|
Kupe
Kupe was a legendary Polynesian explorer who, according to Māori oral history, was the first person to discover New Zealand. He is generally held to have been born to a father from Rarotonga and a mother from Raiatea, and probably spoke a Māori proto-language similar to Cook Islands Māori or Tahitian. His voyage to New Zealand ensured that the land was known to the Polynesians, and he would therefore be responsible for the genesis of the Māori people. Kupe was born in the geographically uncertain Māori homeland of Hawaiki, to a father from Rarotonga and a mother from Raiatea, between 40 and 23 generations ago. The more specific reasons for Kupe's semi-legendary journey, and the migration of Māori in general, have been contested. Māori oral history recounts that Hawaiki and other Polynesian islands were experiencing considerable internal conflict during his time, which is thought to have possibly caused an exodus. Kupe features prominently in the mythology and or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
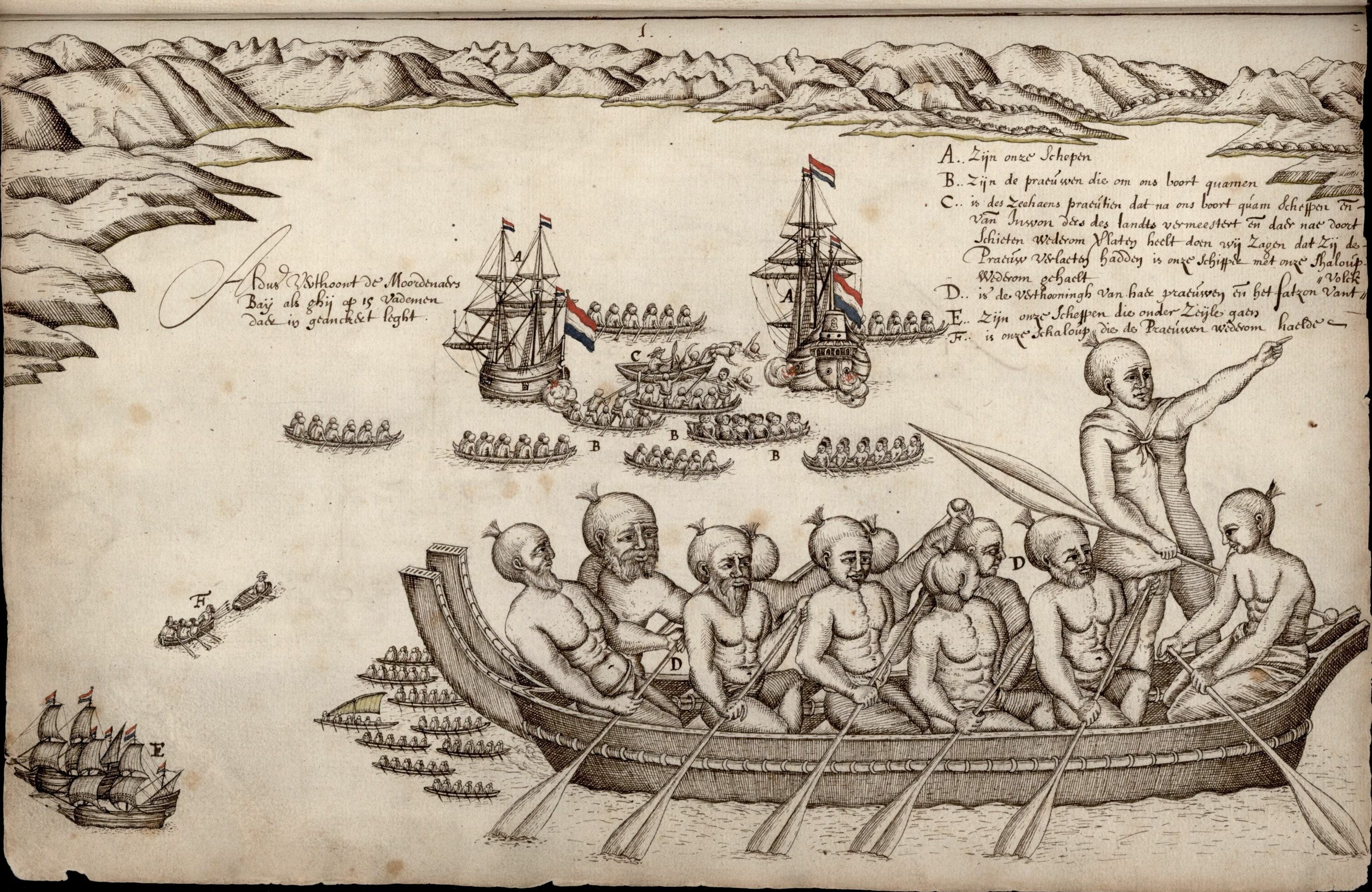
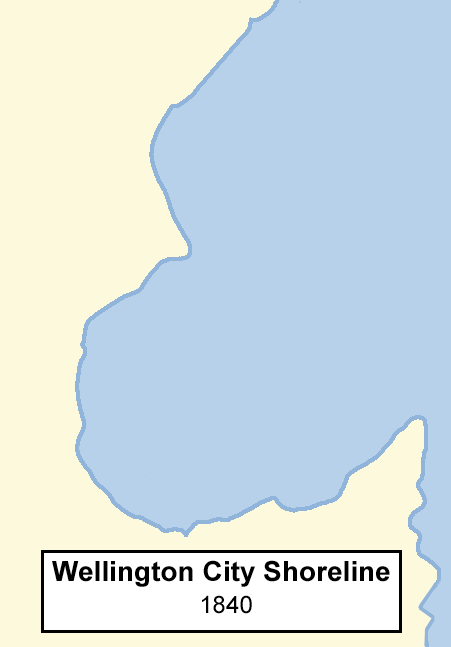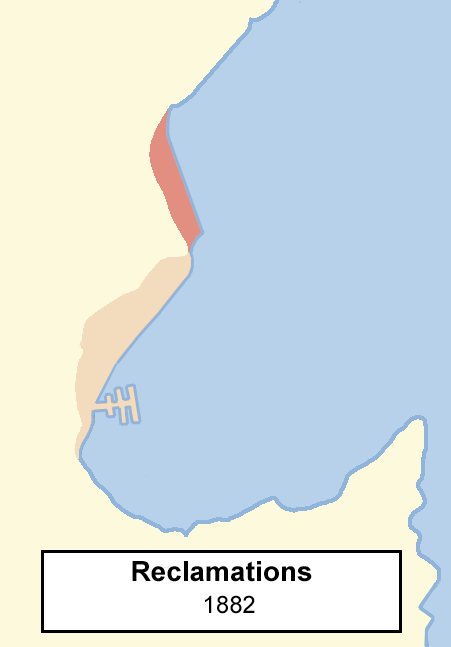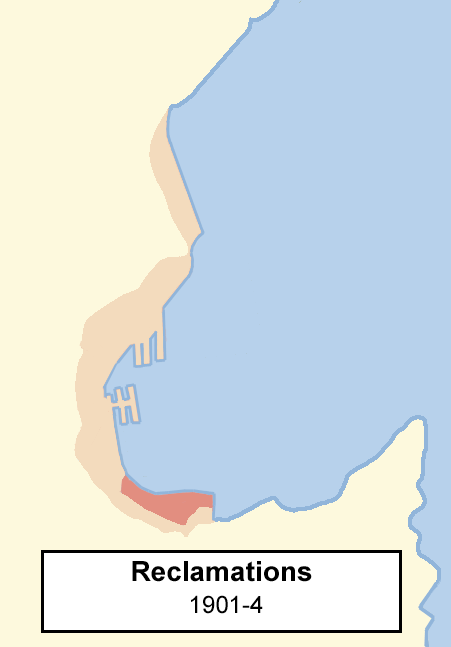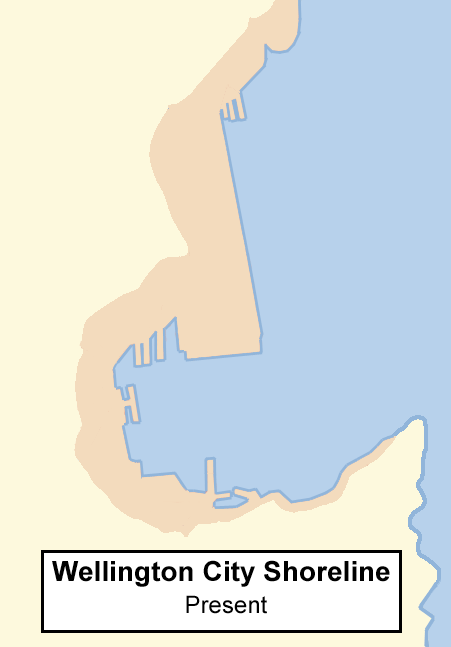
Wellington Harbour
Wellington Harbour ( ), officially called Wellington Harbour / Port Nicholson, is a large natural harbour on the southern tip of New Zealand's North Island. The harbour entrance is from Cook Strait. Central Wellington is located on parts of the western and southern sides of the harbour, and the suburban area of Lower Hutt is to the north and east. The harbour area bounded by a line between Pencarrow Head to Petone foreshore, was officially named Port Nicholson until it assumed its current dual name in 1984. Toponymy The earliest known Māori name for the area, ''Te Upoko-o-te-Ika-a-Māui'', is derived from Māori legend and translates literally as "the head of Māui's fish". ''Te Whanganui-a-Tara'', another Māori name for the area, translates literally as "the great harbour of Tara". It is believed to refer to Tara, a son of the Polynesian explorer Whātonga, who was sent down from the Māhia Peninsula by his father to explore southern lands for their people to se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Te Wheke-a-Muturangi
In Māori mythology, Te Wheke-a-Muturangi is a monstrous octopus destroyed in Whekenui Bay, Tory Channel or at Patea by Kupe the navigator. The octopus was a pet or familiar of Muturangi, a powerful tohunga of Hawaiki. The wheke was nonetheless a wild creature and a guardian. When Kupe reached New Zealand, he encountered the beast off Castlepoint. The giant octopus then fled across Cook Strait, and was chased by Kupe through Tory Channel. Here a great battle took place, and when the octopus appeared to be about to flee, Kupe cut off its arms with his adze, killing it (Tregear 1891: 184, 620). In the traditions of the Ngāti Ranginui people of Tauranga, Te Wheke-a-Muturangi was killed by their ancestor Tamatea, and is not associated with Kupe. New Zealand ethnologist David Simmons has suggested that this may be the more authentic tradition, and that the association with Kupe is found only in problematic sources (Simmons 1976). Another theory for Te Wheke-a-Muturan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
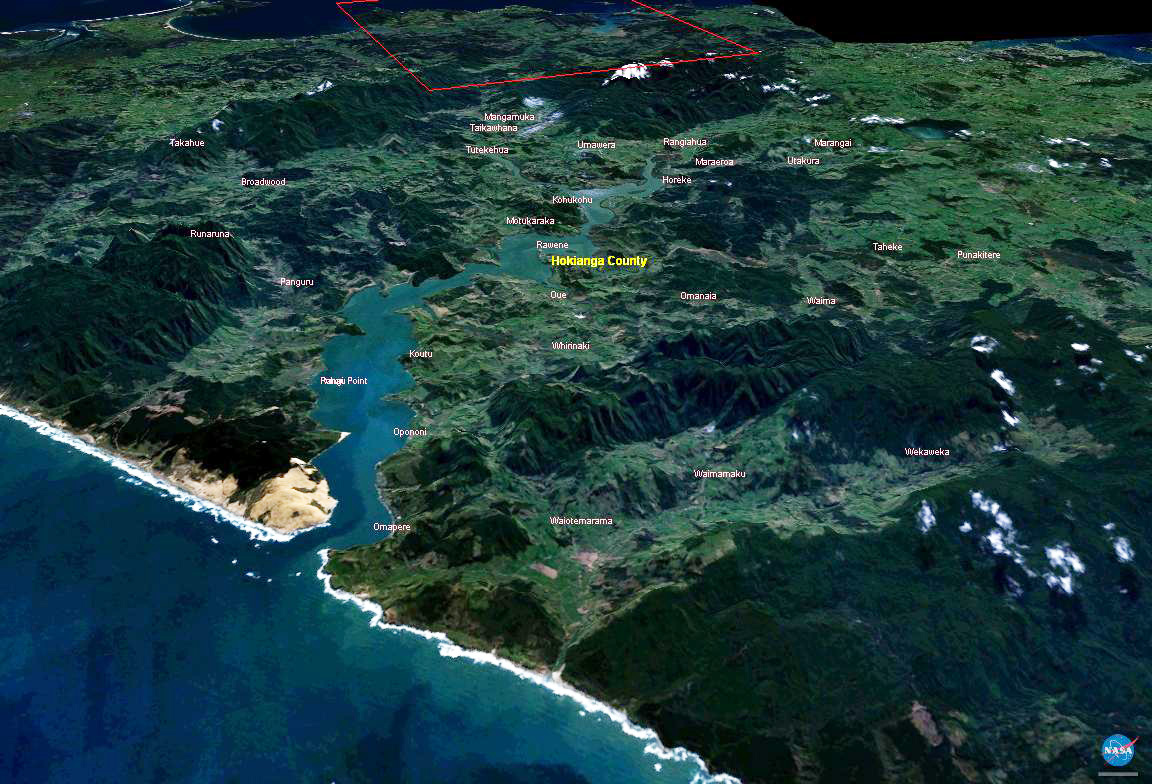
Hokianga
The Hokianga is an area surrounding the Hokianga Harbour, also known as the Hokianga River, a long Estuary, estuarine drowned valley on the west coast in the north of the North Island of New Zealand. The original name, still used by local Māori people, Māori, is ''Te Kohanga o Te Tai Tokerau'' ("the nest of the northern people") or ''Te Puna o Te Ao Marama'' ("the wellspring in the world of light"). The full name of the harbour is Te Hokianga-nui-a-Kupe — "the place of Kupe's great return". Geography The Hokianga is in the Far North (district), New Zealand, Far North District, which is in the Northland Region. The area is northwest of Whangārei City—and west of Kaikohe—by road. The estuary extends inland for from the Tasman Sea. It is navigable for small craft for much of its length, although there is a bar across the mouth. In its upper reaches the Rangiora Narrows separate the mouths of the Waihou and Mangamuka Rivers from the lower parts of the harbour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of island countries, sixth-largest island country by area and lies east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The Geography of New Zealand, country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps (), owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. Capital of New Zealand, New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and subsequently developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori Mythology
Māori mythology and Māori traditions are two major categories into which the remote oral history of New Zealand's Māori people, Māori may be divided. Māori myths concern tales of supernatural events relating to the origins of what was the observable world for the pre-European Māori, often involving gods and demigods. Māori tradition concerns more folkloric legends often involving historical or semi-historical forebears. Both categories merge in to explain the overall origin of the Māori and their connections to the world which they lived in. The Māori did not have a writing system before European contact, beginning in 1769, therefore they relied on oral retellings and recitations memorised from generation to generation. The three forms of expression prominent in Māori and Polynesian oral literature are genealogical recital, poetry, and narrative prose. Experts in these subjects were broadly known as . The rituals, beliefs, and general worldview of Māori society were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngātokimatawhaorua
In Māori tradition, ''Ngātokimatawhaorua'' (or Matawhaorua) was one of the great ocean-going, voyaging canoes that was used in the migrations that settled New Zealand. Matawhaorua was the canoe of Kupe, the Polynesian discoverer of the islands now known as New Zealand. On Kupe's return to Hawaiki, it was re-adzed by Kupe and Nukutawhiti and renamed Ngātokimatawhaorua ("ngā toki" translating as "the adzes"). The rangatira of Ngātokimatawhaorua was Nukutawhiti. Although he predated the iwi Ngāpuhi, he is the ancestor of the great Ngāpuhi rangatira, Rāhiri. A Legend of Ngātokimatawhaorua The departure of Ngātokimatawhaorua coincided with a nova, during which a star shone so brightly that the nights were almost as bright as day. Nukutawhiti spoke a karakia to bring a big wave, and with the help of four Taniwha, the wave pushed the waka towards Aotearoa. The Taniwha are called Āraiteuru, Niua, Puhimoanaariki and Rangiuruhinga. The children on the waka hourua likene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matiu / Somes Island
Matiu / Somes Island is the largest of three islands in the northern half of Wellington Harbour, New Zealand. The island is 24.9 hectares (62 acres) in area, and lies 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) south of the suburb of Petone and the mouth of the Hutt River. Matiu / Somes Island was used as a place of refuge by pre-colonial Māori. Middens and other remnants of habitation have been found on the island. There is also a long and varied European history. The island was used for human quarantine from 1840 until the 1920s. Ships arriving in Wellington Harbour with infectious passengers or crew would disembark them at Matiu / Somes Island for care and treatment before berthing in the city. During both World War I and World War II, "enemy aliens", including long-term residents of New Zealand who originated from enemy countries, were interned on the island. Anti-aircraft gun emplacements were also built on the island during World War II and their remains can be seen today. The island was u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cook Strait
Cook Strait () is a strait that separates the North Island, North and South Islands of New Zealand. The strait connects the Tasman Sea on the northwest with the South Pacific Ocean on the southeast. It is wide at its narrowest point,McLintock, A. H., ed. (1966''Cook Strait''from An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand, updated 18-Sep-2007. Note: This is the distance between the North Island and Arapaoa Island; some sources give a slightly larger reading of around , that between the North Island and the South Island. and has been described as "one of the most dangerous and unpredictable waters in the world". Regular ferry services run across the strait between Picton, New Zealand, Picton in the Marlborough Sounds and Wellington. The strait is named after James Cook, the first Ethnic groups in Europe, European commander to sail through it, in 1770. In Māori language, Māori it is named ''Te Moana-o-Raukawa'', which means ''The Sea of Raukawa''. The waters of Cook Strait are dominated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matahourua
In Māori tradition, ''Matahourua'' was the canoe of the legendary hero Kupe, who, in some accounts, was the discoverer of Aotearoa (New Zealand) See also *List of Māori waka This is a list of Māori people, Māori (canoes). The information in this list represents a compilation of different oral traditions from around New Zealand. These accounts give several different uses for the waka: many carried Polynesians, Poly ... References *R.D. Craig, ''Dictionary of Polynesian Mythology'' (Greenwood Press: New York, 1989). *G. Grey, ''Polynesian Mythology'' (reprint Taplinger Press: New York, 1970). Māori waka Māori mythology {{Māori-myth-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wairarapa
The Wairarapa (; ), a geographical region of New Zealand, lies in the south-eastern corner of the North Island, east of metropolitan Wellington and south-west of the Hawke's Bay Region. It is lightly populated, having several rural service towns, with Masterton being the largest. It is named after its largest lake, Lake Wairarapa. The region is referred to as The Wairarapa, particularly when used after a preposition (e.g., locals will say they live "in the Wairarapa", and travel "to" and "from the Wairarapa"). Boundaries The Wairarapa is shaped like a rectangle, about long (from Palliser Bay north to Woodville) and wide (from the Tararua Range east to the coast). The Ngāti Kahungunu tribe's boundary for the region is similar. Their tribal area begins at Pōrangahau and ends at Turakirae. It is the southernmost of their three rohe (homelands) running down the eastern North Island from Wairoa. For the Rangitāne tribe, the Wairarapa is part of a wider homeland that include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mākaro / Ward Island
Mākaro / Ward island is one of the three small islands in Wellington Harbour, at the southern end of the North Island, New Zealand. Ward Island is on the eastern side of the harbour, about west of the town of Eastbourne. It is about long and wide, with the long axis aligned north–south. The significantly larger Matiu / Somes Island lies about northwest. Etymology The name is derived from a story in Māori mythology that Kupe named the two islands in Wellington Harbour after two of his daughters, nieces, or granddaughters. Ward Island is named after the deputy-governor of the New Zealand Company. In 1997 the New Zealand Geographic Board assigned the official bilingual name of Makaro/Ward island. Formatting was later changed to include a space on each side of the slash: Mākaro / Ward island. History The bulk of Ward Island consists of a steep sided block of yellowy/brown argilite, with a more or less flat top. There is a beach of greywacke shingle along the east sid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |