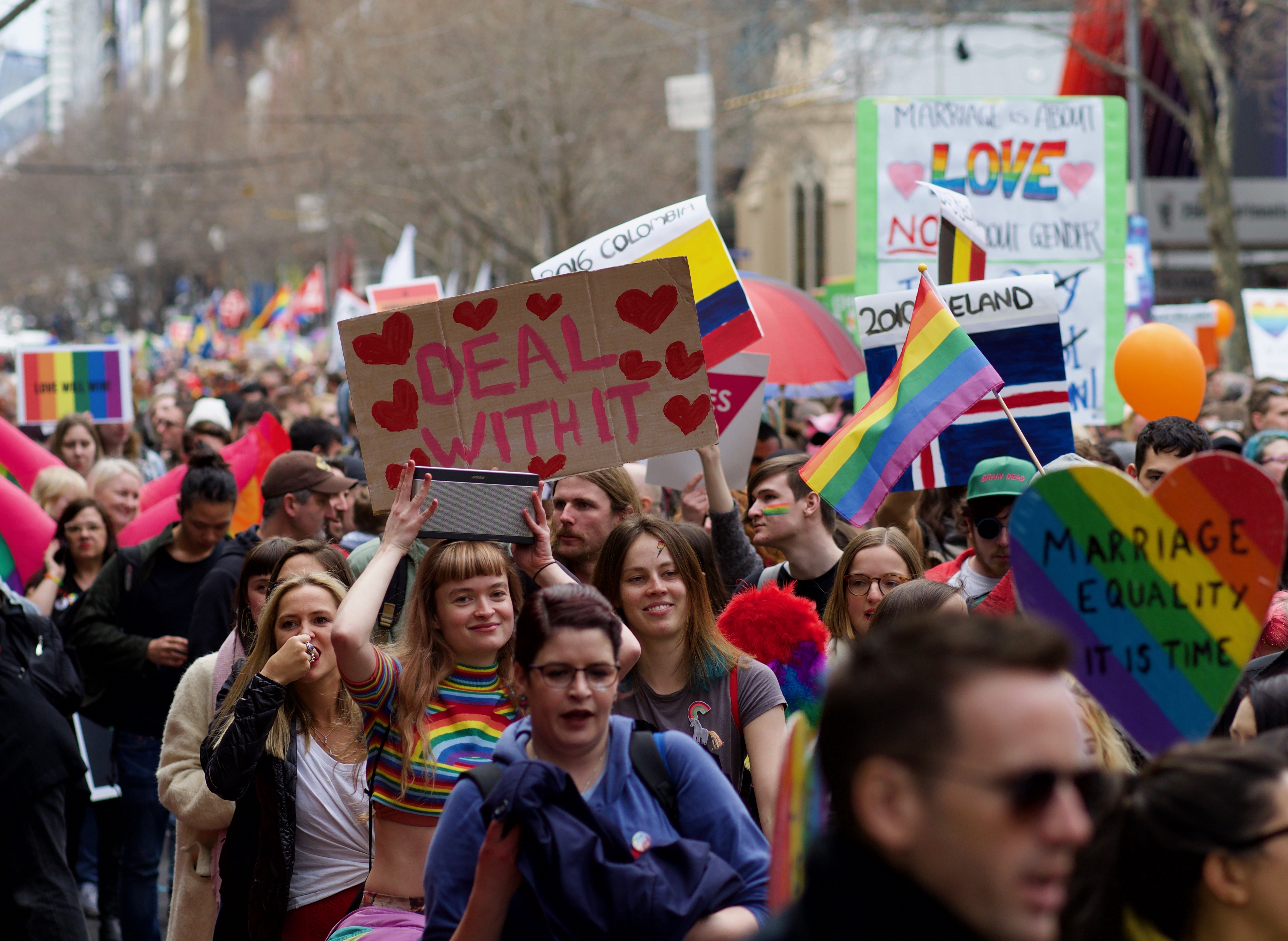|
LGBT History In Australia
This article details the history of the LGBT rights by country or territory, LGBTQ rights movement in Australia, from the colonial era to the present day. Pre-colonialism Whilst identifying as LGBTQ is not uncommon amongst Indigenous Australians today, there is no record of it being a phenomenon in pre-colonial Australian societies. Anthropologists Bill Stanner, Norman Tindale, A. P. Elkin and Ralph Piddington found evidence of polygamy and other non-binary behaviours, but not of homosexuality as such. While there is no evidence of these cultures on mainland Australia, this may not confirm that homosexual and other queer behaviours and identities were absent from mainland Aboriginal Australian culture. An exception is in the Tiwi Islands. While there is not a lot of evidence that there were formal structures and formal roles within mainland Aboriginal communities in the Tiwi Islands, language that names sexual and gender diversity exists, and there is evidence that there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Australia (1788-1850)
The history of Australia is the history of the land and peoples which comprise the Commonwealth of Australia. The modern nation came into existence on 1 January 1901 as a federation of former British colonies. The human history of Australia, however, commences with the arrival of the first ancestors of Aboriginal Australians from Maritime Southeast Asia between 50,000 and 65,000 years ago, and continues to the present day multicultural democracy. Aboriginal Australians settled throughout continental Australia and many nearby islands. The Aboriginal art, artistic, Aboriginal music, musical and Dreamtime, spiritual traditions they established are among the longest surviving in human history. The ancestors of today's ethnically and culturally distinct Torres Strait Islanders arrived from what is now Papua New Guinea around 2,500 years ago, and settled the islands on the northern tip of the Australian landmass. Dutch navigators explored the western and southern coasts in the 17t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooma
Cooma is a town in the south of New South Wales, Australia. It is located south of the national capital, Canberra, via the Monaro Highway. It is also on the Snowy Mountains Highway, connecting Bega, New South Wales, Bega with the Riverina. At the , Cooma had a population of . Cooma is the main town of the Monaro, New South Wales, Monaro region. It is above sea level. The name could have derived from an Indigenous Australian, Aboriginal word ''Coombah'', meaning 'big lake' or 'open country'. Cooma is south of the banks of the Murrumbidgee River, a main tributary of the Murray–Darling basin. Cooma sources its water from the river. History The area now known as Cooma lies on the traditional lands of the Ngarigo people. Cooma was explored by Captain J. M. Currie in 1823. It was first surveyed in 1840, and was gazetted in 1849. Cooma was proclaimed a municipality in 1879. The Main Southern railway line, New South Wales, railway from Sydney was Bombala railway line, extende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Cahill
John Joseph Cahill (21 January 189122 October 1959), also known as Joe Cahill or J. J. Cahill, was a long-serving New South Wales politician, railway worker, trade unionist and New South Wales Labor Party, Labor Party Premier of New South Wales from 1952 to his death in 1959. Born the son of Irish migrants in Redfern, New South Wales, Redfern, Cahill worked for the New South Wales Government Railways from the age of 16 before joining the Australian Labor Party. Being a prominent unionist organiser, including being dismissed for his role in the Australian general strike, 1917, 1917 general strike, Cahill was elected to the Parliament of New South Wales for Electoral district of St George, St George in 1925. After many years of Backbencher, backbench service, including a term outside of parliament, Cahill was appointed Secretary for Public Works (New South Wales), Secretary for Public Works in 1941 and Minister for Local Government (New South Wales), Minister for Local Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South Australia to the west. Its coast borders the Coral Sea, Coral and Tasman Seas to the east. The Australian Capital Territory and Jervis Bay Territory are Enclave and exclave, enclaves within the state. New South Wales' state capital is Sydney, which is also Australia's most populous city. , the population of New South Wales was over 8.3 million, making it Australia's most populous state. Almost two-thirds of the state's population, 5.3 million, live in the Greater Sydney area. The Colony of New South Wales was founded as a British penal colony in 1788. It originally comprised more than half of the Australian mainland with its Western Australia border, western boundary set at 129th meridian east in 1825. The colony then also includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Arrow (newspaper)
''The Arrow'' was a weekly English-language broadsheet newspaper published in Sydney, Australia between 1896 and 1933. The paper had previously been published under two earlier titles, ''The Dead Bird'' and ''Bird O’Freedom'' and also appeared as the ''Saturday Referee and the Arrow''. It was later absorbed by '' The Referee''. History ''The Dead Bird'' was first published on 16 May 1889 by Herbert Allan Risdale, and in 1891 the name was changed to ''Bird O'Freedom''. On 7 March 1896 the name changed to ''The Arrow''. It was published by Harry Markham Evans. The paper was a sporting weekly. In 1916 ''The Arrow'' came into the ownership of Hugh D. McIntosh in 1916, when he acquired the ''Sunday Times''. In 1933 the paper was absorbed by '' The Referee'', another sporting weekly, which began publication in 1886 and ceased publication on 31 August 1939. Digitisation Many issues of the paper have been digitised as part of the Australian Newspapers Digitisation Program, a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyde Park Barracks, Sydney
The Hyde Park Barracks, Sydney is a heritage-listed former barracks, hospital, convict accommodation, mint and courthouse and now museum and café located at Macquarie Street in the Sydney central business district, in the City of Sydney local government area of New South Wales, Australia. Originally constructed between 1817 and 1819 as a brick building and compound to house convict men and boys, it was designed by convict architect Francis Greenway. It is also known as the Mint Building and Hyde Park Barracks Group and Rum Hospital; Royal Mint – Sydney Branch; Sydney Infirmary and Dispensary; Queen's Square Courts; Queen's Square. The site is managed by the Museums of History New South Wales, an agency of the Government of New South Wales, as a living history museum open to the public. The site is inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List as one of 11 pre-eminent Australian Convict Sites as among "the best surviving examples of large-scale convict transportatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, and may also legislate for the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster in London. Parliament possesses legislative supremacy and thereby holds ultimate power over all other political bodies in the United Kingdom and the Overseas Territories. While Parliament is bicameral, it has three parts: the sovereign, the House of Lords, and the House of Commons. The three parts acting together to legislate may be described as the King-in-Parliament. The Crown normally acts on the advice of the prime minister, and the powers of the House of Lords are limited to only delaying legislation. The House of Commons is the elected lower chamber of Parliament, with elections to 650 single-member constituencies held at least every five years under the first-past-the-post system. By constitutional convention, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emu Plains
Emu Plains is a suburb of Sydney in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It is west of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of the City of Penrith and is part of the Greater Western Sydney region. Emu Plains is on the western side of the Nepean River, located at the foot of the Blue Mountains. History Aboriginal culture Prior to European settlement, what is now the suburb of Emu Plains was located on the border of the Western Sydney-based Dharug people and the Southern Highlands-based Gandangara people, whose land extended into the Blue Mountains. The local Dharug people were known as the Mulgoa. They lived a hunter-gatherer lifestyle governed by traditional laws, which had their origins in the Dreamtime. They lived in huts made of bark called 'gunyahs', hunted kangaroos and emus for meat, and gathered yams, berries, and other native plants. European settlement The first British colonizers to visit the area surveyed Emu Plains in August 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babette Smith
Babette Alison Smith (2 April 1942 – 22 November 2021) was an Australian colonial historian, mediator and business executive. She wrote books about the convicts transported to Australia. Early life Born 2 April 1942, Babette Alison Smith (nee Macfarlan) was the daughter of Bruce Panton Macfarlan and Barbara Macfarlan (nee Scott). Her father Bruce saw active service as a Group Captain in the RAAF during WWII, was a barrister and later served as a judge in the Supreme Court of New South Wales. Babette spent her early school years at SCEGGS Redlands, and in 1955 she became a boarder at Frensham, Mittagong. After leaving school, she completed a BA at the University of Sydney while working at the Supreme Court as a judge’s associate to her father. Career Entertainment Industry Babette was a convener of the Opera House Younger Set, a fund-raising group for what was then a vacant site on Bennelong Point. Babette learned the business side of the performing arts through her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Aldrich (historian)
Robert F. Aldrich (born July 29, 1954, in New York) is an Australian historian and writer. Aldrich is Professor Emeritus of European History at the University of Sydney, where he taught from 1981-2021. He researches modern European and colonial history, particularly the French and British empires, as well as the history of modern monarchy. Life After school Aldrich studied history in the United States of America, first at Emory University, Georgia, where he received his undergraduate degree, and afterwards at Brandeis University, Massachusetts, where he gained his Master's and PhD. Aldrich joined the faculty at University of Sydney. He wrote several books on French colonialism in the Pacific and on the history of homosexuality. Awards and recognition In 2002 the French Government awarded Aldrich the Chevalier dans l'Ordre des Palmes Académiques. In 2008 he was elected a Fellow of both the Academy of the Social Sciences in Australia and the Australian Academy of the Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |