|
Kombucha
Kombucha (also tea mushroom, tea fungus, or Manchurian mushroom when referring to the Microbiological culture, culture; Latin name ''Medusomyces gisevii'') is a fermented beverage, fermented, effervescent, Sweetened beverage, sweetened black tea drink. Sometimes the beverage is called kombucha tea to distinguish it from the culture of bacteria and yeast. Juice, spices, fruit, or other flavorings are often added. Commercial kombucha contains minimal amounts of Alcohol (drug), alcohol. Kombucha is named after the Japanese language, Japanese term for Kelp tea, seaweed tea thought to have originated in China, where the drink is traditional. By the early 20th century it spread to Russia, then other parts of Eastern Europe and Germany. Kombucha is now Homebrewing, homebrewed globally, and also bottled and sold commercially. The global kombucha market was worth approximately billion . Kombucha is produced by symbiotic fermentation of sugared tea using a symbiotic culture of bacteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCOBY
Symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) is a culinary symbiosis, symbiotic fermentation Microbial food cultures, culture (Fermentation starter, starter) consisting of lactic acid bacteria (LAB), acetic acid bacteria (AAB), and yeast which arises in the preparation of sour foods and beverages such as kombucha. Beer and wine also undergo fermentation with yeast, but the lactic acid bacteria and acetic acid bacteria components unique to SCOBY are usually viewed as a source of spoilage rather than a desired addition. Both LAB and AAB enter on the surface of barley and malt in beer fermentation and grapes in wine fermentation; LAB lowers the pH of the beer/wine while AAB takes the ethanol produced from the yeast and oxidizes it further into vinegar, resulting in a sour taste and smell. AAB are also responsible for the formation of the cellulose SCOBY. In its most common form, SCOBY is a gelatinous, cellulose-based biofilm or microbial mat found floating at the container's air- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
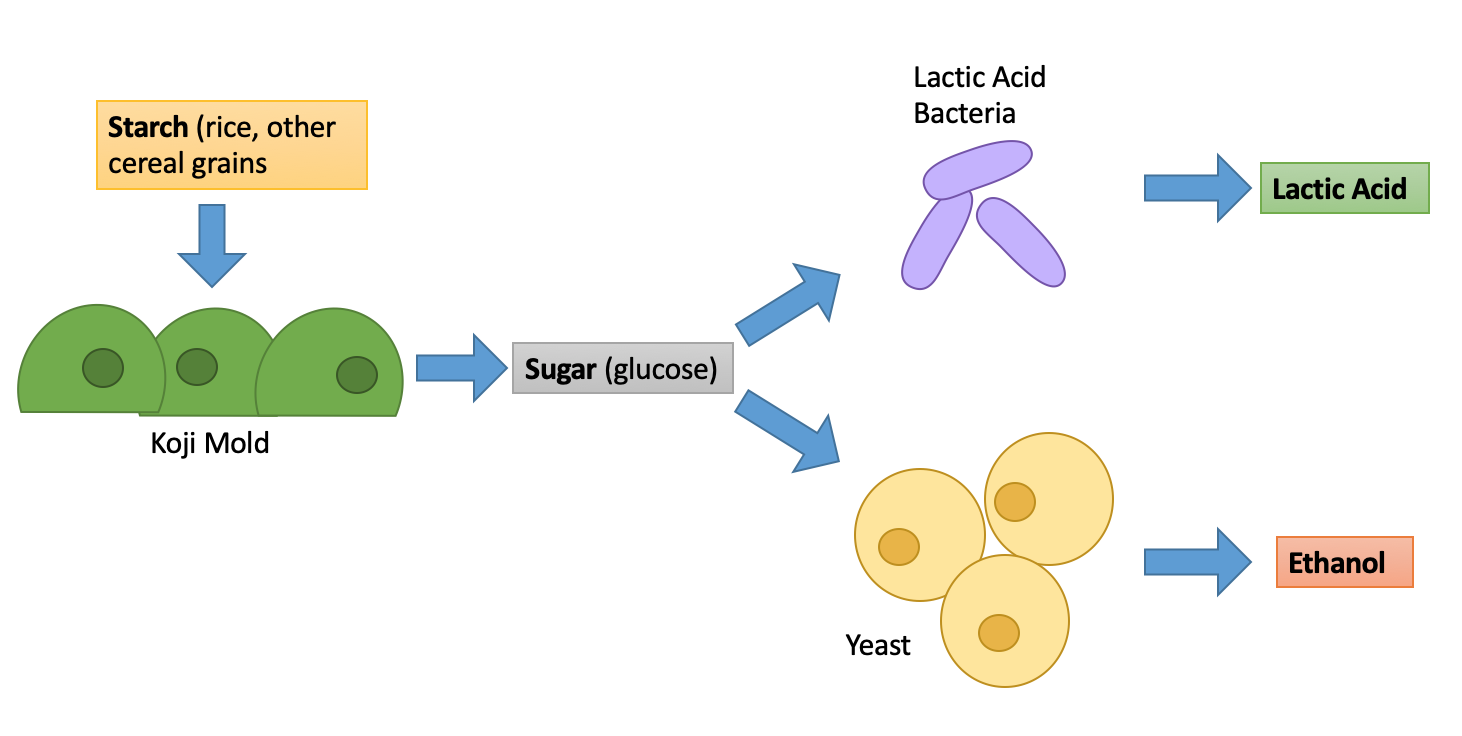
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Some yeast species have the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae, or quickly evolve into a Multicellular organism, multicellular cluster with specialised Organelle, cell organelles function. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 micrometre, μm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 μm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexual reproduction, asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with Mold (fungus), molds, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probiotic
Probiotics are live microorganisms that provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the microbiota in the gut. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria– host interactions and unwanted side effects in rare cases. There is some evidence that probiotics are beneficial for some conditions, such as helping to ease some symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). However, many claimed health benefits, such as treating eczema, or curing vaginal infections lack substantial scientific support. The first discovered probiotic was a certain strain of bacillus in Bulgarian yoghurt, called '' Lactobacillus bulgaricus''. The discovery was made in 1905 by Bulgarian physician and microbiologist Stamen Grigorov. The modern-day theory is generally attributed to Russian Nobel Prize laureate Élie Metchnikoff, who postulated around 1907 that yoghurt-consuming Bulgarian peasants lived longer. A growing probiotics market has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiotic Fermentation
Symbiotic fermentation is a form of fermentation in which multiple organisms (yeasts, acetic acid bacteria, lactic acid bacteria and others) interact in symbiosis in order to produce the desired product. For example, a yeast may produce ethanol, which is then consumed by an acetic acid bacterium. Described early on as the fermentation of sugars following saccharification in a mixed fermentation process. History The earliest mention of the term can be found in a lecture given by Dr. Allan Macfadyen of the Jenner Institute of Preventative Medicine in 1902. Dr. Macfadyen described symbiotic fermentation as noting "a close relationship between the organisms at work, the action of one aiding or modifying the action of the other, whilst both members are more active as a results of the partnership." Fermentative microorganisms have had a deep history as seen by kefir and kumis fermentations of milk by Nomadic tribes in Russia, as well as Japanese koji fermentation (see ''Aspergillus o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermented Beverage
This is a list of fermented foods, which are foods produced or preserved by the action of microorganisms. In this context, Fermentation in food processing, fermentation typically refers to the fermentation of sugar to ethanol, alcohol using yeast, but other fermentation processes involve the use of bacteria such as lactobacillus, including the making of foods such as yogurt and sauerkraut. Many fermented foods are Mass production, mass-produced using industrial fermentation processes. The science of fermentation is known as zymology. Many pickling, pickled or souring, soured foods are fermented as part of the pickling or souring process, but many are simply processed with brine, vinegar, or another acid such as lemon juice. __TOC__ Fermented foods Fermented beans and seeds Fermented cheeses Most cheeses are fermented as part of their production. Fermented condiments Fermented creams and yogurts Fermented grains and grain-based foods Fermented fru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Kefir
Tibicos, or water kefir, is a traditional fermented drink made with water and water kefir grains held in a polysaccharide biofilm matrix created by the bacteria. It is sometimes consumed as an alternative to milk-based probiotic drinks or tea-cultured products such as kombucha. Water kefir is typically made as a probiotic homebrew beverage. The finished product, if bottled, will produce a carbonated beverage. Origin The origin of tibicos grains is not known exactly. In 1889, Martinus Beijerinck conjectured that the grains from the '' ginger beer plant'' were originally brought by the British soldiers while returning to their country from the Crimean War in 1855. This was later dismissed as unsubstantiated by Harry Marshall Ward in 1892 noting its real origins remain a mystery. As a different theory, Lutz (1899) reported "Tibi grains" which were plucked from the leaves of a Mexican cactus (''Opuntia''). These granules then could be reconstituted in a sugar-water solution for pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelp Tea
Kelp tea is a tea made from kelp. It is called ''konbu-cha'' or ''kobu-cha'' (, meaning "Kombu-tea") in Japan, ''haidai-cha'' () in China and ''dasima-cha'' () in Korea. Varieties Japan In Japan, ''konbu-cha'' or ''kobu-cha'' is kelp tea made by pouring boiling water into chopped edible kelp (kombu) and leaching or pouring hot water into powdered kelp.'''' Kelp tea for fortune The tea served on New Year's Day and at weddings is sometime kelp tea'''' because the pronunciation of ''kombu'' is similar to that of the last part of "''yorokobu''" (喜ぶ, meaning "be happy").'''' ''Fuku-cha''(福茶, meaning "fortune tea") is sencha green tea with kelp, umeboshi, kuromame (black beans), and sanshō and is drunk on the last day of the year (Ōmisoka), in New Year, and on the day before the beginning of spring (Setsubun) in Kansai region, wishing a long life. In particular, in New Year, ''oo-buku-cha'' or ''dai-buku-cha'' (, meaning "very good fortune tea"), which is se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidize
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. The oxidation and reduction processes occur simultaneously in the chemical reaction. There are two classes of redox reactions: * Electron-transfer – Only one (usually) electron flows from the atom, ion, or molecule being oxidized to the atom, ion, or molecule that is reduced. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * Atom transfer – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously, the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungal microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular and cell biology, much like '' Escherichia coli'' as the model bacterium. It is the microorganism which causes many common types of fermentation. ''S. cerevisiae'' cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding. Many proteins important in human biology were first discovered by studying their homologs in yeast; these proteins include cell cycle proteins, signaling proteins, and protein-processing enzymes. ''S. cerevisiae'' is currently the only yeast cell known to have Berkeley bodies present, which are involved in particular secretory pathways. Antibodies again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluconacetobacter Xylinus
''Komagataeibacter xylinus'' is a species of bacteria best known for its ability to produce cellulose, specifically bacterial cellulose. History and taxonomy The species was first described in 1886 by Adrian John Brown, who identified the bacteria while studying fermentation. Brown gave the species the name ''Bacterium xylinum''. It has since been known by several other names, mainly ''Acetobacter xylinum'' and ''Gluconacetobacter xylinus''. It was given its current name, with the establishment of the new genus ''Komagataeibacter'', in 2012. It is the type species of the genus. Genome and metabolism ''K. xylinus'' is a member of the acetic acid bacteria, a group of Gram-negative aerobic bacteria that produce acetic acid during fermentation. ''K. xylinus'' is unusual among the group in also producing cellulose. Bacterial cellulose (also sometimes known as nanocellulose) is involved in the formation of biofilms. It is chemically identical to plant cellulose, but has distinct phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osmophilic
An osmophile is an extremophile microorganism adapted to environments generating high osmotic pressures, such as aqueous solutions with high salt or sugar concentrations (''e.g.'', brines or sirups). Osmophiles are similar to halophiles (salt-loving organisms) in that a critical aspect of both types of environment is their low water activity, aW. High sugar concentrations represent a growth-limiting factor for many microorganisms, yet osmophiles protect themselves against this high osmotic pressure by the synthesis of osmoprotectants such as alcohols and amino acids. Many osmophilic microorganisms are yeasts; some bacteria are also osmophilic. Osmophilic yeasts are important because they cause food spoilage in the sugar and sweet goods industry, with products such as fruit juices, fruit juice concentrates, liquid sugars (such as golden syrup), honey, and in some cases marzipan Marzipan is a confectionery, confection consisting primarily of sugar and almond meal (ground almond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of Hydrocarbon, hydrocarbons, conferring Hydrophile, hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur. History The flammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of alcohol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan, J� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |