|
LED Display
A LED display is a flat panel display that uses an array of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as pixels for a video display. Their brightness allows them to be used outdoors where they are visible in the sun for store signs and billboards. In recent years, they have also become commonly used in destination signs on public transport vehicles, as well as variable-message signs on highways. LED displays are capable of providing general illumination in addition to visual display, as when used for stage lighting or other decorative (as opposed to informational) purposes. LED displays can offer higher contrast ratios than a projector and are thus an alternative to traditional projection screens, and they can be used for large, uninterrupted (without a visible grid arising from the bezels of individual displays) video walls. microLED displays are LED displays with smaller LEDs, which poses significant development challenges. Their use in cinemas to replace projectors and projecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MicroLED
MicroLED, also known as micro-LED, mLED or μLED is an emerging flat-panel display technology consisting of arrays of microscopic Light-emitting diode, LEDs forming the individual pixel elements. Inorganic semiconductor microLED (μLED) technology was first invented in 2000 by the research group of Hongxing Jiang and Jingyu Lin of Texas Tech University (TTU) while they were at Kansas State University, Kansas State University (KSU). The first high-resolution and video-capable InGaN microLED microdisplay in VGA format was realized in 2009 by Jiang, Lin and their colleagues at Texas Tech University and III-N Technology, Inc. via active driving of a microLED array by a complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) IC. Compared to LED-backlit LCD, conventional LCD displays, microLED displays offer greatly reduced energy requirements while also offering pixel-level light control and a high contrast ratio. Compared to OLED, OLEDs, the inorganic nature of microLEDs gives them a longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue LED
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet (UV), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
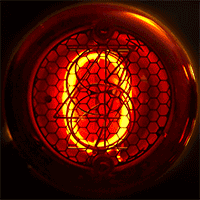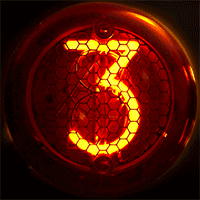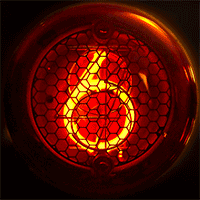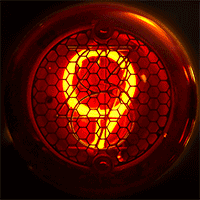
Nixie Tube
A Nixie tube ( ), or cold cathode display, is an electronics, electronic device used for display device, displaying numerals or other information using glow discharge. The glass tube contains a wire-mesh anode and multiple cathodes, shaped like Hindu–Arabic numeral system, numerals or other symbols. Applying power to one cathode surrounds it with an orange glow discharge. The tube is filled with a gas at low pressure, usually mostly neon and a small amount of argon, in a Penning mixture. In later nixies, in order to extend the usable life of the device, a tiny amount of mercury (element), mercury was added to reduce cathode poisoning and sputtering. Although it resembles a vacuum tube in appearance, its operation does not depend on thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode. It is hence a cold cathode tube (a form of gas-filled tube), and is a variant of the neon lamp. Such tubes rarely exceed even under the most severe of operating conditions in a room at ambient te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Display
A display device is an output device for presentation of information in visual or tactile form (the latter used for example in tactile electronic displays for blind people). When the input information that is supplied has an electrical signal the display is called an '' electronic display''. Common applications for ''electronic visual displays'' are television sets or computer monitors. Types of electronic displays In use These are the technologies used to create the various displays in use today. * Liquid-crystal display (LCD) ** Light-emitting diode (LED) backlit LCD ** Thin-film transistor (TFT) LCD ** Quantum dot (QLED) display * Light-emitting diode (LED) display ** OLED display ** AMOLED display ** Super AMOLED display Segment displays Some displays can show only digits or alphanumeric characters. They are called segment displays, because they are composed of several segments that switch on and off to give appearance of desired glyph. The segments are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LED Circuit
In electronics, an LED circuit or LED driver is an electrical circuit used to power a light-emitting diode (LED). The circuit must provide sufficient current to light the LED at the required brightness, but must limit the current to prevent damaging the LED. The voltage drop across a lit LED is approximately constant over a wide range of operating current; therefore, a small increase in applied voltage greatly increases the current. Datasheets may specify this drop as a "forward voltage" (V_) at a particular operating current. Very simple circuits are used for low-power indicator LEDs. More complex, current source circuits are required when driving high-power LEDs for illumination to achieve correct current regulation. Basic circuit The simplest circuit to drive an LED is through a series resistor. It is commonly used for indicators and digital displays in many consumer appliances. However, this circuit is not energy-efficient, because energy is dissipated in the resistor as heat. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components are etched onto a small, flat piece ("chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Integrated circuits are used in a wide range of electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, and televisions, to perform various functions such as processing and storing information. They have greatly impacted the field of electronics by enabling device miniaturization and enhanced functionality. Integrated circuits are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete components, allowing a large transistor count. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design have ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hewlett-Packard Journal
''Hewlett-Packard Journal'' () was a magazine published by Hewlett-Packard (HP) between 1949–1998. The first issue appeared in September 1949. Headquartered in Palo Alto, California Palo Alto ( ; Spanish language, Spanish for ) is a charter city in northwestern Santa Clara County, California, United States, in the San Francisco Bay Area, named after a Sequoia sempervirens, coastal redwood tree known as El Palo Alto. Th ..., it covered technical and product news from HP. The magazine was started as monthly, but then its frequency switched to bimonthly. It is available as web-pages - or as scanned and available on HPs home page as PDF downloads. References {{Reflist External links hpmemoryproject.org: The ''Hewlett-Packard Journal''leapsecond.com: Time & Frequency Articles from ''Hewlett Packard Journal'' Bimonthly magazines published in the United States Monthly magazines published in the United States Defunct computer magazines published in the United States Hewlet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research And Development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in some countries as OKB, experiment and design, is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products. R&D constitutes the first stage of development of a potential new service or the production process. Although R&D activities may differ across businesses, the primary goal of an R&D department is to new product development, develop new products and services. R&D differs from the vast majority of corporate activities in that it is not intended to yield immediate profit, and generally carries greater risk and an uncertain return on investment. R&D is crucial for acquiring larger shares of the market through new products. ''R&D&I'' represents R&D with innovation. Background New product design and development is often a crucial factor in the survival of a company. In a global industrial landscape that is changing fast, firms must continually revise their design and range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HP Labs
HP Labs is the exploratory and advanced research group for HP Inc. HP Labs' headquarters is in Palo Alto, California and the group has research and development facilities in Bristol, UK. The development of programmable desktop calculators, inkjet printing, and 3D graphics are credited to HP Labs researchers. HP Labs was established on March 3, 1966, by Hewlett-Packard founders Bill Hewlett and David Packard, seeking to create an organization not bound by day-to-day business concerns. The labs have downsized dramatically; in August 2007, HP executives drastically diminished the number of projects, down from 150 to 30. As of 2018, HP Labs has just over 200 researchers, compared to earlier staffing levels of 500 researchers. With Hewlett Packard Enterprise being spun off from Hewlett-Packard on November 1, 2015, and the remaining company being renamed to HP Inc., the research lab also spun off Hewlett Packard Labs to Hewlett Packard Enterprise and HP Labs was kept for HP Inc. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Science & Business Media
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second-largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hewlett-Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company. It was founded by Bill Hewlett and David Packard in 1939 in a one-car garage in Palo Alto, California, where the company would remain headquartered for the remainder of its lifetime; this HP Garage is now a designated landmark and marked with a plaque calling it the "Birthplace of 'Silicon Valley. HP developed and provided a wide variety of hardware components, as well as software and related services, to consumers, small and medium-sized businesses (small and medium-sized enterprises, SMBs), and fairly large companies, including customers in government sectors, until the company officially split into Hewlett Packard Enterprise and HP Inc. in 2015. HP initially produced a line of electronic test and measurement equipment. It won its first big contract in 1938 to provide the HP 200B, a variation of its first product, the HP 200A low-distor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |