|
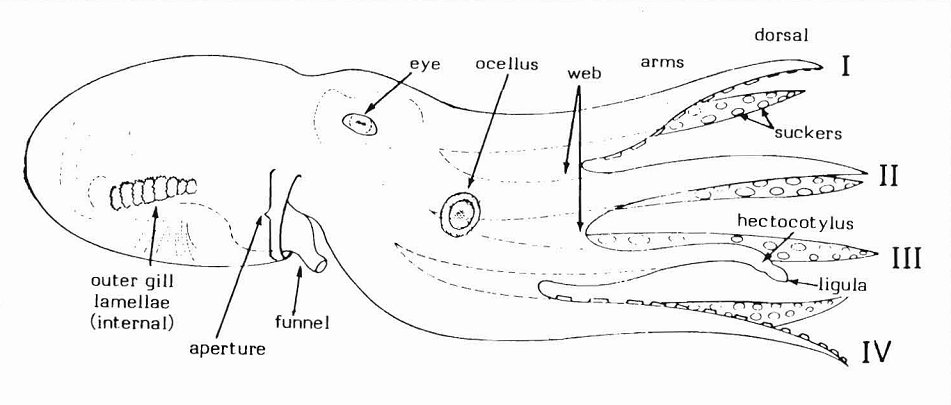
Larger Pacific Striped Octopus
The larger Pacific striped octopus (LPSO), or Harlequin octopus, is a species of octopus known for its intelligence and gregarious nature. The species was first documented in the 1970s and, being fairly new to scientific observation, has yet to be scientifically described. Because of this, LPSO has no official scientific name. Unlike other octopus species which are normally solitary, the LPSO has been reported as forming groups of up to 40 individuals. While most octopuses are cannibalistic and have to exercise extreme caution while mating, these octopuses mate with their ventral sides touching, pressing their beaks and suckers together in an intimate embrace. The LPSO has presented many behaviors that differ from most species of octopus, including intimate mating behaviors, formation of social communities, unusual hunting behavior, and the ability to reproduce multiple times throughout their life. The LPSO has been found to favor the tropical waters of the Eastern Pacific. Appe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octopus
An octopus (: octopuses or octopodes) is a soft-bodied, eight-limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a beaked mouth at the centre point of the eight limbs. An octopus can radically deform its shape, enabling it to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their appendages behind them as they swim. The siphon is used for respiration and locomotion (by water jet propulsion). Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse invertebrates. Octopuses inhabit various ocean habitats, including coral reefs, pelagic waters, and the seabed; some live in the intertidal zone and others at abyssal depths. Most species grow quickly, mature early, and are short-lived. In most species, the male uses a speciall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bivalvia
Bivalvia () or bivalves, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class (biology), class of aquatic animal, aquatic molluscs (marine and freshwater) that have laterally compressed soft bodies enclosed by a calcified exoskeleton consisting of a hinged pair of half-bivalve shell, shells known as valve (mollusc), valves. As a group, bivalves have no head and lack some typical molluscan organs such as the radula and the odontophore. Their gills have evolved into ctenidium (mollusc), ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Common bivalves include clams, oysters, Cockle (bivalve), cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other family (biology), families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. Majority of the class are benthic filter feeders that bury themselves in sediment, where they are relatively safe from predation. Others lie on the sea floor or attach themselves to rocks or other h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molluscs Of Central America
Mollusca is a phylum of protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum after Arthropoda. The number of additional fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000, and the proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat, as numerous groups are freshwater and even terrestrial species. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known extant invertebrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopods Of Oceania
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, whereas in the Nautiloidea, the external shell remains. About 800 living species of cephalopods have been identified. Tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octopuses
An octopus (: octopuses or octopodes) is a soft-bodied, eight-limbed Mollusca, mollusc of the order (biology), order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is symmetry in biology, bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a cephalopod beak, beaked mouth at the centre point of the eight limbs. An octopus can radically deform its shape, enabling it to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their appendages behind them as they swim. The Siphon (mollusc), siphon is used for aquatic respiration, respiration and aquatic locomotion, locomotion (by jet propulsion#Jet-propelled animals, water jet propulsion). Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse invertebrates. Octopuses inhabit various ocean habitats, including coral reefs, pelagic waters, and the seabed; some live in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senescence
Senescence () or biological aging is the gradual deterioration of Function (biology), functional characteristics in living organisms. Whole organism senescence involves an increase in mortality rate, death rates or a decrease in fecundity with increasing age, at least in the later part of an organism's biological life cycle, life cycle. However, the resulting effects of senescence can be delayed. The 1934 discovery that calorie restriction can Life extension, extend lifespans by 50% in rats, the existence of species having negligible senescence, and the existence of potentially immortal organisms such as members of the genus ''Hydra (genus), Hydra'' have motivated research into Life extension, delaying senescence and thus age-related diseases. Rare human mutations can cause accelerated aging diseases. Environmental Gerontogens, factors may affect aging – for example, overexposure to ultraviolet radiation accelerates skin aging. Different parts of the body may age at different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura (meaning "short tailed" in Greek language, Greek), which typically have a very short projecting tail-like abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomen, usually hidden entirely under the Thorax (arthropod anatomy), thorax. Their exoskeleton is often Sclerotization, thickened and hard. They generally have Arthropod leg, five pairs of legs, and they have "Pincers (tool), pincers" or "claws" on the ends of the frontmost pair, scientifically termed the ''chelae''. They are present in all the world's oceans, Freshwater crab, in freshwater, and Terrestrial crab, on land, often hiding themselves in small crevices or burrowing into sediment. Crabs are omnivores, feeding on a variety of food, including a significant proportion of Algae eater, algae, as well as Detritivore, detritus and other invertebrates. Crab meat, Crabs are widely consumed by humans as food, with over 1.5 million tonnes Crab fisheries, caught annually. True crabs first appeared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octopus Chierchiae
''Octopus chierchiae'' is commonly known as the lesser Pacific striped octopus or pygmy zebra octopus. It has been proposed as a model organism for cephalopod research as it is one of the few octopus species with the ability to lay multiple egg clutches ( iteroparity), compared to most octopus species that are semelparous and die after one reproductive event. This makes ''Octopus chierchiae'' a candidate for sustainable and multigenerational laboratory research. Description ''Octopus chierchiae'' is a small octopus found in the central Pacific coast of the Americas, most often in Central America but sightings have been reported as far north as the Gulf of California. It lives in low, intertidal zones at a maximum depth of 40 meters. The largest mantle length recorded for ''Octopus chierchiae'' was 25 millimeters. Newly hatched ''Octopus chierchiae'' are 3.5 mm in length and reach adult size in 250 to 300 days. This is advantageous for research purposes, as other model oct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomatopod
Mantis shrimp are carnivorous marine crustaceans of the order Stomatopoda (). Stomatopods branched off from other members of the class Malacostraca around 400 million years ago, with more than 520 extant species of mantis shrimp known. All living species are in the suborder Unipeltata, which arose around 250 million years ago. They are among the most important predators in many shallow, tropical and subtropical marine habitats. Despite being common in their habitats, they are poorly understood, as many species spend most of their lives sheltering in burrows and holes. Dubbed "sea locusts" by ancient Assyrians, "prawn killers" in Australia, and now sometimes referred to as "thumb splitters" due to their ability to inflict painful wounds if handled incautiously, mantis shrimp possess powerful raptorial appendages that are used to attack and kill prey either by spearing, stunning, or dismembering; the shape of these appendages are often used to classify them into groups: extant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
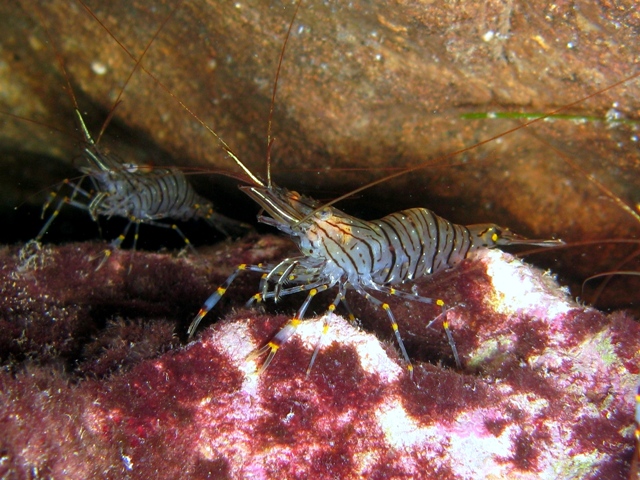
Shrimp
A shrimp (: shrimp (American English, US) or shrimps (British English, UK)) is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily Aquatic locomotion, swimming mode of locomotion – typically Decapods belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchiata, although some Shrimp#Non-decapods, crustaceans outside of this order are also referred to as "shrimp". Any small crustacean may also be referred to as "shrimp", regardless of resemblance. More narrow definitions may be restricted to Caridea, to smaller species of either of the aforementioned groups, or only the Marine life, marine species. Under a broader definition, ''shrimp'' may be synonymous with prawn, covering stalk-eyed swimming crustaceans with long, narrow muscular tails (Abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomens), long whiskers (Antenna (biology), antennae), and slender, Biramous, biramous legs. They swim forward by paddling the swimmerets on the underside of their abdomens, although their escape response is typically repeated flicks wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |