|
Kodaku People
Kodaku people are an indigenous people who live in India. They live in the hills and forest of Chhotanagpur, the bordering area of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh. Their mother tongue, a Munda language, is also called Kodaku language, Kodaku. Some Kodaku people speak Korwa as their mother tongue. They also speak Sadri language, Sadri, Chhattisgarhi, or Kurukh language, Kurukh as their second language. The Kodaku people are mainly concentrated in the northeastern area of Surguja district in Chhattishgarh, southern parts of Palamau, Gadhwa in Jharkhand and the southeastern region of Sonabhadra district of Uttar Pradesh. Kodaku people are now included in Scheduled Tribes by government of India. (along with Abij Maria and Korba community) The name Kodaku originates from 'Kodwa' which means 'digger of the soil'. References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
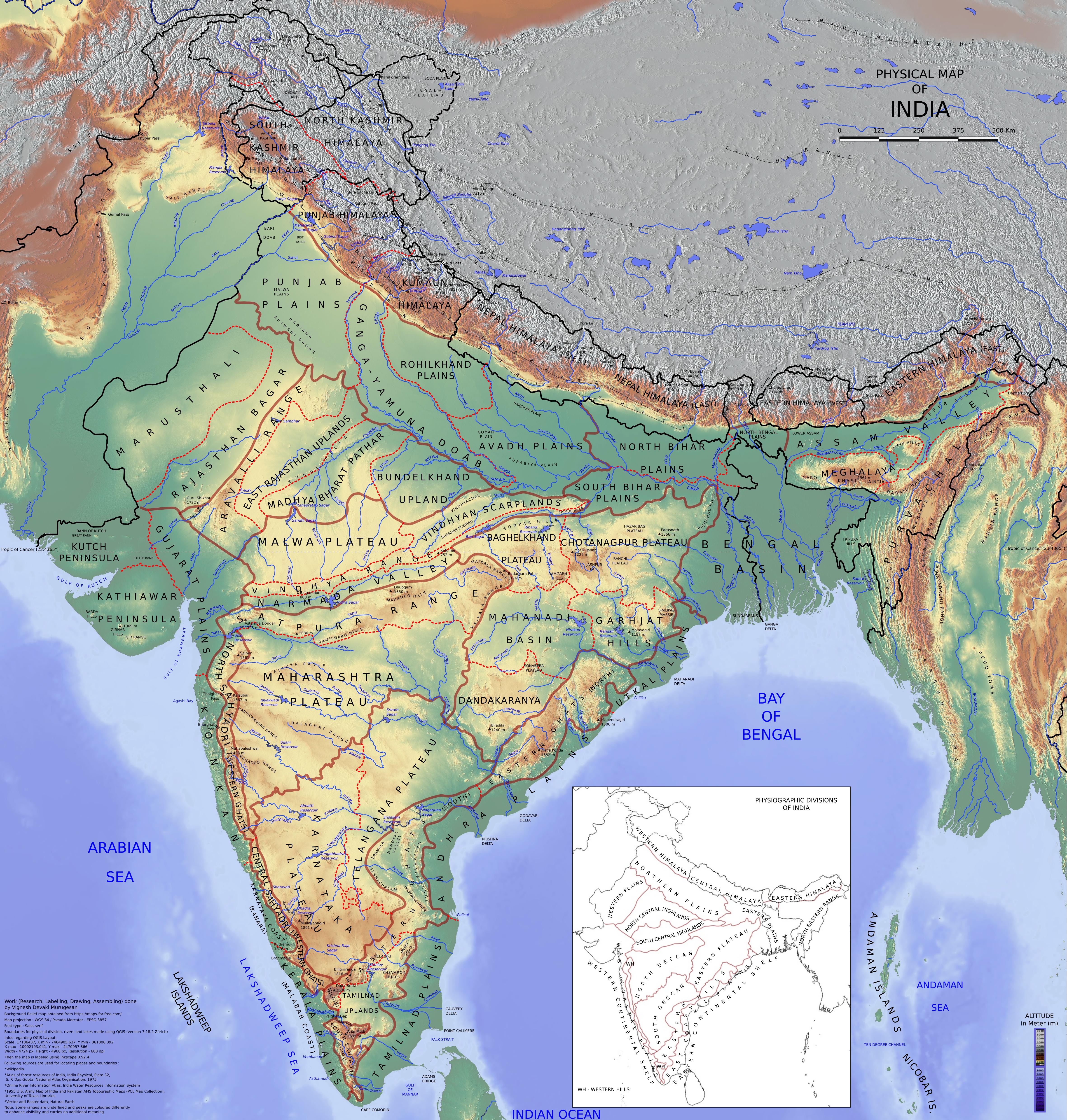
Chhotanagpur
The Chota Nagpur Plateau () is a plateau in eastern India, which covers much of Jharkhand state as well as adjacent parts of Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal and Bihar. The Indo-Gangetic plain lies to the north and east of the plateau, and the basin of the Mahanadi river lies to the south. The total area of the Chota Nagpur Plateau is approximately . Etymology The name ''Nagpur'' is probably taken from Nagavanshis, who ruled in this part of the country. ''Chhota'' (''small'' in Hindi) is the misunderstood name of "Chuita" village in the outskirts of Ranchi, which has the remains of an old fort belonging to the Nagavanshis. Sir John Houlton, ''Bihar, the Heart of India'', pp. 127–128, Orient Longmans, 1949. Geology Formation The Chota Nagpur Plateau is a continental plateau—an extensive area of land thrust above the general land.The plateau is composed of Precambrian rocks (i.e., rocks more than about 540 million years old). The plateau has been formed during th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (; ) is a landlocked States and union territories of India, state in Central India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the List of states and union territories of India by population, seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Pradesh to the northwest, Maharashtra to the southwest, Jharkhand to the northeast, Odisha to the east, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana to the south. Formerly a part of Madhya Pradesh, it was granted statehood on Chhattisgarh Rajyotsava, 1 November 2000 with Raipur as the designated state capital. The Jogimara and Sitabenga Caves, Sitabenga caves in Chhattisgarh, one of the earliest examples of theatre architecture in India, are dated to the Maurya Empire, Mauryan period of 3rd century BCE. The region was split between rivaling dynasties from the sixth to twelfth centuries, and parts of it were bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jharkhand
Jharkhand (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in East India, eastern India. The state shares its border with the states of West Bengal to the east, Chhattisgarh to the west, Uttar Pradesh to the northwest, Bihar to the north and Odisha to the south. It is the List of states and territories of India by area, 15th largest state by area, and the List of states and union territories of India by population, 14th largest by population. Hindi is the official language of the state. The city of Ranchi is its capital and Dumka its sub-capital. The state is known for its waterfalls, hills and holy places; Baidyanath Temple, Baidyanath Dham, Parasnath, Maa Dewri Temple, Dewri and Rajrappa are major religious sites. Jharkhand is primarily rural, with about 24% of its population living in cities as of 2011. Jharkhand suffers from what is sometimes termed a resource curse: it accounts for more than 40% of Mining in India, India's mineral production but 39.1% of its populati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh ( ; UP) is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the List of states and union territories of India by population, most populated state in India as well as the List of first-level administrative divisions by population, most populous country subdivision in the world – more populous than List of countries and dependencies by population, all but four other countries outside of India (China, United States, Indonesia, and Pakistan) – and accounting for 16.5 percent of the population of India or around 3 percent of the total world population. The state is bordered by Rajasthan to the west, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh and Delhi to the northwest, Uttarakhand and Nepal to the north, Bihar to the east, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand to the south. It is the List of states of India by area, fourth-largest Indian state by area covering , accounting for 7.3 percent of the total ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munda Language
The Munda languages are a group of closely related languages spoken by about eleven million people in India, Bangladesh and Nepal. Historically, they have been called the Kolarian languages. They constitute a branch of the Austroasiatic language family, which means they are more distantly related to languages such as the Mon and Khmer languages, to Vietnamese, as well as to minority languages in Thailand and Laos and the minority Mangic languages of South China. Bhumij, Ho, Mundari, and Santali are notable Munda languages. The family is generally divided into two branches: North Munda, spoken in the Chota Nagpur Plateau of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Bihar, Odisha and West Bengal, as well as in parts of Bangladesh and Nepal, and South Munda, spoken in central Odisha and along the border between Andhra Pradesh and Odisha. North Munda, of which Santali is the most widely spoken and recognised as an official language in India, has twice as many speakers as South Munda. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kodaku Language
Korwa, or Kodaku/Koraku (Korku), is a Korwa language of India spoken in Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand. Existing Korwa linguistic documentation includes Bahl (1962), which is based on the Korwa dialect of Dumertoli village, Bagicha Block, Tehsil Jashpurnagar, Raigarh District, Chhattisgarh. Varieties Korwa is a dialect continuum. The two principal varieties are Korwa (Korba) and Koraku (Kodaku), spoken by the Korwa and Kodaku respectively. Out of the Korwa, only the Hill Korwa still speak the language, the others having shifted to regional languages. The Kodaku in Jharkhand call their language "Korwa". Both speak Sadri, Kurukh, or Chhattisgarhi as a second language, or in the case of Sadri sometimes as their first language. Gregory Anderson (2008:195) lists the following locations for Korowa and Koraku. *Korowa (Korwa) is spoken in northeastern Chhattisgarh state, including southern Surguja district, Jashpur district, parts of Raigarh district, and other neighboring areas. K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sadri Language
Nagpuri (also known as Sadri) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in the Indian states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Odisha. It is primarily spoken in the west and central Chota Nagpur plateau region. It is the native language of the Sadan, the Indo-Aryan ethnic group of Chota Nagpur plateau. In addition to native speakers, it is also used as a lingua franca by many tribal groups such as the Kurukh, a Dravidian ethnic group, and the Kharia, Munda, an Austro-asiatic ethnic groups. A number of speakers from these tribal groups have adopted it as their first language. It is also used as a lingua franca among the Tea-garden community of Assam, West Bengal and Bangladesh who were taken as labourers to work in the tea gardens during the British Period. It is known as Baganiya bhasa in the tea garden area of Assam which is influenced by the Assamese language. According to the 2011 Census, it is spoken by 5.1 million people as a first language. Around 7 million speak it as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chhattisgarhi
Chhattisgarhi () is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by approximately 16.25 million people from Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra in India. It is the official language of Chhattisgarh. It is grouped within the Eastern Hindi languages and is counted by the Indian national census as a dialect of Hindi. Phonology Consonants * can also be heard as a tap . Vowels * can also be heard as back . * Nasalization is also phonemically distinctive. Sample text The following is a sample text in Chhattisgarhi, of Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, with a transliteration (IAST) and transcription ( IPA). ; Chhattisgarhi in Devanagari Script सबो लोगन मन के गौरव अऊ अधिकार मन के मामला म जनम ले मिले स्वतंत्रता अऊ बरोबरी मिले हे। ओमन ल बुद्धि अऊ अन्तरात्मा के दे ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurukh Language
Kurukh ( or ; Devanagari: कुँड़ुख़, ), also Kurux, Oraon or Uranw (Devanagari: उराँव, ), is a North Dravidian language spoken by the Kurukh (Oraon) and Kisan people of East India. It is spoken by about two million people in the Indian states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal, Assam, Bihar and Tripura, as well as by 65,000 in northern Bangladesh, 28,600 of a dialect called Uranw in Nepal and about 5,000 in Bhutan. The most closely related language to Kurukh is Malto; together with Brahui, all three languages form the North Dravidian branch of the Dravidian language family. It is marked as being in a "vulnerable" state in UNESCO's list of endangered languages. The Kisan dialect has 206,100 speakers as of 2011. Classification Kurukh belongs to the Northern Dravidian group of the Dravidian family languages, and is closely related to Sauria Paharia and Kumarbhag Paharia, which are often together referred to as Malto. Writing systems Ku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Groups In India
Ethnic groups in South Asia are ethnolinguistic groupings within the diverse populations of South Asia, including the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. Afghanistan is variously considered to be a part of both Central Asia and South Asia, which means Afghans are not always included among South Asians, but when they are, South Asia has a total population of about 2.04 billion. The majority of the population fall within three large linguistic groups: Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, and Iranic. These groups are also further subdivided into numerous sub-groups, castes and tribes. Indo-Aryans form the predominant ethnolinguistic group in India (North India, East India, West India, and Central India), Bangladesh, Pakistan, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and the Maldives. Dravidians form the predominant ethnolinguistic group in southern India, the northern and eastern regions of Sri Lanka and a small pocket of Pakistan. The Iranic peoples also have a signif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scheduled Tribes Of India
A schedule (, ) or a timetable, as a basic time-management tool, consists of a list of times at which possible tasks, events, or actions are intended to take place, or of a sequence of events in the chronological order in which such things are intended to take place. The process of creating a schedule — deciding how to order these tasks and how to commit resources between the variety of possible tasks — is called scheduling,Ofer Zwikael, John Smyrk, ''Project Management for the Creation of Organisational Value'' (2011), p. 196: "The process is called scheduling, the output from which is a timetable of some form". and a person responsible for making a particular schedule may be called a scheduler. Making and following schedules is an ancient human activity. Some scenarios associate this kind of planning with learning life skills. Schedules are necessary, or at least useful, in situations where individuals need to know what time they must be at a specific location to rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |