|
Lasioglossum Zephyrus
''Lasioglossum zephyrus'' is a sweat bee of the family Halictidae, found in the U.S. and Canada. It appears in the literature primarily under the misspelling "''zephyrum''". It is considered a primitively eusocial bee (meaning that they do not have a permanent division of labor within colonies),Batra, S. W. T. 1966. The life cycle and behavior of the primitively social bee ''Lasioglossum zephyrum'' (Halictidae). Univ. Kansas Sci. Bull. 46:359–423. although it may be facultatively solitary (i.e., displaying both solitary and eusocial behaviors).Interactions in colonies of primitively social bees: Artificial colonies of ''Lasioglossum zephyrum'' ''PNAS''. Retrieved 08-27-2011. The species nests in burrows in the soil. Taxonomy and phylogeny |
Halictidae
Halictidae is the second-largest family of bees (clade Anthophila) with nearly 4,500 species. They are commonly called sweat bees (especially the smaller species), as they are often attracted to perspiration. Halictid species are an extremely diverse group that can vary greatly in appearance. These bees occur all over the world and are found on every continent except Antarctica. Usually dark-colored (frequently brown or black) and often metallic, halictids are found in various sizes, colors and patterns. Several species are all or partly green and a few are red, purple, or blue. A number of them have yellow markings, especially the males, which commonly have yellow faces, a pattern widespread among the various families of bees. The family is one of many with short tongues and is best distinguished by the arcuate (strongly curved) basal vein found on the wing. Females in this family tend to be larger than the males. They are the group for which the term 'eusocial' was first coined b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
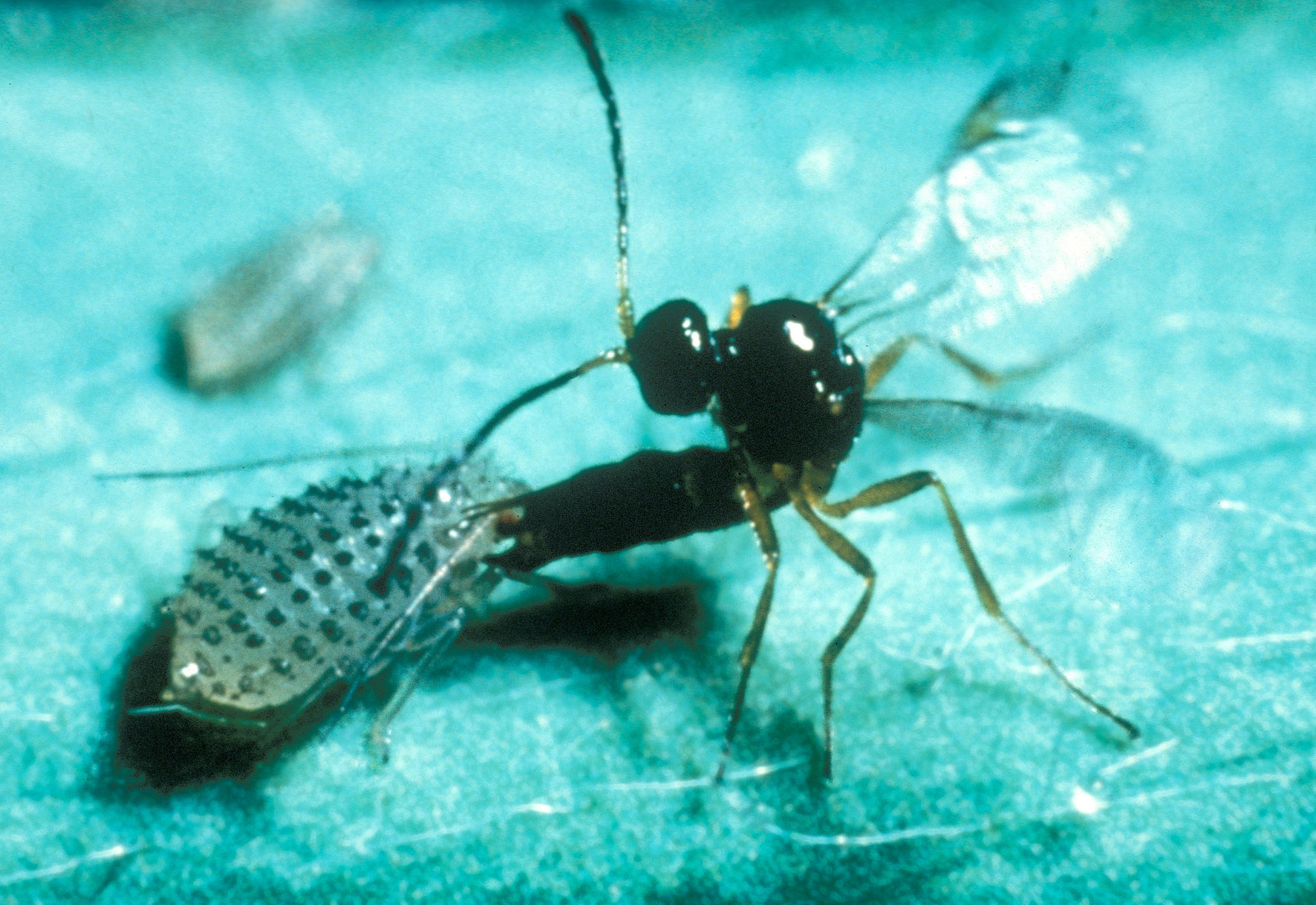
Asian Hornet (Vespa Velutina) & Mermithid Nematode (black Background)
The Asian hornet (''Vespa velutina''), also known as the yellow-legged hornet or Asian predatory wasp, is a species of hornet indigenous to Southeast Asia. It is of concern as an invasive species in some other countries, including most of Europe. Appearance ''Vespa velutina'' is significantly smaller than the European hornet. Typically, queens are in length, and males about . Workers measure about in length. The species has distinctive yellow tarsi (legs). The thorax is a velvety brown or black with a brown abdomen. Each abdominal segment has a narrow posterior yellow border, except for the fourth segment, which is orange. The head is black and the face yellow. Regional forms vary sufficiently in color to cause difficulties in classification, and several subspecies have been variously identified and ultimately rejected; while a history of recognizing subspecies within many of the ''Vespa'' species exists, including ''V.velutina'', the most recent taxonomic revision of the ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insects Described In 1853
Insects (from Latin ') are hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes, and a pair of antennae. Insects are the most diverse group of animals, with more than a million described species; they represent more than half of all animal species. The insect nervous system consists of a brain and a ventral nerve cord. Most insects reproduce by laying eggs. Insects breathe air through a system of paired openings along their sides, connected to small tubes that take air directly to the tissues. The blood therefore does not carry oxygen; it is only partly contained in vessels, and some circulates in an open hemocoel. Insect vision is mainly through their compound eyes, with additional small ocelli. Many insects can hear, using tympanal organs, which may be on the legs or other parts of the body. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lasioglossum
The sweat bee genus ''Lasioglossum'' is the largest of all bee genera, containing over 1800 species in numerous subgenera worldwide.Gibbs, J., et al. (2012)Phylogeny of halictine bees supports a shared origin of eusociality for ''Halictus'' and ''Lasioglossum'' (Apoidea: Anthophila: Halictidae).''Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution'' 65(3), 926-39. They are highly variable in size, coloration, and sculpture; among the more unusual variants, some are cleptoparasites, some are nocturnal, and some are oligolectic. Most ''Lasioglossum'' species nest in the ground, but some nest in rotten logs. Social behavior among species of ''Lasioglossum'' is extraordinarily variable; species are known to exhibit solitary nesting, primitive eusociality, and social parasitism. Colony sizes vary widely, from small colonies of a single queen and four or fewer workers to large colonies of >400 workers and perennial life cycles. The genus ''Lasioglossum'' can be divided into two informal series ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitoid
In evolutionary ecology, a parasitoid is an organism that lives in close association with its host (biology), host at the host's expense, eventually resulting in the death of the host. Parasitoidism is one of six major evolutionarily stable strategy, evolutionary strategies within parasitism, distinguished by the fatal prognosis for the host, which makes the strategy close to predation. Among parasitoids, strategies range from living inside the host (''endoparasitism''), allowing it to continue growing before emerging as an adult, to Paralysis, paralysing the host and living outside it (''ectoparasitism''). Hosts can include other parasitoids, resulting in hyperparasitism; in the case of oak galls, up to five levels of parasitism are possible. Some parasitoids Behavior-altering parasite, influence their host's behaviour in ways that favour the propagation of the parasitoid. Parasitoids are found in a variety of Taxon, taxa across the insect superorder Endopterygota, whose compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomethoca Frigida
''Pseudomethoca'' is a genus of velvet ants in the family Mutillidae. There are at least 20 described species in ''Pseudomethoca''. Species These 24 species belong to the genus ''Pseudomethoca'': * '' Pseudomethoca anthracina'' * '' Pseudomethoca athamas'' * '' Pseudomethoca bequaerti'' (striped velvet ant) * '' Pseudomethoca brazoria'' * '' Pseudomethoca contumax'' * '' Pseudomethoca diligibilis'' Mickel, 1952 * '' Pseudomethoca donaeanae'' * '' Pseudomethoca flammigera'' * '' Pseudomethoca frigida'' * '' Pseudomethoca oceola'' * '' Pseudomethoca oculata'' * '' Pseudomethoca paludata'' * ''Pseudomethoca pergrata'' Cresson, 1902 * '' Pseudomethoca plagiata'' (Gerstäcker, 1874) * ''Pseudomethoca praeclara'' * ''Pseudomethoca propinqua'' (Cresson, 1865) * ''Pseudomethoca puchella'' Mickel, 1952 * ''Pseudomethoca pumila'' Burmeister, 1855 * ''Pseudomethoca quadrinotata'' * ''Pseudomethoca sanbornii'' * ''Pseudomethoca simillima'' (Smith, 1855) * ''Pseudomethoca torrida'' Krombein, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutillidae
Velvet ants (Mutillidae) are a family of more than 7,000 species of wasps whose wingless females resemble large, hairy ants. Their common name velvet ant refers to their resemblance to an ant, and their dense pile of hair, which most often is bright scarlet or orange, but may also be black, white, silver, or gold. Their bright colors serve as aposematic signals. They are known for their extremely painful stings, (the sting of the species '' Dasymutilla klugii'' rated a 3 on the Schmidt pain index and lasts up to 30 minutes), and has resulted in the common name "cow killer" or "cow ant" being applied to the species '' Dasymutilla occidentalis.'' However, mutillids are not aggressive and sting only in defense. In addition, the actual toxicity of their venom is much lower than that of honey bees or harvester ants. Unlike true ants, they are solitary, and lack complex social systems. Distribution Mutillidae can be found worldwide with about 230 genera or subgenera and around 8,0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleptoparasite
Kleptoparasitism (originally spelt clepto-parasitism, meaning "parasitism by theft") is a form of feeding in which one animal deliberately takes food from another. The strategy is Evolutionarily stable strategy, evolutionarily stable when stealing is less costly than direct feeding, such as when food is scarce or when victims are abundant. Many kleptoparasites are arthropods, especially bees and wasps, but including some true flies, dung beetles, bugs, and spiders. Cuckoo bees are specialized kleptoparasites which lay their eggs either on the pollen masses made by other bees, or on the insect hosts of Parasitoid wasp, parasitoid wasps. They are an instance of Emery's rule, which states that insect social parasites tend to be closely related to their hosts. The behavior occurs, too, in vertebrates including birds such as skuas, which persistently chase other seabirds until they disgorge their food, and carnivorous mammals such as spotted hyenas and lions. Other species opportunistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lasioglossum Cephalotes
The sweat bee genus ''Lasioglossum'' is the largest of all bee genera, containing over 1800 species in numerous subgenera worldwide.Gibbs, J., et al. (2012)Phylogeny of halictine bees supports a shared origin of eusociality for ''Halictus'' and ''Lasioglossum'' (Apoidea: Anthophila: Halictidae).''Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution'' 65(3), 926-39. They are highly variable in size, coloration, and sculpture; among the more unusual variants, some are cleptoparasites, some are nocturnal, and some are oligolectic. Most ''Lasioglossum'' species nest in the ground, but some nest in rotten logs. Social behavior among species of ''Lasioglossum'' is extraordinarily variable; species are known to exhibit solitary nesting, primitive eusociality, and social parasitism. Colony sizes vary widely, from small colonies of a single queen and four or fewer workers to large colonies of >400 workers and perennial life cycles. The genus ''Lasioglossum'' can be divided into two informal series bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregarinasina
The gregarines are a group of Apicomplexan alveolates, classified as the Gregarinasina or Gregarinia. The large (roughly half a millimeter) parasites inhabit the intestines of many invertebrates. They are not found in any vertebrates. Gregarines are closely related to both '' Toxoplasma'' and ''Plasmodium'', which cause toxoplasmosis and malaria, respectively. Both protists use protein complexes similar to those that are formed by the gregarines for gliding motility and for invading target cells. This makes the gregarines excellent models for studying gliding motility, with the goal of developing treatment options for both toxoplasmosis and malaria. Thousands of different species of gregarine are expected to be found in insects, and 99% of these gregarine species still need to be described. Each insect species can be the host of multiple gregarine species. One of the most-studied gregarines is '' Gregarina garnhami''. In general, gregarines are regarded as a very successful group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematode
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitic. Parasitic worms (helminths) are the cause of soil-transmitted helminthiases. They are classified along with arthropods, tardigrades and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa. Unlike the flatworms, nematodes have a tubular digestive system, with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species are uncertain. A 2013 survey of animal biodiversity suggested there are over 25,000. Estimates of the total number of extant species are su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
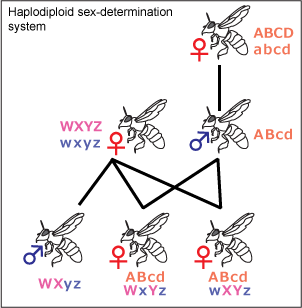
Eusociality
Eusociality ( Greek 'good' and social) is the highest level of organization of sociality. It is defined by the following characteristics: cooperative brood care (including care of offspring from other individuals), overlapping generations within a colony of adults, and a division of labor into reproductive and non-reproductive groups. The division of labor creates specialized behavioral groups within an animal society, sometimes called castes. Eusociality is distinguished from all other social systems because individuals of at least one caste usually lose the ability to perform behaviors characteristic of individuals in another caste. Eusocial colonies can be viewed as superorganisms. Eusociality has evolved among the insects, crustaceans, trematoda and mammals. It is most widespread in the Hymenoptera (ants, bees, and wasps) and in Isoptera (termites). A colony has caste differences: queens and reproductive males take the roles of the sole reproducers, while soldiers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |