|
Koppal District
Koppala district, officially known as Koppala district is an administrative district in the state of Karnataka in India. In the past Koppal was referred to as 'Kopana Nagara'. Hampi, a World heritage center, covers some areas of Koppala District. It is situated approximately 38 km away. Anegundi, is also a famous travel destination. History Koppal, now a district headquarters, is ancient ''Kopana'', a major Jain holy site. Palkigundu and Gavimath, Koppal, Palkigundu is described as the famous ''Indrakila parvata'' of mythology. There is an ancient Shiva temple called the ''Male Malleshwara''. There are two Ashoka inscriptions at ''Palkigundu'' and ''Gavimatha''. Koppal was the capital of a branch of Shilaharas under the Western Chalukya Empire, Chalukyas of Kalyani. In Shivaji's times it was one of the eight ''prant''s or revenue divisions of Southern Maratha Country. During India's First War of Independence, Mundargi Bheema Rao and Hammige Kenchanagouda died fighting the Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
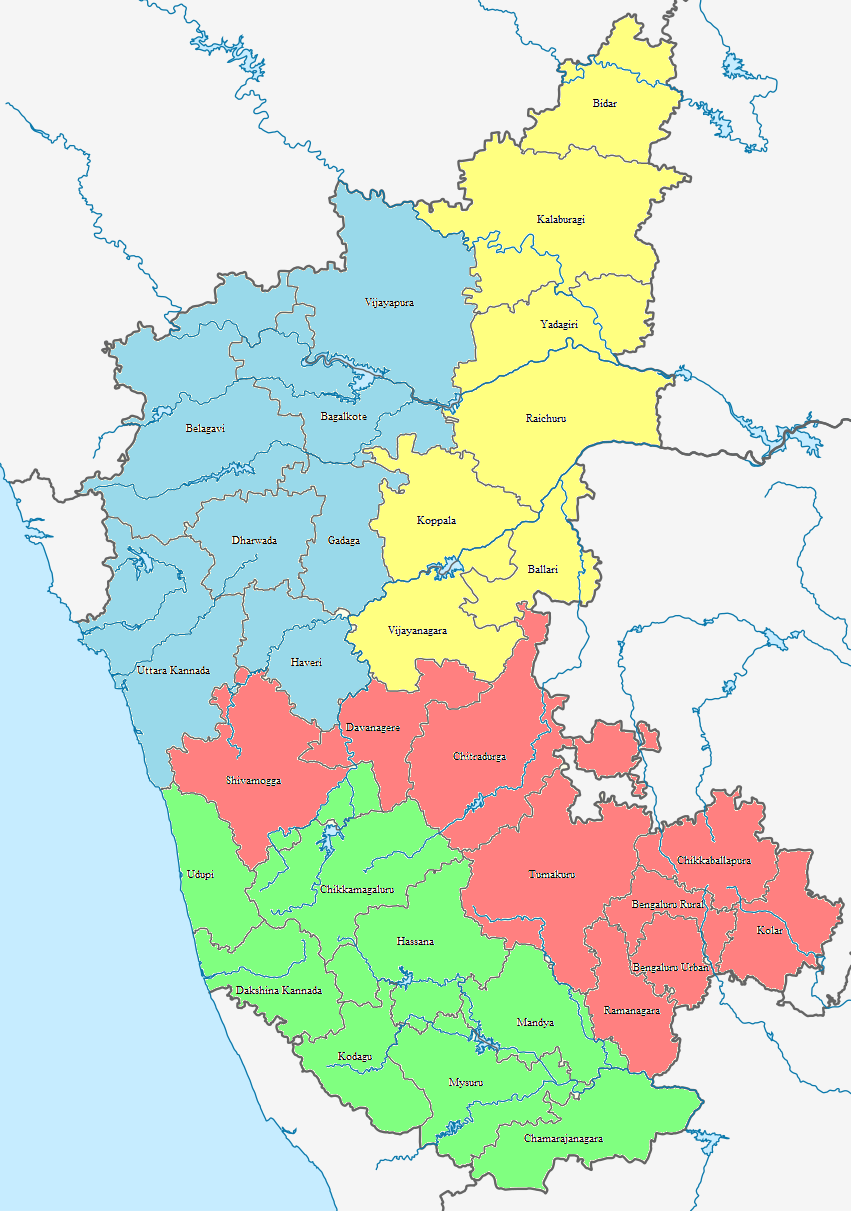
List Of Districts Of Karnataka
The South India, southern Indian States and union territories of India, state of Karnataka consists of 31 districts grouped into 4 administrative divisions, ''viz''., Belagavi division, Belagavi, Bengaluru division, Bengaluru , Kalaburagi division, Gulbarga, and Mysore division, Mysore. Geographically, the state has three principal variants: the western Kanara, coastal stretch, the Malenadu, hilly belt comprising the Western Ghats, and the Bayaluseeme, plains, comprising the plains of the Deccan plateau. History Karnataka took its present shape in 1956, when the former states of Mysore State, Mysore and Coorg State, Coorg were Unification of Karnataka, unified into a linguistically homogenous Kannada-speaking state along with agglomeration of districts of the former states of Bombay State, Bombay, Hyderabad State, Hyderabad, and Madras State, Madras as part of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Reorganisation Act of 1956. The unified Mysore State was made up of ten di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shivaji
Shivaji I (Shivaji Shahaji Bhonsale, ; 19 February 1630 – 3 April 1680) was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle dynasty. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the Sultanate of Bijapur that formed the genesis of the Maratha Empire. In 1674, he was formally crowned the ''Chhatrapati'' of his realm at Raigad Fort. Shivaji offered passage and his service to the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb to invade the declining Sultanate of Bijapur. After Aurangzeb's departure for the north due to a war of succession, Shivaji conquered territories ceded by Bijapur in the name of the Mughals. Following his defeat at the hands of Jai Singh I, the senior most general ("Mirza (noble), Mirza Raja") of the Mughal Empire, in the Battle of Purandar, Shivaji entered into vassalage with the Mughal empire, assuming the role of a Mughal chief and was conferred with the title of ''Raja (title), Raja'' by Aurangzeb. He undertook military expeditions on behalf of the Mughal Empire for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Chalukya Empire
The Western Chalukya Empire ( ) ruled most of the Deccan Plateau, western Deccan, South India, between the 10th and 12th centuries. This Kannada dynasty is sometimes called the ''Kalyani Chalukya'' after its regal capital at Kalyani, today's Basavakalyan in the modern Bidar district of Karnataka state, and alternatively the ''Later Chalukya'' from its theoretical relationship to the 6th-century Chalukya dynasty of Badami. The dynasty is called ''Western Chalukyas'' to differentiate from the contemporaneous Eastern Chalukyas of Vengi, a separate dynasty. Before the rise of these Chalukyas, the Rashtrakuta Empire of Manyakheta controlled most of the Deccan Plateau and Central India for over two centuries. In 973, seeing confusion in the Rashtrakuta empire after a successful invasion of their capital by the ruler of the Paramara dynasty of Malwa, Tailapa II, a feudatory of the Rashtrakuta dynasty ruling from Bijapur district, Karnataka, Bijapur region defeated his overlords and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shilahara
Shilahara was a royal dynasty that established itself in northern and southern Konkan in 8th century CE, present-day Mumbai and Southern Maharashtra ( Kolhapur) during the Rashtrakuta period. The founder of the Shilahara dynasty, Sanaphulla, was a vassal of the Rashtrakuta ruler, Krishna I. The Shilaharas continued to be vassals under the Rashtrakutas until 997, when Aparajit assumed independent rule. The Shilahara dynasty had three branches: the northern Konkan branch, the southern Konkan branch (765–1029) and a third branch in Kolhapur, Satara and Belagavi (940–1215) who were defeated by the Yadavas. North Konkan (Thane) branch (c. 800–1265 CE) After Rashtrakuta power became weak, the last known ruler of this family, Rattaraja, declared his independence. But Chalukya Jayasimha, the younger brother of Vikramaditya, overthrew him and appropriated his possessions. The second northern Shilahara king, Pullashakti, acknowledged the overlordship of the Rashtrak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palkigundu And Gavimath, Koppal
Palkigundu () and Gavimath () near Koppal in Karnataka are two locations where inscriptions of Emperor Ashoka (304–232 BCE) were found. These inscriptions represent some of India's oldest written records, and are part of Ashoka's Minor Rock Edicts. Jain monks used to meditate there. The Palkigundu and Gavimath edicts are in Prakrit, written in Brahmi script. A Kannada translation of the inscriptions is available. At Palkigundu (''palanquin rock''), two huge boulders are topped with a flat-shaped rock forming a canopy. Rough steps lead to the top of the boulders, where a 2,300-year-old inscription is located. Similar edicts have been found in 17 places in India. About 2.5 km to the southeast of Palkigundu, at Gavimath, there is another rock inscription, also an edict from Ashoka. The Gavimath inscription is situated on a boulder in a sheltered place with a rock canopy. Jain monks used both Gavimath and Palkigundu as locations to meditate. Ashoka Edicts at Palkigundu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anegundi
Anegundi, previously called Kishkindha, is a village in Gangavathi, Koppal district, in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is older than Hampi, situated on the northern bank of the Tungabhadra River. Nimvapuram, a nearby village, has a mount of ash believed to be the cremated remains of the king Vaali. History Anegundi was believed to be the monkey kingdom of Kishkindha, with ''Kishkinta'' meaning ''a forest where the monkeys lived''. The epic of Ramayana is at a distance of from the historical site of Hampi. Anjanadri Hill, the birthplace of the god Hanuman, and the mountain Rishimuka are places near and affiliated with Ramayana. It is said to have one of the oldest plateaus on the planet, estimated to be 3,000 million years old. Only local story-tellers refer to Anegundi as the maternal home of ''Bhoodevi'' (Mother Earth). The village, located on the northern bank of River Tungabhadra, was said to be the legendary Kishkindha, a kingdom of the prince Sugriva as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
District
A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municipalities, subdivisions of municipalities, school district, or political district. Etymology The word "district" in English is a Loanword, loan word from French language, French. It comes from Medieval Latin districtus–"exercising of justice, restraining of offenders". The earliest known English-language usage dates to 1611, in the work of lexicographer Randle Cotgrave. By country or territory Afghanistan In Afghanistan, a district (Persian language, Persian ) is a subdivision of a province. There are almost 400 districts in the country. Australia Electoral districts are used in state elections. Districts were also used in several states as cadastral units for land titles. Some were used as squatting districts. Cadastral divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postal Index Number
A Postal Index Number (PIN; sometimes redundantly a PIN code) refers to a six-digit code in the Indian postal code system used by India Post. On 15 August 2022, the PIN system celebrated its 50th anniversary. History The PIN system was introduced on 15 August 1972 by Shriram Bhikaji Velankar, an additional secretary in the Government of India, Government of India's Ministry of Communications (India), Ministry of Communications. The system was introduced to simplify the manual sorting and delivery of mail by eliminating confusion over incorrect addresses, similar place names, and different languages used by the public. PIN structure The first digit of a PIN indicates the zone, the second indicates the sub-zone, and the third, combined with the first two, indicates the sorting district within that zone. The final three digits are assigned to individual post offices within the sorting district. Postal zones There are nine postal zones in India, including eight regional zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Standard Time
Indian Standard Time (IST), sometimes also called India Standard Time, is the time zone observed throughout the Republic of India, with a time offset of UTC+05:30. India does not observe daylight saving time or other seasonal adjustments. In military and aviation time, IST is designated E* ("Echo-Star"). It is indicated as ''Asia/Kolkata'' in the IANA time zone database. History The Indian Standard Time was adopted on 1 January 1906 during the British era with the phasing out of its precursor Madras Time (Railway Time), and after Independence in 1947, the Union government established IST as the official time for the whole country, although Kolkata and Mumbai retained their own local time (known as Calcutta Time and Bombay Time) until 1948 and 1955, respectively. The Central observatory was moved from Chennai to a location at Shankargarh Fort in Allahabad district, so that it would be as close to UTC+05:30 as possible. Daylight Saving Time (DST) was used brief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a second or third language for 15 million speakers in Karnataka. It is the official and administrative language of Karnataka. It also has scheduled status in India and has been included among the country's designated classical languages.Kuiper (2011), p. 74R Zydenbos in Cushman S, Cavanagh C, Ramazani J, Rouzer P, ''The Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics: Fourth Edition'', p. 767, Princeton University Press, 2012, Kannada was the court language of a number of dynasties and empires of South India, Central India and the Deccan Plateau, namely the Kadamba dynasty, Western Ganga dynasty, Nolamba dynasty, Chalukya dynasty, Rashtrakutas, Western Chalukya Empire, Seuna dynasty, kingdom of Mysore, Nayakas of Keladi, Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |