|
Laryngotracheal Reconstruction
Laryngotracheal reconstruction is a surgical procedure that involves expanding or removing parts of the airway to widen a narrowing within it, called laryngotracheal stenosis or subglottic stenosis. Types Anterior and Posterior grafts Anterior grafts can be performed using tissue from the thyroid ala cartilage or the costal cartilage. Posterior grafts are generally made using costal cartilage. Resection Techniques Cricotracheal resection Tracheal resection Slide tracheoplasty Combined Expansion and Resection Techniques Slide tracheoplasty into cricoid split Slide tracheoplasty with tracheal resection History The first description of the anterior cricoid split appears in the early 1900s by Killian and the first description of the posterior cricoid split is credited to Galebsky in 1927. In 1938, Looper rotated the hyoid bone to augment a stenotic adult laryngeal fracture sustained in a railroad accident. In 1968, Lapidot used this principle in piglets to show that a flap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laryngotracheal Stenosis
Laryngotracheal stenosis refers to abnormal narrowing of the central air passageways. This can occur at the level of the larynx, trachea, carina or main bronchi. In a small number of patients narrowing may be present in more than one anatomical location. Presentation The most common symptom of laryngotracheal stenosis is gradually-worsening breathlessness (dyspnea) particularly when undertaking physical activities (exertional dyspnea). The patient may also experience added respiratory sounds which in the more severe cases can be identified as stridor but in many cases can be readily mistaken for wheeze. This creates a diagnostic pitfall in which many patients with laryngotracheal stenosis are incorrectly diagnosed as having asthma and are treated for presumed lower airway disease. This increases the likelihood of the patient eventually requiring major open surgery for benign disease and can lead to tracheal cancer presenting too late for curative surgery to be performed. Cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subglottic Stenosis
Subglottic stenosis is a congenital or acquired narrowing of the subglottic airway. It can be congenital, acquired, iatrogenic, or very rarely, idiopathic. It is defined as the narrowing of the portion of the airway that lies between the vocal cords and the lower part of the cricoid cartilage. In a normal infant, the subglottic airway is 4.5-5.5 millimeters wide, while in a premature infant, the normal width is 3.5 millimeters. Subglottic stenosis is defined as a diameter of under 4 millimeters in an infant. Acquired cases are more common than congenital cases due to prolonged intubation being introduced in the 1960s. It is most frequently caused by certain medical procedures or external trauma, although infections and systemic or autoimmune diseases can also cause it. Signs and symptoms Symptoms may range from stridor during exercise to complete obstruction of the airway. In idiopathic cases, symptoms may be mistaken for asthma. In congenital cases, symptoms occur soon after bir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costal Cartilage
Costal cartilage, also known as rib cartilage, are bars of hyaline cartilage that serve to prolong the ribs forward and contribute to the elasticity of the walls of the thorax. Costal cartilage is only found at the anterior ends of the ribs, providing medial extension. Differences from ribs 1-12 The first seven pairs are connected with the sternum; the next three are each articulated with the lower border of the cartilage of the preceding rib; the last two have pointed extremities, which end in the wall of the abdomen. Like the ribs, the costal cartilages vary in their length, breadth, and direction. They increase in length from the first to the seventh, then gradually decrease to the twelfth. Their breadth, as well as that of the intervals between them, diminishes from the first to the last. They are broad at their attachments to the ribs, and taper toward their sternal extremities, excepting the first two, which are of the same breadth throughout, and the sixth, seventh, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
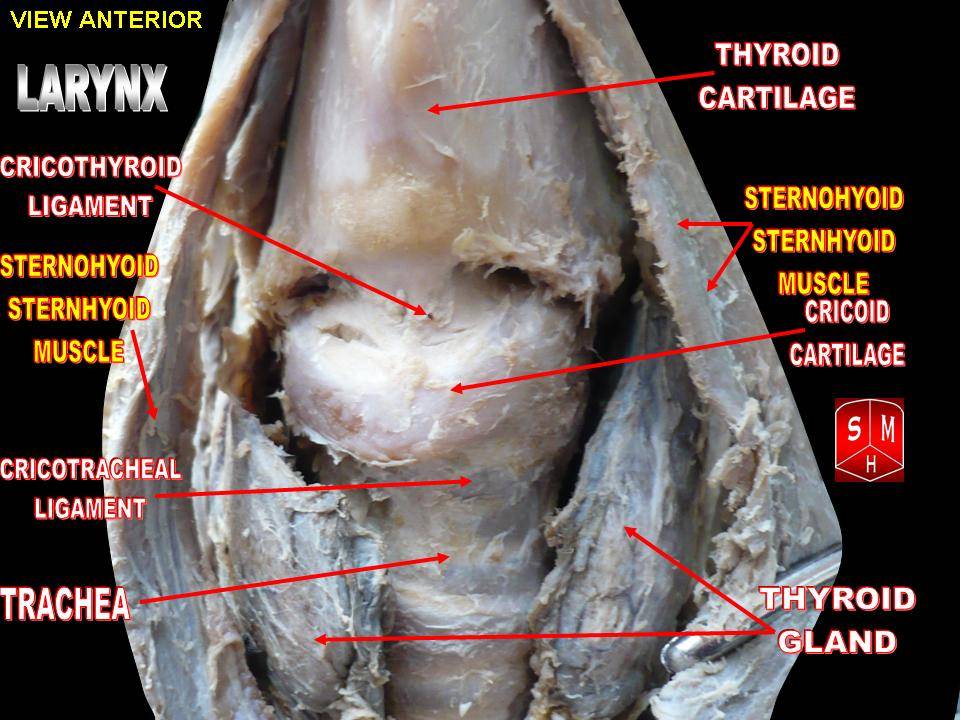
Cricotracheal Ligament
The cricotracheal ligament connects (the inferior border of) the cricoid cartilage superiorly, and the first tracheal cartilage ring inferiorly. It is continuous with the tracheal perichondrium The perichondrium (from Greek and ) is a layer of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the cartilage of developing bone. It consists of two separate layers: an outer fibrous layer and inner chondrogenic layer. The fibrous layer conta ... and resembles the fibrous membrane which connects the cartilaginous rings of the trachea to each other. References Ligaments of the head and neck {{respiratory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. At the top of the trachea, the cricoid cartilage attaches it to the larynx. The trachea is formed by a number of horseshoe-shaped rings, joined together vertically by overlying annular ligaments of trachea, ligaments, and by the trachealis muscle at their ends. The epiglottis closes the opening to the larynx during swallowing. The trachea begins to form in the second month of embryo development, becoming longer and more fixed in its position over time. Its epithelium is lined with columnar epithelium, column-shaped cells that have hair-like extensions called cilia, with scattered goblet cells that produce protective mucins. The trachea can be affected by inflammation or infection, usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Cerclage
Cervical cerclage, also known as a cervical stitch, is a treatment for cervical weakness, when the cervix starts to shorten and open too early during a pregnancy causing either a late miscarriage or preterm birth. In women with a prior spontaneous preterm birth and who are pregnant with one baby, and have shortening of the cervical length less than 25 mm, a cerclage prevents a preterm birth and reduces death and illness in the baby. The treatment consists of a strong suture sewn into and around the cervix early in the pregnancy, usually between weeks 12 to 14, and then removed towards the end of the pregnancy when the greatest risk of miscarriage has passed. The procedure is performed under local anaesthesia, usually by way of a spinal block. It is typically performed on an outpatient basis by an obstetrician-gynecologist. Usually the treatment is done in the first or second trimester of pregnancy, for a woman who has had one or more late miscarriages in the past. The word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perichondrium
The perichondrium (from Greek and ) is a layer of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the cartilage of developing bone. It consists of two separate layers: an outer fibrous layer and inner chondrogenic layer. The fibrous layer contains fibroblasts, which produce collagenous fibres. The chondrogenic layer remains undifferentiated and can form chondroblasts. Perichondrium can be found around the perimeter of elastic cartilage and hyaline cartilage. Perichondrium is a type of irregular collagenous ordinary connective tissue, and also functions in the growth and repair of cartilage. Perichondrium contains type I collagen Type I collagen is the most abundant collagen of the human body, consisting of around 90% of the body's total collagen in vertebrates. Due to this, it is also the most abundant protein type found in all vertebrates. Type I forms large, eosinop ... and type XII collagen. References External links * Iowa Histology Index 4/iv-05' - "Slide 12, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cricoid Cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment site for muscles, cartilages, and ligaments involved in opening and closing the airway and in producing speech. Anatomy The cricoid cartilage is the only laryngeal cartilage to form a complete circle around the airway. It is smaller yet thicker and tougher than the thyroid cartilage above. It articulates superiorly with the thyroid cartilage, and the paired arytenoid cartilage. Inferiorly, the trachea attaches onto it. It occurs at the level of the C6 vertebra. Structure The posterior part of the cricoid cartilage (cricoid lamina) is somewhat broader than the anterior and lateral part (cricoid arch). Its shape is said to resemble a signet ring. Cricoid arch The cricoid arch is the curved and vertically narrow anterior portion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Mucosa
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed '' lamina propria''. The oral cavity has sometimes been described as a mirror that reflects the health of the individual. Changes indicative of disease are seen as alterations in the oral mucosa lining the mouth, which can reveal systemic conditions, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiency, or the local effects of chronic tobacco or alcohol use. The oral mucosa tends to heal faster and with less scar formation compared to the skin. The underlying mechanism remains unknown, but research suggests that extracellular vesicles might be involved. Classification Oral mucosa can be divided into three main categories based on function and histology: * ''Lining mucosa'', nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium, found almost everywhere else in the oral cavity, including the: ** ''Alveolar mucosa'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robin T
Robin most commonly refers to several species of passerine birds. Robin may also refer to: Animals * Australasian robins, red-breasted songbirds of the family Petroicidae * Many members of the subfamily Saxicolinae (Old World chats), including: **European robin (''Erithacus rubecula'') ** Bush-robin **Forest robin **Magpie-robin **Scrub robin ** Robin-chat ** Bagobo robin **White-starred robin **White-throated robin ** Blue-fronted robin **Larvivora (6 species) **Myiomela (3 species) * Some red-breasted New-World true thrushes (''Turdus'') of the family Turdidae, including: ** American robin (''T. migratorius'') (so named by 1703) ** Rufous-backed thrush (''T. rufopalliatus'') ** Rufous-collared thrush (''T. rufitorques'') ** Formerly other American thrushes, such as the clay-colored thrush (''T. grayi'') * Pekin robin or Japanese (hill) robin, archaic names for the red-billed leiothrix (''Leiothrix lutea''), red-breasted songbirds * Sea robin, a fish with small "legs" (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorocebus
''Chlorocebus'' is a genus of medium-sized primates from the family of Old World monkeys. Six species are currently recognized, although some people classify them all as a single species with numerous subspecies. Either way, they make up the entirety of the genus ''Chlorocebus''. Confusingly, the terms "vervet monkey" and "green monkey" are sometimes used to refer to the whole genus ''Chlorocebus'', though they also refer more precisely to species ''vervet monkey, Chlorocebus pygerythrus'' and ''green monkey, Chlorocebus sabaeus'', respectively, neither of which is the type species for ''Chlorocebus''. This article uses the term ''Chlorocebus'' consistently for the genus and the common names only for the species. The native range (biology), range of these monkeys is sub-Saharan Africa from Senegal and Ethiopia south to South Africa. However, in previous centuries, a number of them were taken as pets by early Caribbean settlers and slave traders, and were transported across the At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |