 |
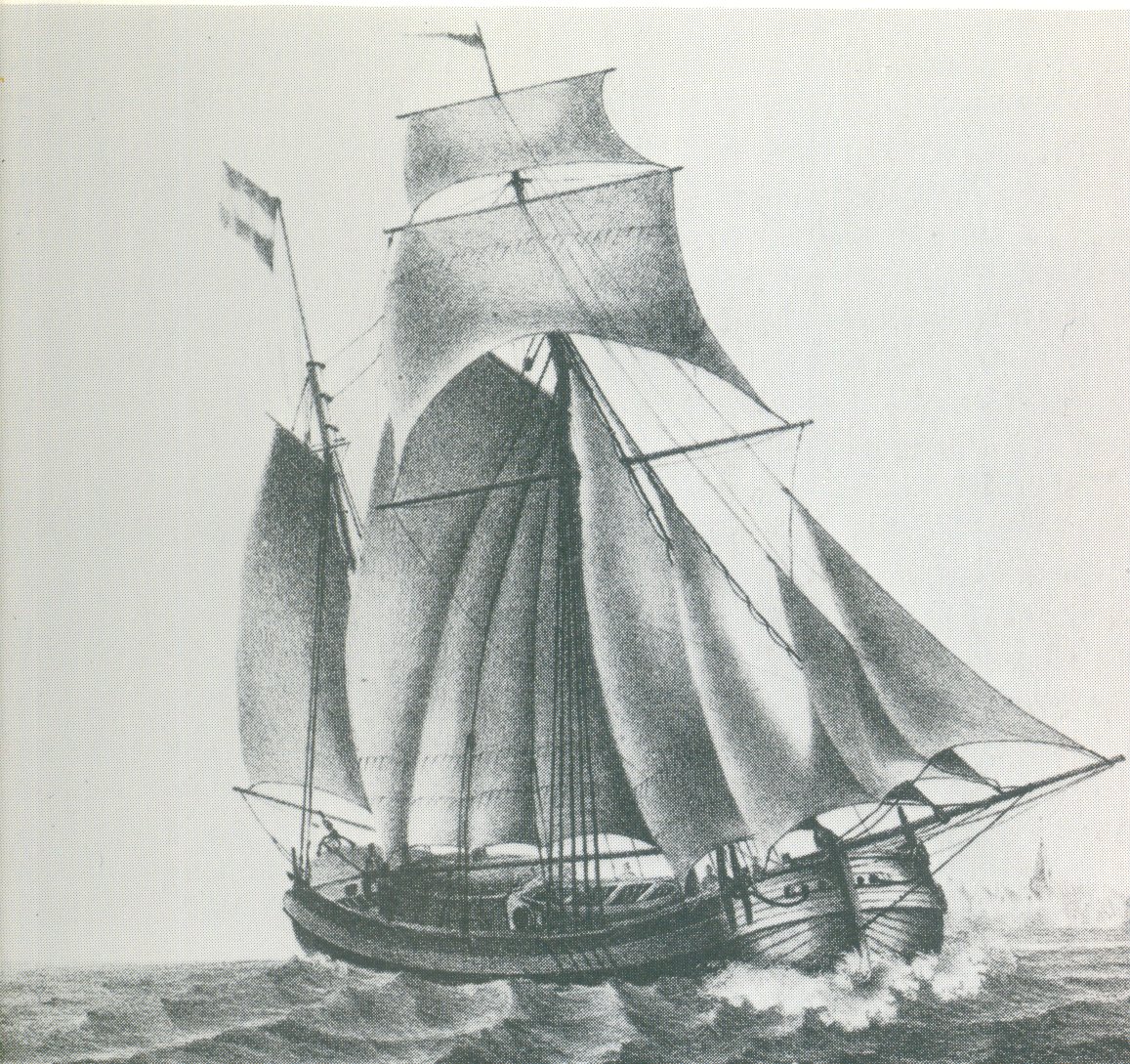
Koff (ship Type)
A koff is a historical type of sailing vessel that was used for coastal shipping off Belgium, the Netherlands, and Germany in the 18th and 19th centuries. A typical koff had one and a half masts with a gaff rigged main sail and spanker and one or two square sails in the main top. The hull was plump with a flat bottom and a heavily rounded, raised bow and stern. Smaller koffs could be equipped with leeboards. Due to the shallow draught, koffs were especially suited for inshore shipping in shallow waters. The koff had been developed in the late 17th century in the Netherlands. Smaller than the fluyt, its rounded bow and stern provided however for more storage on board. This made it a popular type that saw increasing service. Koffs were often counted among the galiots by contemporary sources because the differences are very subtle: the galiot was considered more slender and therefore more elegant. On the koff, a deckhouse could be installed between the two masts which would pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The Netherlands consists of Provinces of the Netherlands, twelve provinces; it borders Germany to the east and Belgium to the south, with a North Sea coastline to the north and west. It shares Maritime boundary, maritime borders with the United Kingdom, Germany, and Belgium. The official language is Dutch language, Dutch, with West Frisian language, West Frisian as a secondary official language in the province of Friesland. Dutch, English_language, English, and Papiamento are official in the Caribbean Netherlands, Caribbean territories. The people who are from the Netherlands is often referred to as Dutch people, Dutch Ethnicity, Ethnicity group, not to be confused by the language. ''Netherlands'' literally means "lower countries" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of , making it the most populous member state of the European Union. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The Capital of Germany, nation's capital and List of cities in Germany by population, most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in the territory of modern Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
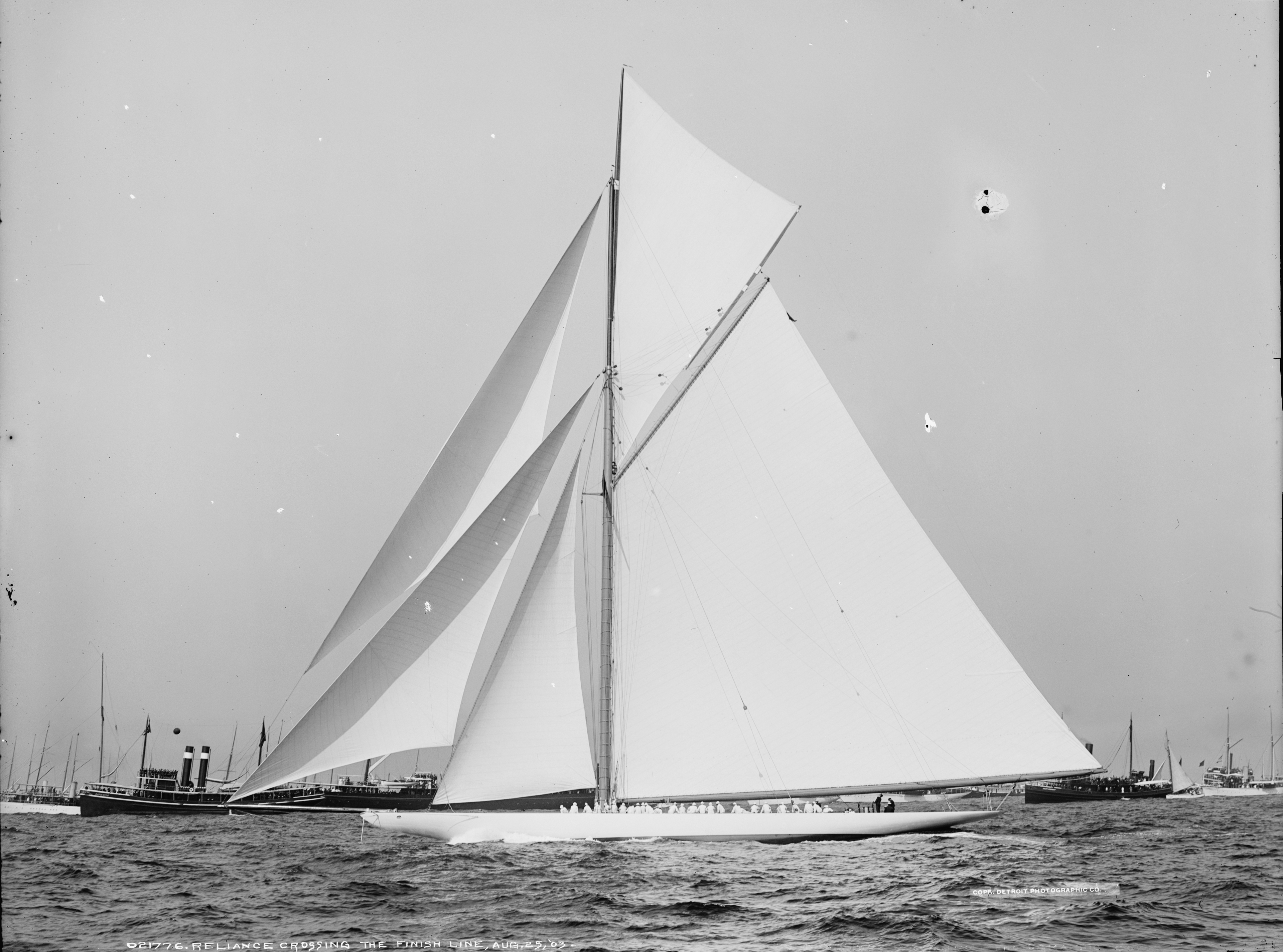 |
Gaff Rig
Gaff rig is a sailing rig (configuration of sails, mast and stays) in which the sail is four-cornered, fore-and-aft rigged, controlled at its peak and, usually, its entire head by a spar (pole) called the ''gaff''. Because of the size and shape of the sail, a gaff rig will have running backstays rather than permanent backstays. The gaff enables a fore-and-aft sail to be four sided, rather than triangular. A gaff rig typically carries 25 percent more sail than an equivalent Bermuda rig for a given hull design. A sail hoisted from a gaff is called a gaff-rigged sail. Description Gaff rig remains the most popular fore-aft rig for schooner and barquentine mainsails and other course sails, and spanker sails on a square rigged vessel are always gaff rigged. On other rigs, particularly the sloop, ketch and yawl, gaff rigged sails were once common but have now been largely replaced by the Bermuda rig sail, which, in addition to being simpler than the gaff rig, usually all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Spanker (sail)
On a square rig Square rig is a generic type of sail plan, sail and rigging arrangement in which a sailing ship, sailing vessel's primary driving sails are carried on horizontal spar (sailing), spars that are perpendicular (or wikt:square#Adjective, square) to t ...ged ship, the spanker is a gaff-rigged fore-and-aft sail set from, and aft of, the aftmost mast. Spankers are also called ''driver'', ''jigger'', and ''pusher'' sail. On a schooner of four or more masts, the spanker is the sail on the mast nearest the stern. The spanker is a small sail, but as it is so far aft of the balance point of the hull, it has strong leverage. When sheeted in, the spanker is important in driving the boat to a new tack. References Sailing rigs and rigging {{Water-transport-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Square Rig
Square rig is a generic type of sail plan, sail and rigging arrangement in which a sailing ship, sailing vessel's primary driving sails are carried on horizontal spar (sailing), spars that are perpendicular (or wikt:square#Adjective, square) to the median plane of the keel and masts of the vessel. These spars are called and their tips, outside the lifts, are called the . A ship mainly rigged so is called a square-rigger. In "customs and traditions of the Royal Navy, Jackspeak" (Royal Navy slang), it also refers to the uniforms of the Royal Navy, dress uniform of Junior Ratings. History Single sail square rigs were used by the ancient Egyptians, the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Romans, and the Celts. Later the Scandinavians, the Germanic peoples, and the Slavs adopted the single square-rigged sail, with it becoming one of the defining characteristics of the classic “Viking” ships.The Viking ship's single square-rigged sail. http://Longshipco.org/sail.html Retrieved 2018-8- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Bow (ship)
The bow () is the forward part of the hull of a ship or boat, the point that is usually most forward when the vessel is underway. The aft end of the boat is the stern. Prow may be used as a synonym for bow or it may mean the forward-most part of the bow above the waterline. Function A ship's bow should be designed to enable the hull to pass efficiently through the water. Bow shapes vary according to the speed of the boat, the seas or waterways being navigated, and the vessel's function. Where sea conditions are likely to promote pitching, it is useful if the bow provides reserve buoyancy; a flared bow (a raked stem with flared topsides) is ideal to reduce the amount of water shipped over the bow. Ideally, the bow should reduce the resistance and should be tall enough to prevent water from regularly washing over the top of it. Large commercial barges on inland waterways rarely meet big waves and may have remarkably little freeboard at the bow, whereas fast military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Leeboard
A leeboard is a form of pivoting keel used largely by sailboats, very often in lieu of a fixed keel. Typically mounted in pairs on each side of a hull, leeboards function much like a centreboard, allowing shallow-draft craft to ply waters inaccessible to fixed-keel boats. Only the leeward side leeboard is used at any time, as it submerges when the boat heels under the force of the wind. A disadvantage, where there is an inadequate fixed keel, is that leeboards typically ship (bear) little ballast, and being on the far ( lee) side delays the onset of unballasted craft's heeling, that is, inhibits the effect of putting up a good, constant resistance against the wind. The classical, archetypal definition of ballast is a low, central weight to optimise centre of mass, to reduce turning moment and therefore resistance to the boat keeling over; however, the centre of gravity tends to be higher in self-righting vessels. Modern developments allow leeboards to act as a speed-enh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Draft (hull)
The draft or draught of a ship is a determined depth of the vessel below the waterline, measured vertically to its hull's lowest—its propellers, or keel, or other reference point. Draft varies according to the loaded condition of the ship. A deeper draft means the ship will have greater vertical depth below the waterline. Draft is used in under keel clearance calculations, where the draft is calculated with the available depth of water (from Electronic navigational charts) to ensure the ship can navigate safely, without grounding. Navigators can determine their draught by calculation or by visual observation (of the ship's painted load lines). Related terminology A ship's draft/draught is the "depth of the vessel below the waterline measured vertically to the lowest part of the hull, propellers, or other reference point". That is, the draft or draught is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Fluyt
A fluyt (archaic Dutch language, Dutch: ''fluijt'' "flute"; ) is a Dutch type of sailing ship, sailing vessel originally designed by the shipwrights of Hoorn as a dedicated ship transport, cargo vessel. Originating in the Dutch Republic in the 16th century, the vessel was designed to facilitate transoceanic delivery with the maximum of space and crew efficiency. Unlike rivals, it was not built for conversion in wartime to a warship, so it was simpler and cheaper to build and carried twice the cargo, and could be handled by a smaller crew. Construction by specialized shipyards using new tools made it half the cost of rival ships. These factors combined to sharply lower the cost of transportation for Dutch merchants, giving them a major competitive advantage, particularly with bulk goods. The fluyt was a significant factor in the 17th-century rise of the Dutch thalassocracy, seaborne empire. In 1670 the Dutch merchant marine totalled 568,000 tons of shipping—about half the European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Galiot
A galiot, galliot or galiote, was a small galley boat propelled by sail or oars. There are three different types of naval galiots that sailed on different seas. A ''galiote'' was a type of French flat-bottom river boat or barge and also a flat-bottomed boat with a simple sail for transporting wine. Naval vessels * Mediterranean (16th–17th centuries) : Historically, a galiot was a type of ship with oars, also known as a half-galley, then, from the 17th century forward, a ship with sails and oars. As used by the Barbary pirates against the Republic of Venice, a galiot had two masts and about 16 pairs of oars. Warships of the type typically carried between two and ten cannons of small caliber, and between 50 and 150 men. It was a Barbary galiot, captained by Barbarossa I, that captured two Papal vessels in 1504. * North Sea (17th–19th centuries) : A galiot was a type of Dutch or German merchant ship of 20 to 400 tons ( bm), similar to a ketch, with a rounded fore and aft li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |