|
Kush Nama
Kush-Nama (), is a Persian epic poem and part of a mythical history of Iran written by Ḥakim Iranshān (or Irānshāh) ibn Abu l-Khayr between the years 501-04/1108-11. Manuscript and background A critical edition of the poem based on unique manuscript of the work is found in a collection held in the British Museum (OR 2780) and published in a critical edition by Professor Jalal Matini, and in an English translation by Kaveh L Hemmat. The manuscript collection contains five epic poems: Asadi Tusi's Garshasp-nama, Ahmad Tabrizi's ''Shāhanshāh-nāma'', ''Tārikh-e Changiz Khān va Jāneshinānash'' "The History of Genghis Khan and his Successors", the '' Bahman-nama'', and the ''Kush-nama''. It originally also contained the ''Shahnameh'', however, this portion was separated from the rest of the codex. Much of the epic was likely based on one or more Middle Persian prose texts.Saghi Gazerani, “Kush-e Pildandān, the Anti-Hero: Polemics of Power in Late Antique Iran,” ''Ira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Language
Persian ( ), also known by its endonym and exonym, endonym Farsi (, Fārsī ), is a Western Iranian languages, Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian languages, Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible standard language, standard varieties, respectively Iranian Persian (officially known as ''Persian''), Dari, Dari Persian (officially known as ''Dari'' since 1964), and Tajik language, Tajiki Persian (officially known as ''Tajik'' since 1999).Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" in ''Media Insight Central Asia #27'', August 2002. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate society, Persianate history in the cultural sphere o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faridun
use both this parameter and , birth_date to display the person's date of birth, date of death, and age at death) --> , death_place = , death_cause = , resting_place = , resting_place_coordinates = , burial_place = , other_names = Afereydun(آفریدون) , known_for = Victory over Azhi Dahaka , spouse = Arnavaz Shahrnaz , partner = , children = Salm TurIraj , parents = , mother = Faranak , father = Abtin , relatives = Fereydun (, ; New Persian: , ''Fereydūn/Farīdūn'') is an Iranian mythical king and hero from the Pishdadian dynasty. He is known as an emblem of victory, justice, and generosity in Persian literature. According to Abolala Soudavar, Fereydun is partially a reflection of Cyrus the Great (), the first Achaemenid King of Kings. Etymology All of the forms of the name shown above derive, by regular sound laws, from Proto-Ira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tur (mythology)
Tur (; , ) is a character in the Persian epic Shahnameh. He is the second son of the legendary Iranian king Fereydun and brother of both Salm and Iraj. His name, meaning "brave", was given to him by his father when the young prince bravely fights the dragon that had attacked him and his brothers. When Fereydun divides his empire among his sons, he gives Turkistan and China to his second son Tur. This is the beginning of the Turanians, the neighbor and rival of the Iranians. Some of the most important characters of Shahnameh, such as Afrasiab, are his descendants. He was killed by Manuchehr. Family tree See also * Arya (Iran) * Turya (Avesta) * Turan * Aniran Anērān (Middle Persian, ) or Anīrân ( Modern Persian, ) is an ethno-linguistic term that signifies "non-Iranian" or "non-Iran" (non-Aryan). Thus, in a general sense, 'Aniran' signifies lands where Iranian languages are not spoken. In a pejorati ... External linksA king's book of kings: the Shah-nameh of Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mazandaran
Mazandaran Province (; ) is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. Its capital is the city of Sari, Iran, Sari. Located along the southern coast of the Caspian Sea and in the adjacent Central Alborz mountain range and Hyrcanian forests, it is bordered clockwise by Russia (across the sea), Golestan Province, Golestan, Semnan Province, Semnan, Tehran Province, Tehran, Alborz Province, Alborz, Qazvin Province, Qazvin, and Gilan Province, Gilan Provinces. Mazandaran, founded in 1937, covers an area of 23,842 km2. The province has diverse natural resources, notably large offshore reservoirs of oil and natural gas. The diverse natural habitats of the province include plains, prairies, forests and rainforest stretching from the sandy beaches of the Caspian Sea to the rugged and snowcapped Alborz sierra, including Mount Damavand, one of the highest Summit, peaks and volcanoes in Asia. Mazandaran is a major producer of Fish farming, farmed fish, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract of the Nile (south of Aswan in southern Egypt) or more strictly, Al Dabbah, Sudan, Al Dabbah. It was the seat of one of the earliest civilizations of ancient Africa, the Kerma culture, which lasted from around 2500 BC until its conquest by the New Kingdom of Egypt under Pharaoh Thutmose I around 1500 BC, whose heirs ruled most of Nubia for the next 400 years. Nubia was home to several African empires, empires, most prominently the Kingdom of Kush, which conquered Egypt in the eighth century BC during the reign of Piye and ruled the country as its Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt, 25th Dynasty. From the 3rd century BC to 3rd century AD, northern Nubia was invaded and annexed to Egypt, ruled by the Ptolemaic Kingdom, Greeks and Roman Empire, R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
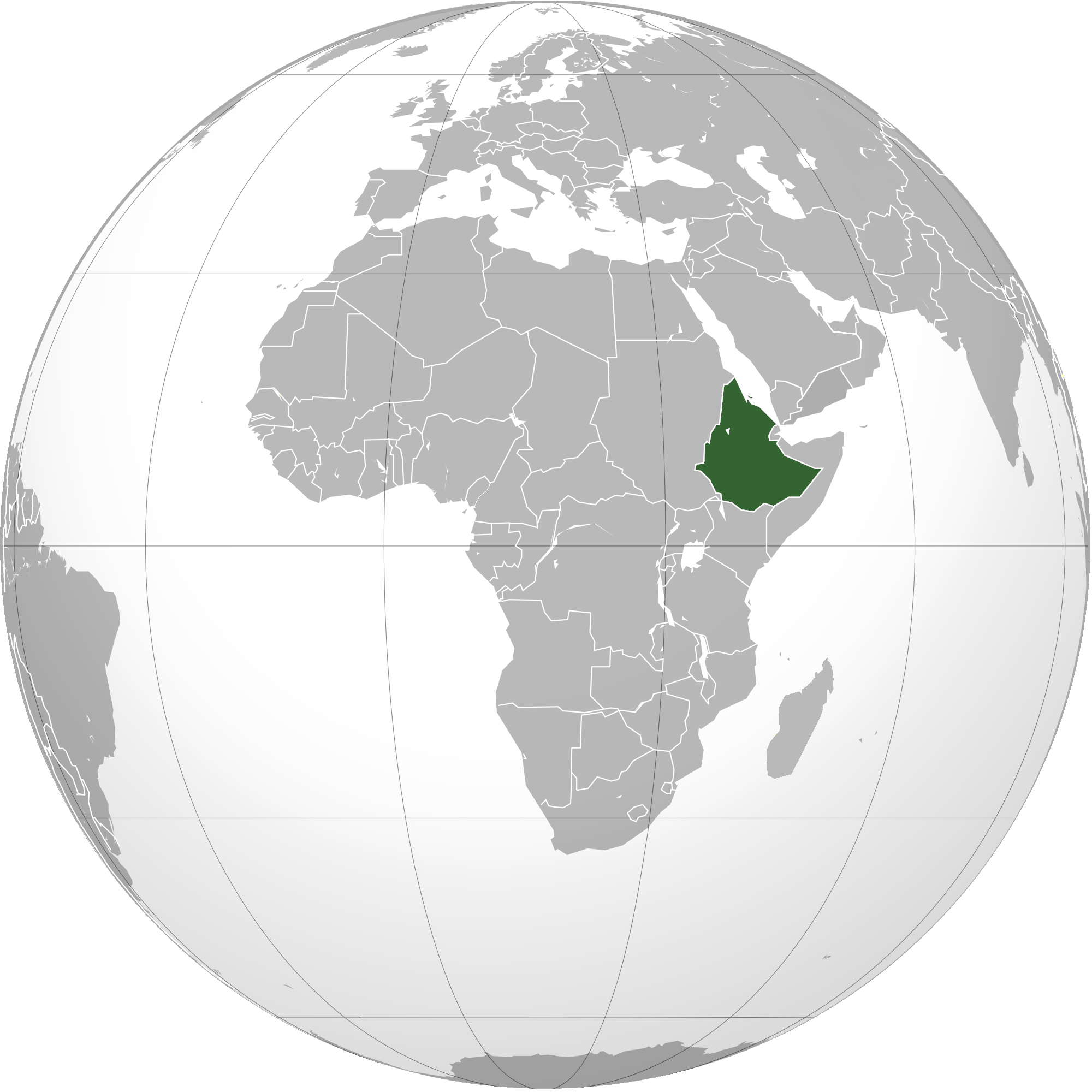
Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire, historically known as Abyssinia or simply Ethiopia, was a sovereign state that encompassed the present-day territories of Ethiopia and Eritrea. It existed from the establishment of the Solomonic dynasty by Yekuno Amlak around 1270 until the 1974 Ethiopian coup d'état, 1974 coup d'état by the Derg, which ended the reign of the final Emperor, Haile Selassie. In the late 19th century, under Emperor Menelik II, the Menelik II's conquests, empire expanded significantly to the south, and in 1952, Federation of Ethiopia and Eritrea, Eritrea was federated under Selassie's rule. Despite being surrounded by hostile forces throughout much of its history, the empire maintained a kingdom centered on its Orthodox Tewahedo, ancient Christian heritage. Founded in 1270 by Yekuno Amlak, who claimed to descend from the last Kingdom of Aksum, Aksumite king and ultimately King Solomon and the Queen of Sheba, it replaced the Agaw people, Agaw Zagwe Kingdom, kingdom of the Za ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthia
Parthia ( ''Parθava''; ''Parθaw''; ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great in the 6th century BC, and formed part of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire after the Wars of Alexander the Great, 4th-century BC conquests of Alexander the Great. The region later served as the political and cultural base of the Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian Parni people and Arsacid dynasty, rulers of the Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD). The Sasanian Empire, the last state of History of Iran, pre-Islamic Iran, also held the region and maintained the Seven Great Houses of Iran, seven Parthian clans as part of their feudal aristocracy. Name The name "Parthia" is a continuation from Latin language, Latin ', from Old Persian ', which was the Parthian language self-designator signifying "of the Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxus
The Amu Darya ( ),() also shortened to Amu and historically known as the Oxus ( ), is a major river in Central Asia, which flows through Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Afghanistan. Rising in the Pamir Mountains, north of the Hindu Kush, the Amu Darya is formed by the confluence of the Vakhsh and Panj rivers, in the Tigrovaya Balka Nature Reserve on the border between Afghanistan and Tajikistan, and flows from there north-westwards into the southern remnants of the Aral Sea. In its upper course, the river forms part of Afghanistan's northern border with Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan. In ancient history, the river was regarded as the boundary of Greater Iran with Turan, which roughly corresponded to present-day Central Asia.B. SpulerĀmū Daryā in Encyclopædia Iranica, online ed., 2009 The Amu Darya has a flow of about 70 cubic kilometres per year on average. Names In classical antiquity, the river was known as the in Latin and () in Greek — a cle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damavand
Mount Damavand ( ) is a dormant stratovolcano and is the highest peak in Iran and Western Asia, the highest volcano in Asia, and the 3rd highest volcano in the Eastern Hemisphere (after Mount Kilimanjaro and Mount Elbrus), at an elevation of . Damāvand has a special place in Persian mythology and folklore. It is in the middle of the Alborz range, adjacent to ''Varārū'', ''Sesang'', ''Gol-e Zard'', and ''Mīānrūd''. It is near the southern coast of the Caspian Sea, in Amol City, Mazandaran State, northeast of the city of Tehran. Mount Damāvand is the 12th most prominent peak in the world and is part of the Volcanic Seven Summits mountaineering challenge. Symbolism and mythology Damavand is a significant mountain in Persian mythology. It is the symbol of Iranian resistance against despotism and foreign rule in Persian poetry and literature. In Zoroastrian texts and mythology, the three-headed dragon Aži Dahāka was chained within Mount Damāvand, there to rema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia, south of the fertile plains of Southern Russia in Eastern Europe, and north of the mountainous Iranian Plateau. It covers a surface area of (excluding the highly saline lagoon of Garabogazköl to its east), an area approximately equal to that of Japan, with a volume of . It has a salinity of approximately 1.2% (12 g/L), about a third of the salinity of average seawater. It is bounded by Kazakhstan to the northeast, Russia to the northwest, Azerbaijan to the southwest, Iran to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southeast. The name of the Caspian Sea is derived from the ancient Iranian peoples, Iranic Caspians, Caspi people. The sea stretches from north to south, with an average width of . Its gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amol
Amol ( ; ) is a city in the Central District (Amol County), Central District of Amol County, Mazandaran province, Mazandaran province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. Amol is located on the Haraz River bank. It is situated less than south of the Caspian Sea and less than north of the Alborz mountains. It is northeast of Tehran, and west of the provincial capital, Sari, Iran, Sari. It is one of the oldest cities in Iran, and a historic city, with its foundation dating back to the Amardi tribe, who inhabited the region in the Iron Age. Amol is the center of industry and culture of Mazandaran, the rice capital of Iran, and one of the most important cities of the transportation, agriculture, and tourism industries in Iran. It is known as the ''History, Science and Philosophy city'', ''City that does not die'' and ''Hezar Sangar city''. History Pre-Islamic era According to the city government, the name is derived from ''Amardi'', a tribe mentioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilan
Gilan Province () is one of the 31 provinces of Iran, in the northwest of the country and southwest of the Caspian Sea. Its capital is the city of Rasht. The province lies along the Caspian Sea, in Iran's Region 3, west of the province of Mazandaran, east of the province of Ardabil, and north of the provinces of Zanjan and Qazvin. It borders Azerbaijan ( Astara District) in the north. The northern section of the province is part of the territory of South (Iranian) Talysh. At the center of the province is Rasht. Other cities include Astaneh-ye Ashrafiyeh, Astara, Fuman, Hashtpar, Lahijan, Langarud, Masuleh, Manjil, Rudbar, Rudsar, Shaft, Siahkal, and Sowme'eh Sara. The main port is Bandar-e Anzali, formerly known as Bandar-e Pahlavi. History Paleolithic Early humans were present at Gilan since Lower Paleolithic. Darband Cave is the earliest known human habitation site in Gilan province; it is located in a deep tributary canyon of the Siah Varud and contains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |