|
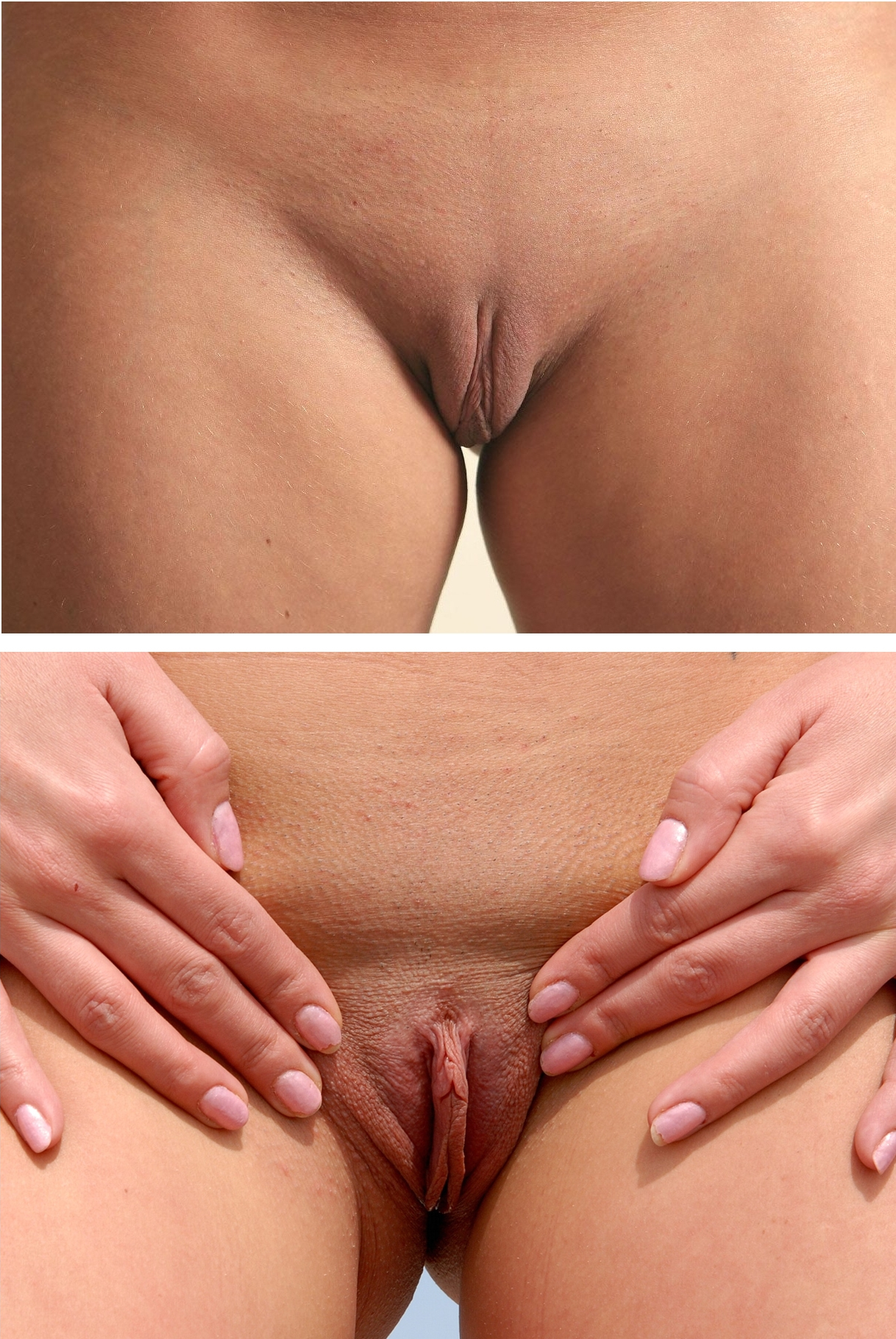
Labia Minora
The labia minora (Latin for 'smaller lips', : labium minus), also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin that are part of the primate vulva, extending outwards from the inner Vagina#Vaginal opening and hymen, vaginal and Urethral meatus, urethral openings to encompass the Vulval vestibule, vestibule. At the glans clitoridis, each labium splits, above forming the clitoral hood, and below the frenulum of the clitoris. At the bottom, the labia meet at the ''labial commissure''. The labia minora vary widely in size, color and shape from individual to individual. The labia minora are situated between the labia majora and together form the labia. The labia minora are Homology (biology), homologous to the penile raphe and ventral penile skin in males. Structure and functioning The labia minora extend from the clitoris obliquely downward, laterally, and backward on either side of the vulval vestibule, ending between the bottom of the vulval vestibule and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labia Majora
In primates, and specifically in humans, the labia majora (: labium majus), also known as the outer lips or outer labia, are two prominent Anatomical terms of location, longitudinal skin folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora, they form the labia of the vulva. The labia majora are Homology (biology), homologous to the male scrotum. Etymology ''Labia majora'' is the Latin plural for big ("major") lips. The Latin term ''labium/labia'' is used in anatomy for a number of usually paired parallel structures, but in English, it is mostly applied to two pairs of parts of the vulva—labia majora and labia minora. Traditionally, to avoid confusion with other lip-like structures of the body, the vulvar labia were termed by anatomists in Latin as ''labia majora (''or ''minora) pudendi.'' Embryology Embryologically, they develop from labioscrotal folds. The labia majora after puberty may become of a darker color than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulval Vestibule
The vulval vestibule (also known as the vulvar vestibule or vestibule of vagina) is the part of the vulva between the labia minora. At the innermost part are the vaginal introitus and urinary meatus. The Bartholin's and Skene's glands each have two openings to the vestibule on the inside. The outer edge, marked by a coloration difference in the tissues, is called Hart's line, named after David Berry Hart. The vestibule represents the distal end of the urogenital sinus of the embryo.''Manual of Obstetrics''. (3rd ed.). Elsevier. pp. 1–16. . Structure Structures opening in the vulval vestibule are the urethra ( urinary meatus), vagina, Bartholin's glands, and Skene's glands. The external urethral orifice is placed about 25–30 millimetres (1–1.2 in) behind the clitoris and immediately in front of that of the vagina; it usually assumes the form of a short, sagittal cleft with slightly raised margins. Nearby are the openings of the Skene's ducts. The vaginal ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labia Majora
In primates, and specifically in humans, the labia majora (: labium majus), also known as the outer lips or outer labia, are two prominent Anatomical terms of location, longitudinal skin folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora, they form the labia of the vulva. The labia majora are Homology (biology), homologous to the male scrotum. Etymology ''Labia majora'' is the Latin plural for big ("major") lips. The Latin term ''labium/labia'' is used in anatomy for a number of usually paired parallel structures, but in English, it is mostly applied to two pairs of parts of the vulva—labia majora and labia minora. Traditionally, to avoid confusion with other lip-like structures of the body, the vulvar labia were termed by anatomists in Latin as ''labia majora (''or ''minora) pudendi.'' Embryology Embryologically, they develop from labioscrotal folds. The labia majora after puberty may become of a darker color than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate. The external urethral sphincter is a striated muscle that allows voluntary control over urination. The Internal urethral sphincter, internal sphincter, formed by the involuntary smooth muscles lining the bladder neck and urethra, receives its nerve supply by the Sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. The internal sphincter is present both in males and females. Structure The urethra is a fibrous and muscular tube which connects the urinary bladder to the external urethral meatus. Its length differs between the sexes, because it passes through the penis in males. Male In the human male, the urethra is on average long and opens at the end of the external urethral meatus. The urethra is divided into four parts in men, named after the lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Garrett Anderson And Obstetric Hospital
The Elizabeth Garrett Anderson and Obstetric Hospital and its predecessor organisations provided health care to women in central London from the mid-Victorian era. It was named after Elizabeth Garrett Anderson, one of Britain's first female physicians, and its work continues in the modern Elizabeth Garrett Anderson wing of University College Hospital, part of UCLH NHS Foundation Trust. History In 1866, Elizabeth Garrett Anderson, with financial backing from her father, founded and became General Medical Attendant to St Mary's Dispensary in Seymour Place, where she worked for over 20 years. This dispensary developed into the New Hospital for Women in 1872. It was established to enable poor women to obtain medical help from qualified female practitioners - in that era a very unusual thing. In 1874 it moved to Marylebone Road, on a site now occupied by The Landmark Hotel. The foundation stone for new purpose-built facilities in Euston Road was laid by the Princess of Wales i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differences Of Vagina With Open And Closed Legs
Difference commonly refers to: * Difference (philosophy), the set of properties by which items are distinguished * Difference (mathematics), the result of a subtraction Difference, The Difference, Differences or Differently may also refer to: Music * ''Difference'' (album), by Dreamtale, 2005 * ''The Difference'' (album), Pendleton, 2008 * "The Difference" (The Wallflowers song), 1997 * "Differences" (song), by Ginuwine, 2001 * ''Differently'' (album), by Cassie Davis, 2009 ** "Differently" (song), by Cassie Davis, 2009 * "Difference", a song by Benjamin Clementine from the 2022 album ''And I Have Been'' * "The Difference", a song by Matchbox Twenty from the 2002 album '' More Than You Think You Are'' * "The Difference", a song by Westlife from the 2009 album ''Where We Are'' * "The Difference", a song by Nick Jonas from the 2016 album '' Last Year Was Complicated'' * "The Difference", a song by Meek Mill featuring Quavo, from the 2016 mixtape '' DC4'' * "The Difference", a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pudendal Cleft
In primates, and specifically in humans, the labia majora (: labium majus), also known as the outer lips or outer labia, are two prominent longitudinal skin folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora, they form the labia of the vulva. The labia majora are homologous to the male scrotum. Etymology ''Labia majora'' is the Latin plural for big ("major") lips. The Latin term ''labium/labia'' is used in anatomy for a number of usually paired parallel structures, but in English, it is mostly applied to two pairs of parts of the vulva—labia majora and labia minora. Traditionally, to avoid confusion with other lip-like structures of the body, the vulvar labia were termed by anatomists in Latin as ''labia majora (''or ''minora) pudendi.'' Embryology Embryologically, they develop from labioscrotal folds. The labia majora after puberty may become of a darker color than the skin outside them and grow pubic hair on their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labia Minora Variation
The labia are the major externally visible structures of the vulva. In humans and other primates, there are two pairs of labia: the ''labia majora'' (outer lips) are large and thick folds of skin that cover the vulva's other parts, while the ''labia minora'' (inner lips) are the folds of skin between the outer labia that surround and protect the urethral and vaginal openings, as well as the glans clitoridis. In other mammals, the labia majora are not present and the labia minora are instead referred to as the '' labia vulvae''. Etymology ''Labium'' (plural ''labia'') is a Latin-derived term meaning "lip". ''Labium'' and its derivatives (including labial, labrum) are used to describe any lip-like structure, but in the English language, ''labia'' often specifically refers to parts of the vulva. Structure The labia majora are lip-like structures consisting mostly of skin and adipose (fatty) tissue, which extend on either side of the vulva to form the pudendal cleft through t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural integrity. Although this epithelium is referred to as squamous, many cells within the layers may not be flattened; this is due to the convention of naming epithelia according to the cell type at the surface. In the deeper layers, the cells may be columnar or cuboidal. There are no intercellular spaces. This type of epithelium is well suited to areas in the body subject to constant abrasion, as the thickest layers can be sequentially sloughed off and replaced before the basement membrane is exposed. It forms the outermost layer of the skin and the inner lining of the mouth, esophagus and vagina. In the epidermis of skin in mammals, reptiles, and birds, the layer of keratin in the outer layer of the stratified squamous epithelial surface is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
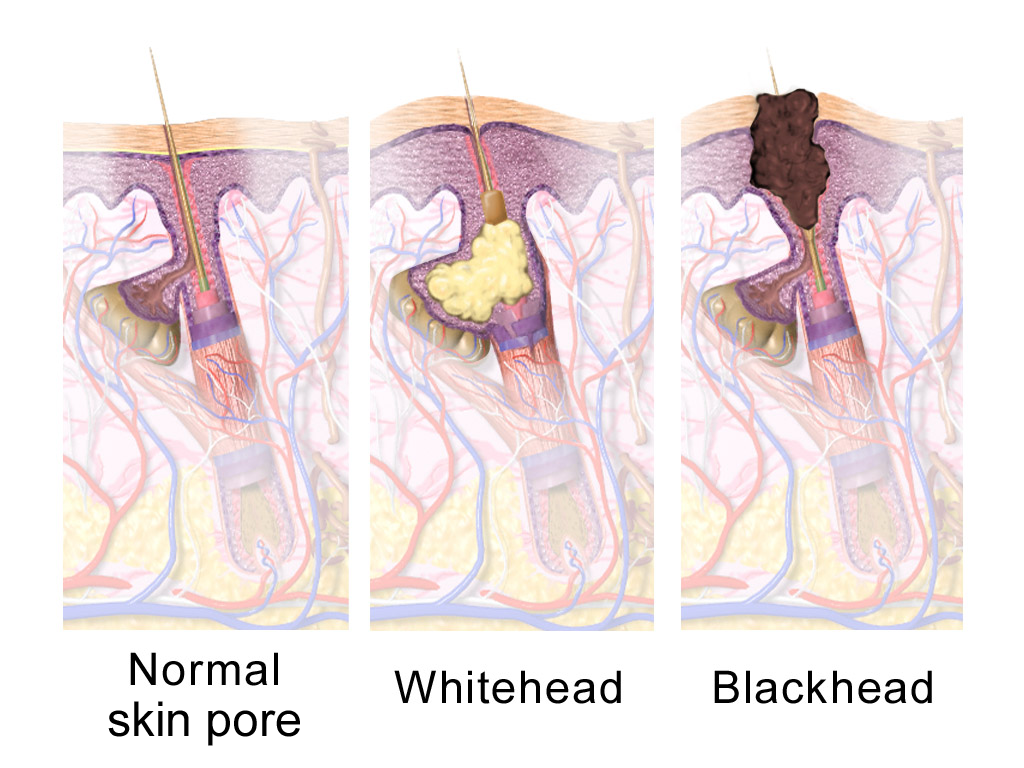
Sebaceous Gland
A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipples, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipples. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals. Structure Location In humans, sebaceous glands are found throughout all areas of the skin, except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There are two types of sebaceous glands: those connected to hair follicles and those that ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Stimulation
Sexual stimulation is anything that leads to sexual arousal or orgasm. This thing can be physical or of other senses, and is known as a stimulus. Sexual stimulation is a broad term, usually understood to mean physical touching of the genitals or other body parts. The term can, however, include stimuli affecting the mind ( sexual fantasy), or senses other than touch (such as sight, smell, or hearing). Sufficient physical stimulation of the genitals usually results in an orgasm. Stimulation can be by oneself (masturbation or sexual fantasy) or by a sexual partner (sexual intercourse or other sexual activity), by use of objects or tools, or by some combination of these methods. Some people practice orgasm control, whereby a person or their partner controls the level of stimulation to prolong the experience leading up to orgasm. Physical sexual stimulation Physical sexual stimulation consists of touching the genitals or other erogenous zones. Genital Masturbation, ero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clitoral Erection
Clitoral erection (also known as clitoral tumescence or female erection) is a physiological phenomenon where the clitoris becomes enlarged and firm. Clitoral erection is the result of a complex interaction of psychological, neural, vascular, and endocrine factors, and is usually, though not exclusively, associated with sexual arousal. Erections should eventually subside, and the prolonged state of clitoral erection even while not aroused is a condition that could become painful. This swelling and shrinking to a relaxed state seems linked to nitric oxide's effects on tissues in the clitoris, similar to its role in penile erection. Physiology The clitoris is the homolog to the penis in the male. Similarly, the clitoris and its erection can subtly differ in size. The visible part of the clitoris, the glans clitoridis, varies in size from a few millimeters to one centimeter and is located at the front junction of the labia minora (inner lips), above the opening of the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |