|
Lambdavirus LvO276
''Lambdavirus'' is a genus of viruses in the class ''Caudoviricetes''. Bacteria serve as natural hosts, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. There are five species in this genus. Taxonomy The following species are recognized: * ''Lambdavirus DE3'' * ''Lambdavirus HK629'' * ''Lambdavirus HK630'' * ''Lambda phage, Lambdavirus lambda'' * ''Lambdavirus lvO276'' The genus also includes several unclassified viruses—including the corynebacteriophage, corynephages β and ω, which infect ''Corynebacterium diphtheriae'' and carry the deadly diphtheria toxin.NCBICorynephage beta(species)NCBICorynephage omega(species) Structure Lambdaviruses are viral envelope, nonenveloped, with a head and tail. The head is about 60 nm in diameter, consisting of 72 capsomers (T=7, levo). Genome All species have been fully sequenced. They range between 42k and 49k nucleotides, with 56 to 73 proteins. Life cycle The virus attaches to the host cell's adhesion receptors using its te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of List of virus species, virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siphoviridae
''Siphoviridae'' was a family of double-stranded DNA viruses in the order '' Caudovirales''. The family ''Siphoviridae'' and order '' Caudovirales'' have now been abolished, with the term siphovirus now used to refer to the morphology of viruses in this former family. Bacteria and archaea serve as natural hosts. The family had 1,166 species, assigned to 366 genera and 22 subfamilies. The characteristic structural features are a non-enveloped head and non-contractile tail. Structure Viruses in the former family ''Siphoviridae'' are non-enveloped, with icosahedral and head-tail geometries ( morphotype B1) or a prolate capsid (morphotype B2), and T=7 symmetry. Their diameters are around 60 nm. Members of this family are also characterized by their filamentous, cross-banded, non-contractile tails, usually with short terminal and subterminal fibers. Genomes are double stranded and linear, around 50 kb in length. Life cycle Viral replication is cytoplasmic. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
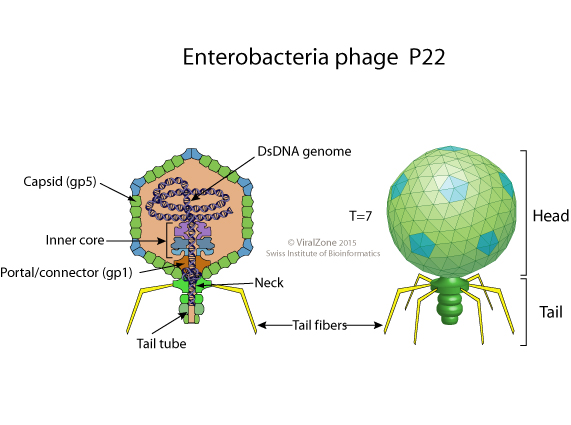
Lederbergvirus P22
Salmonella virus P22 is a bacterial virus (bacteriophage) that infects ''Salmonella typhimurium''. Like many phages, it has been used in molecular biology to induce mutations in cultured bacteria and to introduce foreign genetic material. P22 has been used in generalized transduction and is an important tool for investigating ''Salmonella'' genetics. Morphology, classification and relatives P22 shares many similarities in genetic structure and regulation with bacteriophage λ. It is a temperate double stranded DNA phage as well as a lambdoid phage since it carries control of gene expression regions and early operons similar to those of bacteriophage λ. However, the genes which encode proteins that build the virion are different from those of bacteriophage λ. P22 has a 60 nm diameter icosahedral (T=7) virion head and a short tail. This virion morphology puts P22 in the formal ''Podoviridae'' group. Traditionally, P22 is associated with viruses with similar geno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tl2011virus
TL or Tl may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Teens' love, Japanese erotic fiction marketed towards women * Télé Liban, a Lebanese television network * ''Turn Left'' (newspaper), Cornell University student publication Language * Tl (digraph), a digraph representing a voiceless alveolar lateral affricate in some languages * Tagalog language (ISO 639 alpha-2 code: tl) Organisations * Airnorth (IATA airline code TL), an airline * Public transport in the Lausanne Region, a transport company * ''Teknisk Landsforbund'', the Danish Union of Professional Technicians * Team Liquid, a professional gaming and eSports team and community website Science and technology * Liquidus temperature, the maximum temperature at which crystals can co-exist with the melt * Teralitre (Tl or TL), a metric unit of volume or capacity * Thallium, symbol Tl, a chemical element * Thermoluminescence dating, in geochronology * Total length in fish measurement * Transmission loss (TL), in acoustics, elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudovirales
''Caudoviricetes'' is a class of viruses known as tailed viruses and head-tail viruses (''cauda'' is Latin for "tail"). It is the sole representative of its own phylum, ''Uroviricota'' (from ''ouros'' (ουρος), a Greek word for "tailed" + -viricota). Under the Baltimore classification scheme, the ''Caudoviricetes'' are group I viruses as they have double stranded DNA (dsDNA) genomes, which can be anywhere from 18,000 base pairs to 500,000 base pairs in length. The virus particles have a distinct shape; each virion has an icosahedral head that contains the viral genome, and is attached to a flexible tail by a connector protein. The order encompasses a wide range of viruses, many containing genes of similar nucleotide sequence and function. However, some tailed bacteriophage genomes can vary quite significantly in nucleotide sequence, even among the same genus. Due to their characteristic structure and possession of potentially homologous genes, it is believed these viruse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriophage HK97
Bacteriophage HK97, often shortened to HK97, is a species of virus that infects ''Escherichia coli'' and related bacteria. It is named after Hong Kong (HK), where it was first located. HK97 has a double-stranded DNA genome. Assembly and maturation The major capsid protein of HK97, called gp5, cross-links upon maturation to form a chain-mail like structure. While DNA is being packaged into the capsid, the capsid expands by nearly 5 nm and changes from spherical to icosahedral in shape. The HK97 assembly pathway begins with self-assembly of gp5 into pentamers and hexamers. A protease, called gp4, cleaves gp5 at its N-terminus The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amin .... Attachment of a portal protein, gp3, coupled with conformational changes leads to the formation of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Committee On Taxonomy Of Viruses
The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclature for viruses. The ICTV develops a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropriately describe, name, and classify every virus taxon. The members of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses are considered expert virologists. The ICTV was formed from and is governed by the Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies. Detailed work, such as identifying new taxa and delimiting the boundaries of species, genera, families, etc. typically is performed by study groups of experts in the families. History The International Committee on Nomenclature of Viruses (ICNV) was established in 1966, at the International Congress for Microbiology in Moscow, to standardize the naming of virus taxa. The ICVN published its first report in 1971. For viruses infecting vertebrates, the first report i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |