|
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago. Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Europe, and Asia and profoundly affected Earth's climate by causing a major expansion of deserts, along with a large drop in sea levels. Based on changes in position of ice sheet margins dated via cosmogenic nuclide, terrestrial cosmogenic nuclides and radiocarbon dating, growth of ice sheets in the southern hemisphere commenced 33,000 years ago and maximum coverage has been estimated to have occurred sometime between 26,500 years ago and 20,000 years ago. After this, deglaciation caused an abrupt rise in sea level. Decline of the West Antarctica ice sheet occurred between 14,000 and 15,000 years ago, consistent with evidence for another abrupt rise in the sea level about 14,500 years ago. Glacier fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CLIMAP
Climate: Long range Investigation, Mapping, and Prediction, known as CLIMAP, was a major research project of the 1970s and 80s to produce a map of climate conditions during the Last Glacial Maximum. The project was funded by the National Science Foundation as part of the International Decade of Ocean Exploration (1970s) and is based in large part of the collection and analysis of a very large number of sediment cores to create a snapshot of conditions across the oceans. The CLIMAP project also resulted in maps of vegetative zones across the continents and the estimated extent of glaciation at the time. Most CLIMAP results aim to describe the Earth as it was 18 thousand years ago, but there was also an analysis to look at conditions during the previous interglacial—120 thousand years ago (CLIMAP 1981). CLIMAP has been a cornerstone of paleoclimate research and remains the most used sea surface temperature reconstruction of the global ocean during the last glacial maximum (Yin and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact geographical extent varies depending on the definition: in the narrow sense, the area constituted by three Chinese provinces of Heilongjiang, Jilin, and Liaoning as well as the eastern Inner Mongolian prefectures of China, prefectures of Hulunbuir, Hinggan League, Hinggan, Tongliao, and Chifeng; in a broader sense, historical Manchuria includes those regions plus the Amur river basin, parts of which were ceded to the Russian Empire by the Manchu-led Qing dynasty during the Amur Annexation of 1858–1860. The parts of Manchuria ceded to Russia are collectively known as Outer Manchuria or Russian Manchuria, which include present-day Amur Oblast, Primorsky Krai, the Jewish Autonomous Oblast, the southern part of Khabarovsk Krai, and the easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states since the lengthy conquest of Siberia, which began with the fall of the Khanate of Sibir in 1582 and concluded with the annexation of Chukotka in 1778. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to roughly a quarter of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk, and Omsk are the largest cities in the area. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic concept and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia spans the entire expanse of land from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, with the Ural River usually forming the southernmost portion of its western boundary, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Mass
In meteorology, an air mass is a volume of air defined by its temperature and humidity. Air masses cover many hundreds or thousands of square miles, and adapt to the characteristics of the surface below them. They are classified according to latitude and their continental or maritime source regions. Colder air masses are termed polar or arctic, while warmer air masses are deemed tropical. Continental and superior air masses are dry, while maritime and monsoon air masses are moist. Weather fronts separate air masses with different density (temperature or moisture) characteristics. Once an air mass moves away from its source region, underlying vegetation and body of water, water bodies can quickly modify its character. Classification schemes tackle an air mass's characteristics, as well as modification. Classification and notation The Tor Bergeron, Bergeron classification is the most widely accepted form of air mass classification, though others have produced more refined versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
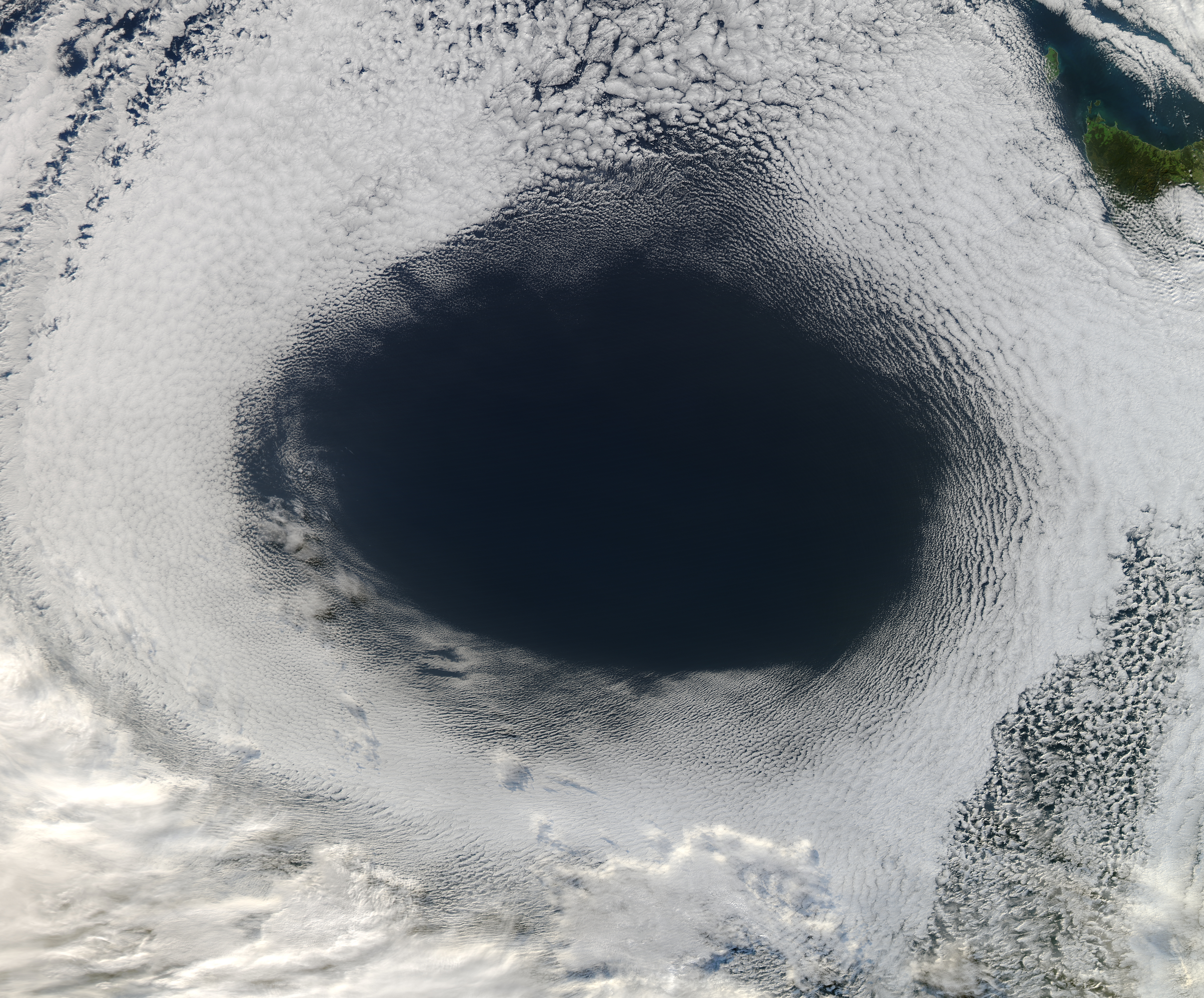
Anticyclone
A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interplays between the relatively larger-scale dynamics of an entire planet's atmospheric circulation. The strongest high-pressure areas result from masses of cold air which spread out from polar regions into cool neighboring regions. These highs weaken once they extend out over warmer bodies of water. Weaker—but more frequently occurring—are high-pressure areas caused by atmospheric subsidence: Air becomes cool enough to precipitate out its water vapor, and large masses of cooler, drier air descend from above. Within high-pressure areas, winds flow from where the pressure is highest, at the center of the area, towards the periphery where the pressure is lower. However, the direction is not straight from the center outwards, but curved du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Asia
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Japan, Japan, Economy of South Korea, South Korea, and Economy of Taiwan, Taiwan are among the world's largest and most prosperous. East Asia borders North Asia to the north, Southeast Asia to the south, South Asia to the southwest, and Central Asia to the west. To its east is the Pacific Ocean. East Asia, especially History of China, Chinese civilization, is regarded as one of the earliest Cradle of civilization#China, cradles of civilization. Other ancient civilizations in East Asia that still exist as independent countries in the present day include the History of Japan, Japanese, History of Korea, Korean, and History of Mongolia, Mongolian civilizations. Various other civilizations existed as independent polities in East Asia in the past ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east. Europe shares the landmass of Eurasia with Asia, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the Drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea, and the waterway of the Bosporus, Bosporus Strait. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea with its outlets, the Bosporus and Dardanelles." Europe covers approx. , or 2% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface (6.8% of Earth's land area), making it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow
Snow consists of individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes. It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout its life cycle, starting when, under suitable conditions, the ice crystals form in the atmosphere, increase to millimeter size, precipitate and accumulate on surfaces, then metamorphose in place, and ultimately melt, slide, or Sublimation (phase transition), sublimate away. Snowstorms organize and develop by feeding on sources of atmospheric moisture and cold air. Snowflakes Nucleation, nucleate around particles in the atmosphere by attracting supercooling, supercooled water droplets, which Freezing, freeze in hexagonal-shaped crystals. Snowflakes take on a variety of shapes, basic among these are platelets, needles, columns, and Hard rime, rime. As snow accumulates into a snowpack, it may blow into drifts. Over time, accumulated snow m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwealth usage), snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation; their water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate, so fog and mist do not fall. (Such a non-precipitating combination is a colloid.) Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated with water vapor: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called shower (p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Cap
In glaciology, an ice cap is a mass of ice that covers less than of land area (usually covering a highland area). Larger ice masses covering more than are termed ice sheets. Description By definition, ice caps are not constrained by topographical features (i.e., they must lie over the top of mountains). By contrast, ice masses of similar size that ''are'' constrained by topographical features are known as ice fields. The ''dome'' of an ice cap is usually centred on the highest point of a massif. Ice flows away from this high point (the ice divide) towards the ice cap's periphery. Ice caps significantly affect the geomorphology of the area they occupy. Plastic moulding, gouging and other glacial erosional features become present upon the glacier's retreat. Many lakes, such as the Great Lakes in North America, as well as numerous valleys have been formed by glacial action over hundreds of thousands of years. The Antarctic and Greenland contain 99% of the ice volume on earth, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment
''Nature Reviews Earth & Environment'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Nature Portfolio. It was established in 2020. The editor-in-chief is Graham Simpkins. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: *Science Citation Index Expanded *Scopus According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 37.214, ranking it 2nd out of 279 journals in the category "Environmental Sciences" and 1st out of 201 journals in the category "Geosciences, Multidisciplinary". References External links * Nature Research academic journals English-language journals Earth and atmospheric sciences journals Environmental science journals Academic journals establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |