|
Languages Of Bhutan
There are two dozen languages of Bhutan, all members of the Tibeto-Burman language family except for Nepali, which is an Indo-Aryan language, and the Bhutanese Sign Language. Dzongkha, the national language, is the only native language of Bhutan with a literary tradition, though Lepcha and Nepali are literary languages in other countries. Other non-Bhutanese minority languages are also spoken along Bhutan's borders and among the primarily Nepali-speaking Lhotshampa community in South and East Bhutan. Chöke (or Classical Tibetan) is the language of the traditional literature and learning of the Buddhist monastics. Sino-Tibetan languages Geographically, since Bhutan is predominantly located on the Tibetan plateau, almost all spoken languages of the country belong to the family of Sino-Tibetan languages, or more specifically, the Bodish sprachbund. Dzongkha and other Tibetic languages The Central Bodish languages are a group of related Tibetic languages descended from Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gongduk Language
Gongduk or Gongdu (, it is also known as Gongdubikha) is an Endangered language, endangered Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino-Tibetan language spoken by about 1,000 people in a few inaccessible villages located near the Kuri Chhu river in the Gongdue Gewog of Mongar District in eastern Bhutan. The names of the villages are Bala, Dagsa, Damkhar, Pam, Pangthang, and Yangbari (''Ethnologue''). History The people are said to have come from hunters that would move from place to place at times. The language is notable for only being discovered by linguists in 1991. Currently, George van Driem is working towards the completion of a description of Gongduk based on his work with native speakers in the Gongduk area. Classification Gongduk has complex verbal morphology, which Ethnologue considers a retention from Proto-Tibeto-Burman language, Proto-Tibeto-Burman, and is lexically highly divergent.Blench, R. & Post, M. W. (2013)Rethinking Sino-Tibetan phylogeny from the perspective of Northe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dakpa Language
The Takpa or Dakpa language (), ''Dakpakha'', known in India as Tawang Monpa, also known as Brami in Bhutan, is an East Bodish language spoken in the Tawang district of Arunachal Pradesh, and in northern Trashigang District in eastern Bhutan, mainly in Kyaleng (Shongphu gewog), Phongmed Gewog, Dangpholeng and Lengkhar near Radi Gewog. Van Driem (2001) describes Takpa as the most divergent of Bhutan's East Bodish languages, though it shares many similarities with Bumthang. SIL reports that Takpa may be a dialect of the Brokpa language and that it been influenced by the Dzala language whereas Brokpa has not. Takpa is mutually unintelligible with Monpa of Zemithang and Monpa of Mago-Thingbu. Monpa of Zemithang is another East Bodish language, and is documented in Abraham, et al. (2018).Abraham, Binny, Kara Sako, Elina Kinny, Isapdaile Zeliang. 2018. Sociolinguistic Research among Selected Groups in Western Arunachal Pradesh: Highlighting Monpa'. SIL Electronic Survey Reports ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
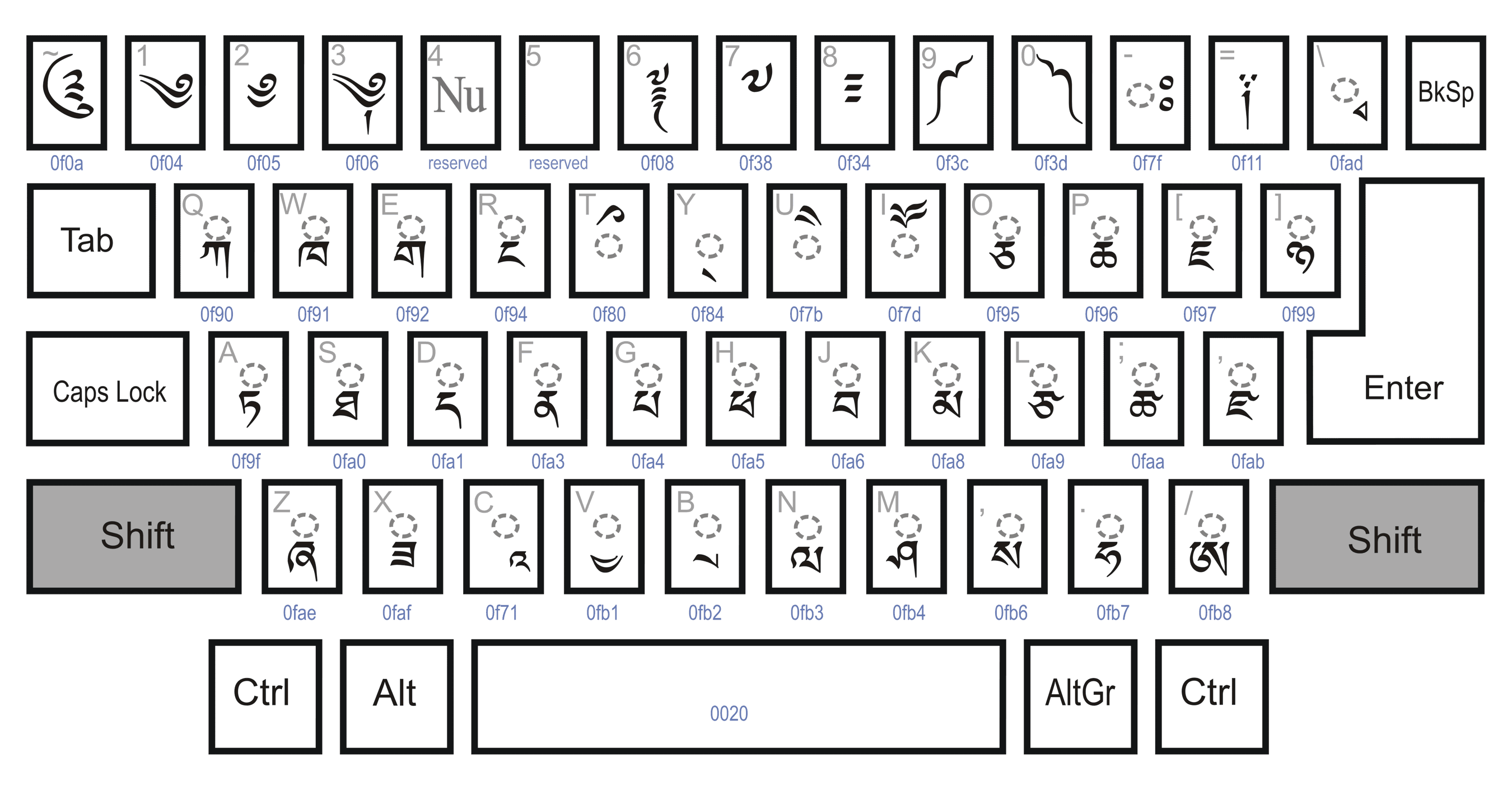
Dzongkha Keyboard Layout
The Dzongkha keyboard layout scheme is designed as a simple means for inputting Dzongkha (རྫོང་ཁ) and classical Tibetan (ཆོས་སྐད) text on computers. This keyboard layout was standardized by the Dzongkha Development Commission (DDC) and the Department of Information Technology and Telecom, Bhutan, Department of Information Technology and Telecom (DITT) of the Royal Government of Bhutan in 2000. It was updated in 2009 to accommodate additional characters added to the Unicode & ISO 10646 standards since the initial version. Since the arrangement of keys essentially follows the usual order of the Dzongkha and Tibetan alphabet, the layout can be quickly learned by anyone familiar with this alphabet. Subjoined (combining) consonants are entered using the Shift key. The Dzongkha (dz) keyboard layout is included in the XFree86 distribution. Keyboard layout Dzongkha (Bhutan) - dz-BT Alternative Dzongkha inputDzongkha Keyboard & Input Methods - National Lib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhutanese Sign Language
Bhutanese Sign Language (BhSL; in Dzongkha) is the indigenous sign language of Bhutan Bhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia, in the Eastern Himalayas between China to the north and northwest and India to the south and southeast. With a population of over 727,145 and a territory of , ..., used especially at the Wangsel Institute for the Deaf, Paro, Bhutan. Bhutan set up the program for the deaf in a hearing school in Thimphu ca. 2000, and the first dedicated school, in Paro, was approved in 2013. Part of government funding for deaf education includes developing Bhutanese Sign Language as the language of instruction. Development includes at least creating vocabulary for technical subjects, and deciding on which regional signs to use where they differ. It is not clear if there are multiple sign languages in Bhutan, or merely local differences in vocabulary. It is unknown whether Bhutanese Sign Language is related to Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government of India, alongside English language, English, and is the ''lingua franca'' of North India. Hindi is considered a Sanskritisation (linguistics), Sanskritised Register (sociolinguistics), register of Hindustani. Hindustani itself developed from Old Hindi and was spoken in Delhi and neighbouring areas. It incorporated a significant number of Persian language, Persian loanwords. Hindi is an Languages with official status in India, official language in twelve states (Bihar, Gujarat , Mizoram , Maharashtra ,Chhattisgarh, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand), and six Union territory, union territories (Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Delhi, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ʼOle Language
ʼOle, also called ʼOlekha or Black Mountain Monpa, is a moribund, possibly Sino-Tibetan language spoken natively by 1 person in the Black Mountains of Wangdue Phodrang and Trongsa Districts in western Bhutan. The term ʼOle refers to a clan of speakers. Geographic distribution According to the ''Ethnologue'', ʼOlekha is spoken in the following locations of Bhutan. *Trongsa District: 3 enclaves west of Mangde river *Wangdue Phodrang District: Adha, Jangji, Rukha, Thrumzur, and Wangling villages Dialects are separated by the Black Mountains. Classification ʼOle forms a distinct branch of Sino-Tibetan/Tibeto-Burman. it is not closely related to Tshangla language of eastern Bhutan, also called "Monpa" and predating Dzongkha in the region, which belongs to a different branch of the family. Gerber (2018) notes that Black Mountain Mönpa has had extensive contact with Gongduk before the arrival of East Bodish languages in Bhutan. The following comparative vocabulary tabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lhokpu Language
Lhokpu, also ''Lhobikha'' or ''Taba-Damtoe-Bikha'', is one of the autochthonous languages of Bhutan spoken by the Lhop people. It is spoken in southwestern Bhutan along the border of Samtse and Chukha Districts. Van Driem (2003) leaves it unclassified as a separate branch within the Sino-Tibetan language family. Phonology Vowels Consonants Classification George van Driem (2001:804) notes that Lhokpu, although unclassified, may be more closely related to the Kiranti languages than to Lepcha. Gerber, et al. (2016) also notes a particularly close relationship between Lhokpu and Kiranti. Furthermore, van Driem (2001:804–805) notes that Dzongkha, the national language of Bhutan, may in fact have a Lhokpu substratum. Grollmann & Gerber (2017) consider Lhokpu to have a particularly close relationship with Dhimal and Toto. Name Lhokpu is spoken by the Lhop—a Dzongkha term meaning "Southerners"—, who "represent the aboriginal dungDung population of western Bhutan. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamang Language
Tamangic language is spoken mainly in Tamangsaling Land in Nepal, Sikkim, West Bengal (Darjeeling) and North-Eastern India. It comprises Eastern Tamang, Northwestern Tamang, Southwestern Tamang, Eastern Gorkha Tamang, and Western Tamang. Lexical similarity between Eastern Tamang (which is regarded as the most prominent) and other Tamang languages varies between 81% and 63%. For comparison, the lexical similarity between Spanish and Portuguese is estimated at 89%. Ethnologue report for Spanish Dialects ''Ethnologue'' divides Tamang into the following varieties due to mutual unintelligibility. *Eastern Tamang: 759,000 in Nepal (2000 WCD). Population total all countries: 773,000. Sub-dialects are as follows. **Outer-Eastern Tamang (Sailung Tamang) **Central-Eastern Tamang (Temal Tamang) **Southwestern Tamang (Kath-Bhotiya, Lama Bhote, Murmi, Rongba, Sain, Tamang Gyoi, Tamang Gyot, Tamang Lengmo, Tamang Tam) *Western Tamang: 323,000 (2000 WCD). Sub-dialects are as follows. ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newar Language
Newar (; , ) is a Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Newar people, the indigenous inhabitants of Nepal Mandala, which consists of the Kathmandu Valley and surrounding regions in Nepal. The language is known officially in Nepal as Nepal Bhasa, a name that has been historically used for the language. The term "Newari" is also used to refer to the language, although the Indic ''-i'' suffix is considered inappropriate by some Newar speakers. The language served as the official language of Nepal during the Malla dynasty (Nepal), Malla dynasty since the 14th century till the end of dynasty in 1769 during which the language was referred as "Nepal Bhasa", a term which literally means "Nepalese Language". However, the language is not the same as Nepali language, Nepali, an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language and the current official language of Nepal, which only got the name Nepali in the 1930s. Newar literature, Literature in Newar is one of the oldest i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepcha Language
Lepcha language, or Róng language ( Lepcha: ; ''Róng ríng''), is a Tibeto-Burman language spoken by the Lepcha people in Sikkim, India and parts of West Bengal, Nepal, and Bhutan. Despite spirited attempts to preserve the language, Lepcha has already effectively been lost everywhere in favour of Nepali. The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) lists Lepcha as an endangered language with the following characterization. The Lepcha language is spoken in Sikkim and Darjeeling district in West Bengal of India. The 1991 Indian census counted 39,342 speakers of Lepcha. Lepcha is considered to be one of the indigenous languages of the area in which it is spoken. Unlike most other languages of the Himalayas, the Lepcha people have their own indigenous script (the world's largest collection of old Lepcha manuscripts is kept in Leiden, with over 180 Lepcha books). Lepcha is the language of instruction in some schools in Sikkim. In comparison to o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |