurectomy of a sensory nerve is often followed, months later, by the emergence of new, more intense pain, sensory nerve neurectomy is rarely performed. The concept of nerve block sometimes includes ''central nerve block'', which includes epidural and spinal anaesthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Pectoral Nerve
The medial pectoral nerve (also known as the medial anterior thoracic nerve) is (typically) a branch of the medial cord of the brachial plexus and is derived from spinal nerve roots C8-T1. It provides motor innervation to the pectoralis minor muscle, and the lower half (sternal part) of the pectoralis major muscle. It runs along the inferior border of the pectoralis minor muscle. Damage to the medial pectoral nerve can result in inability to elevate the shoulder. Anatomy Origin The medial pectoral nerve usually arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus; it can however occasionally arise directly from the anterior division of the inferior trunk of the brachial plexus. It is derived from the eighth cervical (C8) and first thoracic (T1) spinal nerve roots. The origin is situated posterior to the axillary artery. Course and relations It passes behind the first part of the axillary artery, curves forward between the axillary artery and vein, and unites in front of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachial Plexus Injury
A brachial plexus injury (BPI), also known as brachial plexus lesion, is an injury to the brachial plexus, the network of nerves that conducts signals from the spinal cord to the shoulder, arm and hand. These nerves originate in the fifth, sixth, seventh and eighth cervical (C5–C8), and first thoracic (T1) spinal nerves, and innervate the muscles and skin of the chest, shoulder, arm and hand. Brachial plexus injuries can occur as a result of shoulder trauma (e.g. dislocation), tumours, or inflammation, or obstetric. Obstetric injuries may occur from mechanical injury involving shoulder dystocia during difficult Childbirth#Mechanical fetal injury, childbirth, with a prevalence of 1 in 1000 births. "The brachial plexus may be injured by falls from a height on to the side of the head and shoulder, whereby the nerves of the plexus are violently stretched. The brachial plexus may also be injured by direct violence or gunshot wounds, by violent traction on the arm, or by efforts at red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avulsion Injury
In medicine, an avulsion is an injury in which a body structure is torn off by either trauma or surgery (from the Latin ''avellere'', meaning "to tear off"). The term most commonly refers to a surface trauma where all layers of the skin have been torn away, exposing the underlying structures (i.e., subcutaneous tissue, muscle, tendons, or bone). This is similar to an abrasion but more severe, as body parts such as an eyelid or an ear can be partially or fully detached from the body. Skin avulsions The most common avulsion injury, skin avulsion, often occurs during motor vehicle collisions. The severity of avulsion ranges from skin flaps (minor) to degloving (moderate) and amputation of a finger or limb (severe). Suprafascial avulsions are those in which the depth of the removed skin reaches the subcutaneous tissue layer, while subfascial avulsions extend deeper than the subcutaneous layer.Jeng, S.F., & Wei, F.C. (1997, May). Classification and reconstructive options in foot pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauterization
Cauterization (or cauterisation, or cautery) is a medical practice or technique of burning a part of a body to remove or close off a part of it. It destroys some tissue in an attempt to mitigate bleeding and damage, remove an undesired growth, or minimize other potential medical harm, such as infections when antibiotics are unavailable. The practice was once widespread for treatment of wounds. Its utility before the advent of antibiotics was said to be effective at more than one level: *To prevent exsanguination *To close amputations Cautery was historically believed to prevent infection, but current research shows that cautery actually increases the risk for infection by causing more tissue damage and providing a more hospitable environment for bacterial growth. Actual cautery refers to the metal device, generally heated to a dull red glow, that a physician applies to produce blisters, to stop bleeding of a blood vessel, and for other similar purposes., page 16. The main f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage." Pain motivates organisms to withdraw from damaging situations, to protect a damaged body part while it heals, and to avoid similar experiences in the future. Congenital insensitivity to pain may result in reduced life expectancy. Most pain resolves once the noxious stimulus is removed and the body has healed, but it may persist despite removal of the stimulus and apparent healing of the body. Sometimes pain arises in the absence of any detectable stimulus, damage or disease. Pain is the most common reason for physician consultation in most developed countries. It is a major symptom in many medical conditions, and can interfere with a person's quality of life and general fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracoacromial Artery
The thoracoacromial artery (acromiothoracic artery; thoracic axis) is a short trunk that arises from the second part of the axillary artery, its origin being generally overlapped by the upper edge of the pectoralis minor. Structure Projecting forward to the upper border of the Pectoralis minor, it pierces the coracoclavicular fascia The clavipectoral fascia (costocoracoid membrane; coracoclavicular fascia) is a strong fascia situated under cover of the clavicular portion of the pectoralis major. It occupies the interval between the pectoralis minor and subclavius, and pr ... and divides into four branches—pectoral, acromial, clavicular, and deltoid. Additional images File:Gray523.png, The axillary artery and its branches. References External links * * * - "Pectoral Region: Thoracoacromial Artery and its Branches" * - "The axillary artery and its major branches shown in relation to major landmarks." {{Authority control Arteries of the upper limb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sensation (including pain) in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, providing local anesthesia, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sensation in the entire body and causes unconsciousness. Local anesthetics are most commonly used to eliminate pain during or after surgery. When it is used on specific nerve pathways ( local anesthetic nerve block), paralysis (loss of muscle function) also can be induced. Classification LAs are of 2 types: *Clinical LAs: ** amino amide LAs ** amino ester LAs *Synthetic LAs **Cocaine derivatives Synthetic cocaine-derived LAs differ from cocaine because they have a much lower abuse potential and do not cause hypertension vasoconstriction (with few exceptions). The suffix "-caine" at the ends of these medication names is derived from the word "cocaine", because cocaine was formerly used as a local anesthetic. Examples Short Duration of Act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuromuscular-blocking Drug
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs, or Neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBAs), block transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcholine (Nm) receptors. In clinical use, neuromuscular block is used adjunctively to anesthesia to produce paralysis, firstly to paralyze the vocal cords, and permit endotracheal intubation, and secondly to optimize the surgical field by inhibiting spontaneous ventilation, and causing relaxation of skeletal muscles. Because the appropriate dose of neuromuscular-blocking drug may paralyze muscles required for breathing (i.e., the diaphragm), mechanical ventilation should be available to maintain adequate Respiration (physiology), respiration. This class of medications helps to reduce patient movement, breathing, or ventilator dyssynchrony and allows lower insufflation pressures during laparoscopy. It has several indication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spasm
A spasm is a sudden involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, such as the bladder. A spasmodic muscle contraction may be caused by many medical conditions, including dystonia. Most commonly, it is a muscle cramp which is accompanied by a sudden burst of pain. A muscle cramp is usually harmless and ceases after a few minutes. It is typically caused by ion imbalance or muscle fatigue. There are other causes of involuntary muscle contractions, and some of these may cause a health problem. A series of spasms, or permanent spasms, is referred to as a "spasmism". Description and causes Spasms occur when the part of the brain that controls movement malfunctions, causing involuntary muscle activity. A spasm may be a muscle contraction caused by abnormal nerve stimulation or by abnormal activity of the muscle itself. Causes The cause of spasms is often unknown, but it can be due to an inherited genetic problem, a side effect of medicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
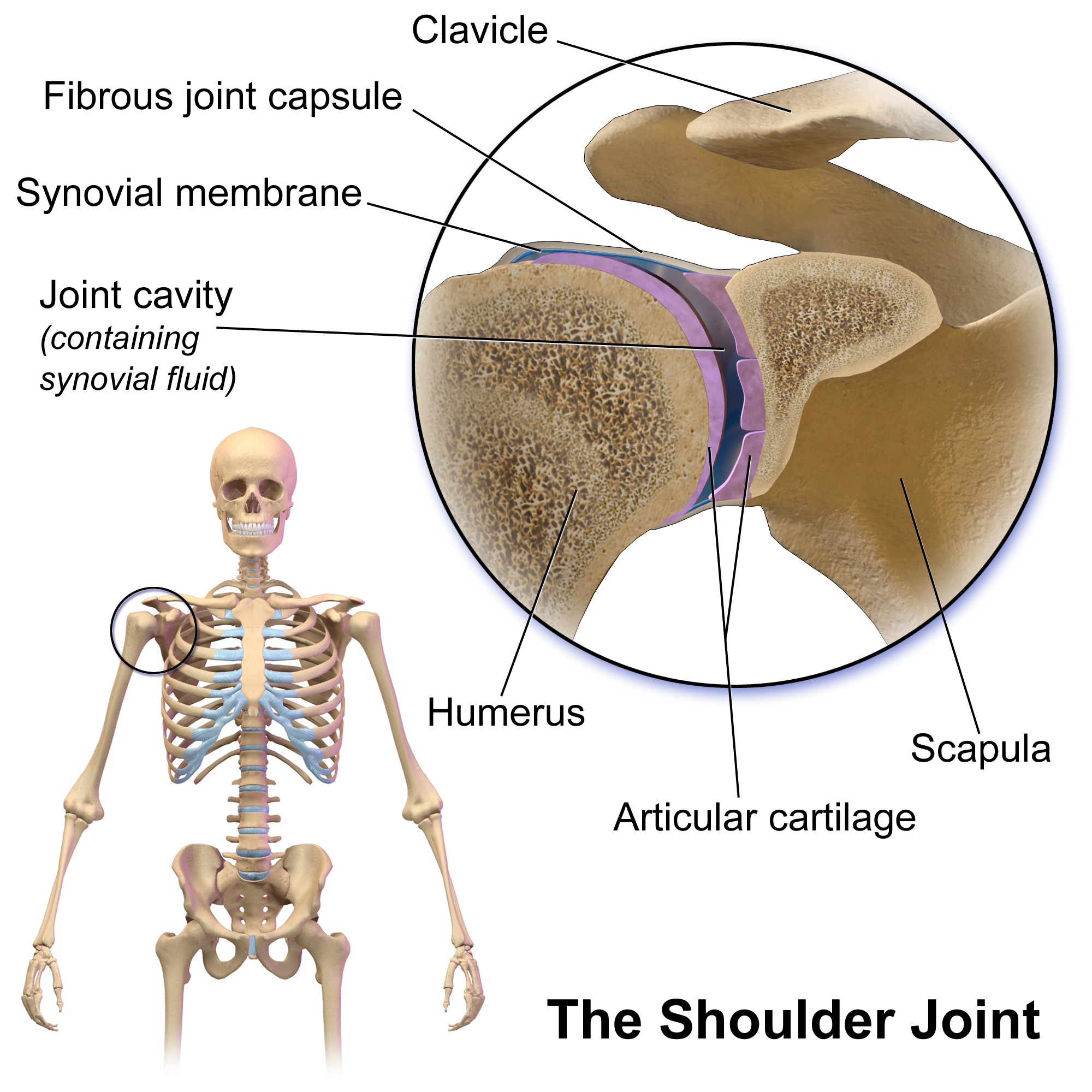
Shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder make up the shoulder joints. The shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral joint, is the major joint of the shoulder, but can more broadly include the acromioclavicular joint. In human anatomy, the shoulder joint comprises the part of the body where the humerus attaches to the scapula, and the head sits in the glenoid cavity. The shoulder is the group of structures in the region of the joint. The shoulder joint is the main joint of the shoulder. It is a ball and socket joint that allows the arm to rotate in a circular fashion or to hinge out and up away from the body. The joint capsule is a soft tissue envelope that encircles the glenohumeral joint and attaches to the scapula, humerus, and head of the biceps. It is lined by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |