|
Ladbroke Grove Rail Crash
The Ladbroke Grove rail crash (also known as the Paddington rail crash) was a rail accident which occurred on 5 October 1999 at Ladbroke Grove in London, England, when a Thames Trains-operated passenger train Signal passed at danger, passed a signal at danger, colliding almost head-on with a First Great Western-operated passenger train. With 31 people killed and 417 injured, it was one of the worst rail accidents in 20th-century British history. It was the second major crash on the Great Western Main Line in just over two years, the first being the Southall rail crash of September 1997, a few miles west of this crash. Both crashes would have been prevented by an operational Automatic_Train_Protection_(United_Kingdom), automatic train protection (ATP) system, wider fitting of which had been rejected on cost grounds. The crash severely damaged public confidence in the management and regulation of safety of rail transport in Great Britain, Britain's privatised railway system. A p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladbroke Grove, London
Ladbroke Grove ( ) is a road in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea, London, England, which passes through Kensal Green and Notting Hill, running north–south between Harrow Road and Holland Park Avenue. It is also the name of the surrounding area including parts of Kensal Town, Latimer Road, Kensal Green and Westbourne Park, straddling the W10 and W11 postal districts. Ladbroke Grove tube station is on the road, at the point where it is crossed by the Westway. Ladbroke Grove is the nearest tube station to Portobello Road Market. The adjacent bridge and nearby section of the Westway were regenerated in 2007 in a partnership including Urban Eye, Transport for London and London Underground. It is the main road on the route of the annual Notting Hill Carnival. The northern end between the Harrow Road and Kensal House is in Kensal Green, the middle section between Barlby Road and the A40 flyover in North Kensington, and the southern end between Lancaster Road and H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Her Majesty's Railway Inspectorate
Established in 1840, His Majesty's Railway Inspectorate (HMRI) is the organisation responsible for overseeing safety on Britain's railways and tramways. It was previously a separate non-departmental public body, but from 1990 to April 2006 it was part of the Health and Safety Executive. It was then transferred to the Office of Rail and Road and ceased to exist by that name in May 2009 when it was renamed the Safety Directorate. However, in summer 2015 its name was re-established as the safety arm of ORR. Modern HMRI inspectorate The modern HMRI within the Office of Road and Rail (ORR) identifies as "The Railway Inspectorate". HMRI works in tandem with the rest of the ORR, and as such may be consulted on matters effecting industry efficiency. Internally, most of HMRI's inspectors are part of the Railway Safety Directorate (RSD) of the ORR, although some Railway Performance and Planning (RPP) engineers have some more limited powers as warranted HMRI individuals. HMRI's role a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-track Railway
A double-track railway usually involves running one track in each direction, compared to a single-track railway where trains in both directions share the same track. Overview In the earliest days of railways in the United Kingdom, most lines were built as double-track because of the difficulty of co-ordinating operations before the invention of the telegraph. The lines also tended to be busy enough to be beyond the capacity of a single track. In the early days the Board of Trade did not consider any single-track railway line to be complete. In the earliest days of railways in the United States most lines were built as single-track for reasons of cost, and very inefficient timetable working systems were used to prevent head-on collisions on single lines. This improved with the development of the telegraph and the train order system. Operation Handedness In any given country, rail traffic generally runs to one side of a double-track line, not always the same side as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. British Railways was formed on 1 January 1948 as a result of the Transport Act 1947, which nationalised the Big Four British railway companies along with some other (but not all) smaller railways. Profitability of the railways became a pressing concern during the 1950s, leading to multiple efforts to bolster performance, including some line closures. The 1955 Modernisation Plan formally directed a process of dieselisation and electrification to take place; accordingly, steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction (except for the narrow-gauge Vale of Rheidol Railway tourist lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Signal
A railway signal is a visual display device that conveys instructions or provides warning of instructions regarding the driver's authority to proceed. The driver interprets the signal's indication and acts accordingly. Typically, a signal might inform the driver of the speed at which the train may safely proceed or it may instruct the driver to stop. Application and positioning of signals Originally, signals displayed simple stop or proceed indications. As traffic density increased, this proved to be too limiting and refinements were added. One such refinement was the addition of distant signals on the approach to stop signals. The distant signal gave the driver warning that they were approaching a signal which might require a stop. This allowed for an overall increase in speed, since train drivers no longer had to drive at a speed within sighting distance of the stop signal. Under timetable and train order operation, the signals did not directly convey orders to the tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 43 (HST)
The British Rail Class 43 (HST) is the TOPS classification used for the InterCity 125 ''High Speed Train'' (formerly Classes 253 and 254) Diesel locomotive#Diesel-electric, diesel-electric power cars, built by British Rail Engineering Limited from 1975 to 1982, and in service in the UK since 1976. The class is officially the Railway speed record#Fuel-electric, fastest diesel locomotive in the world, with an absolute maximum speed of , and a regular service speed of . The record run was led by 43102 (43302) and trailed by 43159. History and background In the early 1970s, the British Railways Board made the decision to replace its main-line express diesel traction. Financial limitations were tight, so mass electrification was not possible. As a result, a new generation of high-speed diesel trains had to be developed. Experience with the high-speed locomotives had shown that a low axle weight was essential to avoid damage to the track at sustained high speed, and that high-sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Mark 3
The British Rail Mark 3 is a type of passenger railway carriage, carriage developed in response to growing competition from passenger airline, airlines and the automobile, car in the 1970s. A variant of the Mark 3 became the rolling stock for the InterCity 125, High Speed Train (HST). Originally conceived as locomotive-hauled coaching stock, the first coaches built were for the prototype HST in 1972. Production coaches entered service between 1975 and 1988, and multiple-unit designs based on the Mark 3 bodyshell continued to be built until the early 1990s. Most of the surviving fleet of the Mark 3 and its derivatives were still in revenue service on the British railway network in 2020, however, as of 7 April 2021, 300 carriages have been sent for scrap. Introduction Under the chairmanship of Stanley Raymond, it was decided to reduce journey times further on long-distance trains by increasing line speed to , where practical – the maximum considered possible on Britain's Victor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InterCity 125
The InterCity 125 (originally Inter-City 125) or High Speed Train (HST) is a diesel-powered High-speed rail, high-speed passenger train built by British Rail Engineering Limited between 1975 and 1982. A total of 95 sets were produced, each comprising two British Rail Class 43 (HST), Class 43 power cars, one at each end, and a rake (train)#R, rake of seven or eight British Rail Mark 3, Mark 3 coaches. The name is derived from its top operational speed of . At times, the sets have been classified as British Rail Classes 253, 254 and 255. British Rail (BR) initially developed the HST as an interim measure in the early 1970s, as delays and cost concerns began to threaten their primary high-speed train project, the Advanced Passenger Train (APT). The HSTs are now widely considered to be among the most successful trains to have operated on the British railway network, both in terms of their initial impact and their longevity: their introduction into service between 1976 and 1982 res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
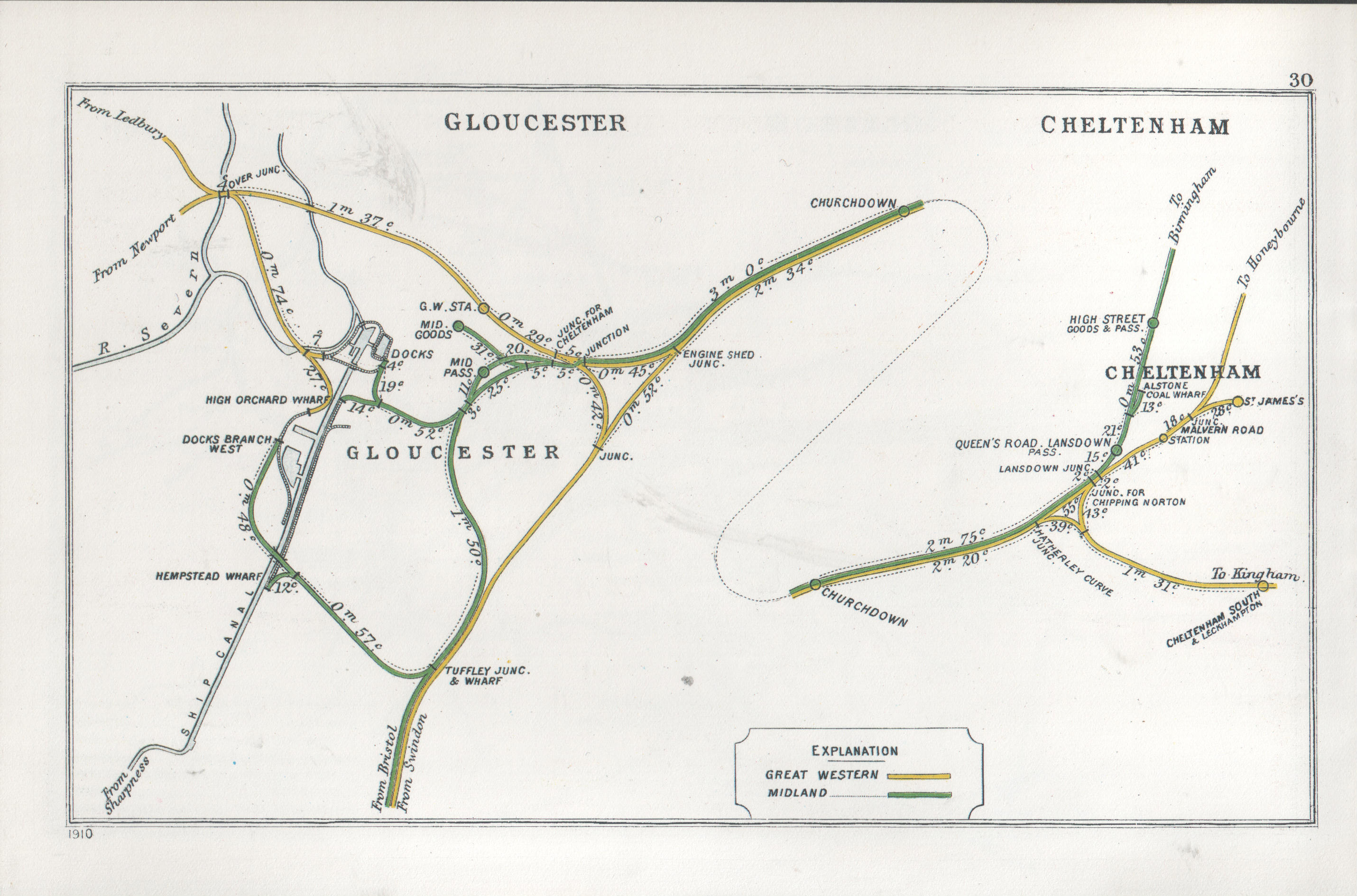
Cheltenham Spa Railway Station
Cheltenham Spa railway station serves the spa town of Cheltenham, in Gloucestershire, England. Situated on the Cross-Country Route, Bristol–Birmingham main line, it is managed by Great Western Railway (train operating company), Great Western Railway, although most services are operated by CrossCountry. The station is about one mile from the town centre. The official name of the station is ''Cheltenham''; however, when the station was renamed in 1925, the London, Midland and Scottish Railway chose to add ''Spa'' to the station name. It is a regional interchange and the second busiest station in Gloucestershire, as well as one of the busiest railway stations in South West England. History The first railway to Cheltenham was the broad-gauge Cheltenham and Great Western Union Railway (C&GWUR), authorised by Act of Parliament in 1836, and opened between Cheltenham and Gloucester in 1840. In the same year, the Birmingham and Gloucester Railway (B&GR) opened its line between Che ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Of England
The West of England is an area of South West England around the River Avon. The area has a local government combined authority that consists of the unitary authorities of Bristol, South Gloucestershire, and Bath and North East Somerset. The combined authority is led by the Mayor of the West of England Helen Godwin. The city of Bristol is the region's largest population centre. Before the region, from 1974 until 1996, the area was under the County of Avon with North Somerset. Background The term has been used in the Bristol and Bath area since at least the 18th century. The Royal Bath and West of England Society was named the Bath and West of England Society in 1790. The Royal West of England Academy received its present title in 1913. More recently the term has been used by organisations such as the West of England Partnership,West of England Partn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Wales
South Wales ( ) is a Regions of Wales, loosely defined region of Wales bordered by England to the east and mid Wales to the north. Generally considered to include the Historic counties of Wales, historic counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire (historic), Monmouthshire, south Wales extends westwards to include Carmarthenshire and Pembrokeshire. In the western extent, from Swansea westwards, local people would probably recognise that they lived in both south Wales and west Wales. The Brecon Beacons National Park covers about a third of south Wales, containing Pen y Fan, the highest British mountain south of Cadair Idris in Snowdonia. A point of some discussion is whether the first element of the name should be capitalised: 'south Wales' or 'South Wales'. As the name is a geographical expression rather than a specific area with well-defined borders, style guides such as those of the BBC and ''The Guardian'' use the form 'south Wales'. In a more authoritative style guide, the Wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |