|
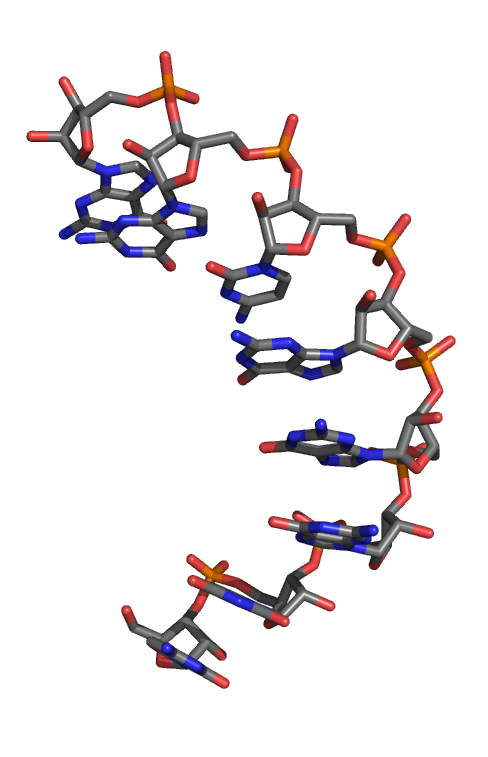
L-Ribonucleic Acid Aptamer
An L-ribonucleic acid aptamer (L-RNA aptamer, trade name Spiegelmer) is an RNA-like molecule built from L-ribose units. It is an artificial oligonucleotide named for being a mirror image of natural oligonucleotides. L-RNA aptamers are a form of aptamers. Due to their L-nucleotides, they are highly resistant to degradation by nucleases. L-RNA aptamers are considered potential drugs and are currently being tested in clinical trials. Features Chemical properties L-RNA aptamers, built using L-ribose, are the enantiomers of natural oligonucleotides, which are made with D-ribose. Nucleic acid aptamers, including L-RNA aptamers, contain adenosine monophosphate, guanosine monophosphate, cytidine monophosphate, uridine monophosphate, a phosphate group, a nucleobase and a ribose sugar. Biological characteristics Like other aptamers, L-RNA aptamers are able to bind molecules such as peptides, proteins, and substances of low molecular weight. The affinity of L-RNA aptamers to their targ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the substance and water molecule to split into two parts. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is the ribose derivative deoxyribose, the polymer is DNA. Nucleic acids are naturally occurring chemical compounds that serve as the primary information-carrying molecules in cells and make up the genetic material. Nucleic acids are found in abundance in all living things, where they create, encode, and then store information of every living cell of every life-form on Earth. In turn, they function to transmit and express that information inside and outside the cell nucleus to the interior operations of the cell and ultimately to the next generation of each living organism. The encoded information i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghrelin
Ghrelin (; or lenomorelin, INN) is a hormone produced by enteroendocrine cells of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the stomach, and is often called a "hunger hormone" because it increases the drive to eat. Blood levels of ghrelin are highest before meals when hungry, returning to lower levels after mealtimes. Ghrelin may help prepare for food intake by increasing gastric motility and stimulating the secretion of gastric acid. Ghrelin activates cells in the anterior pituitary gland and hypothalamic arcuate nucleus, including neuropeptide Y neurons that initiate appetite. Ghrelin stimulates brain structures having a specific receptor – the growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1A ( GHSR-1A). Ghrelin also participates in regulation of reward cognition, learning and memory, the sleep-wake cycle, taste sensation, reward behavior, and glucose metabolism. History and name Ghrelin was discovered after the ghrelin receptor (called growth hormone secretagogue type 1A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complement Component 5a
C5a is a protein fragment released from cleavage of complement component C5 by protease C5-convertase into C5a and C5b fragments. C5b is important in late events of the complement cascade, an orderly series of reactions which coordinates several basic defense mechanisms, including formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC), one of the most basic weapons of the innate immune system, formed as an automatic response to intrusions from foreign particles and microbial invaders. It essentially pokes microscopic pinholes in these foreign objects, causing loss of water and sometimes death. C5a, the other cleavage product of C5, acts as a highly inflammatory peptide, encouraging complement activation, formation of the MAC, attraction of innate immune cells, and histamine release involved in allergic responses. The origin of C5 is in the hepatocyte, but its synthesis can also be found in macrophages, where it may cause local increase of C5a. C5a is a chemotactic agent and an anaphylat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CXCL12
The stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1), also known as C-X-C motif chemokine 12 (CXCL12), is a chemokine protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CXCL12'' gene on chromosome 10. It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types. Stromal cell-derived factors 1-alpha and 1-beta are small cytokines that belong to the chemokine family, members of which activate leukocytes and are often induced by proinflammatory stimuli such as lipopolysaccharide, TNF, or IL1. The chemokines are characterized by the presence of 4 conserved cysteines that form 2 disulfide bonds. They can be classified into 2 subfamilies. In the CC subfamily, the cysteine residues are adjacent to each other. In the CXC subfamily, they are separated by an intervening amino acid. The SDF1 proteins belong to the latter group. CXCL12 signaling has been observed in several cancers. The ''CXCL12'' gene also contains one of 27 SNPs associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease. Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCL2
''For the ICAO airport code see Candle Lake Airpark, for the diradical compound see Dichlorocarbene.'' The chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) is also referred to as monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1) and small inducible cytokine A2. CCL2 is a small cytokine that belongs to the CC chemokine family. CCL2 tightly regulates cellular mechanics and thereby recruits monocytes, memory T cells, and dendritic cells to the sites of inflammation produced by either tissue injury or infection. Genomics In the human genome, CCL2 and many other CC chemokines are located on chromosome 17 (17q11.2-q21.1). The gene span is 1,927 bases and the CCL2 gene resides on the Watson (plus) strand. The CCL2 gene has three exons and two introns. The CCL2 protein precursor contains a signal peptide of 23 amino acids. In turn, the mature CCL2 is 76 amino acids long. The CCL2 predicted weight is 11.025 kiloDaltons (kDa). Population genetics In humans, the levels of CCL2 can vary considerably. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemokines
Chemokines (), or chemotactic cytokines, are a family of small cytokines or signaling proteins secreted by cells that induce directional movement of leukocytes, as well as other cell types, including endothelial and epithelial cells. In addition to playing a major role in the activation of host immune responses, chemokines are important for biological processes, including morphogenesis and wound healing, as well as in the pathogenesis of diseases like cancers. Cytokine proteins are classified as chemokines according to behavior and structural characteristics. In addition to being known for mediating chemotaxis, chemokines are all approximately 8-10 kilodaltons in mass and have four cysteine residues in conserved locations that are key to forming their 3-dimensional shape. These proteins have historically been known under several other names including the ''SIS family of cytokines'', ''SIG family of cytokines'', ''SCY family of cytokines'', ''Platelet factor-4 superfamily'' or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery. Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, DNA Genographic Projects and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. Comparing healthy and mutated DNA sequences can diagnose different diseases including various cancers, characterize antibody repertoire, and can be used to guide patient treatment. Having a quick way to sequence DNA allows for faster and more individualized medical care to be administered, and for more organisms to be identified and cataloged. The rapid speed of sequencing attained with m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epitope
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The epitope is the specific piece of the antigen to which an antibody binds. The part of an antibody that binds to the epitope is called a paratope. Although epitopes are usually non-self proteins, sequences derived from the host that can be recognized (as in the case of autoimmune diseases) are also epitopes. The epitopes of protein antigens are divided into two categories, conformational epitopes and linear epitopes, based on their structure and interaction with the paratope. Conformational and linear epitopes interact with the paratope based on the 3-D conformation adopted by the epitope, which is determined by the surface features of the involved epitope residues and the shape or tertiary structure of other segments of the antigen. A conformational epitope is formed by the 3-D conformation adopted by the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid ''residues'' form the second-largest component ( water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) to a large enough amount to study in detail. PCR was invented in 1983 by the American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation; Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications including biomedical research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |