|
Koch Languages
The Koch languages are a small group of Boro-Garo languages a sub-branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages spoken in Northeast India. Burling (2012) calls this the "Rabha group". They are: * Atong *Koch *Ruga *Rabha The Rajbongshi, who currently speak an Indo-Aryan language The Indo-Aryan languages (or sometimes Indic languages) are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of the early 21st century, they have more than 800 million speakers, primarily concentrated in India, Pa ..., used to speak a Koch language. Footnotes References * George van Driem (2001) ''Languages of the Himalayas: An Ethnolinguistic Handbook of the Greater Himalayan Region.'' Brill. Sal languages Languages of India {{st-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sal Languages
The Sal languages are a branch of Sino-Tibetan languages spoken in northeast India, parts of Bangladesh, and Burma. Alternative names '' Ethnologue'' calls the group "Jingpho–Konyak–Bodo", while Scott DeLancey (2015) refers to it as "Bodo-Konyak-Jinghpaw" (BKJ). Glottolog lists this branch as �Brahmaputran (brah1260)��. Classification within Sino-Tibetan Scott DeLancey (2015)DeLancey, Scott. 2015. "Morphological Evidence for a Central Branch of Trans-Himalayan (Sino-Tibetan)." ''Cahiers de linguistique - Asie oriental'' 44(2):122-149. December 2015. considers the Sal languages, which he refers to as ''Bodo-Konyak-Jinghpaw'' (BKJ), to be part of a wider Central Tibeto-Burman group. Internal classification noted that the Bodo–Garo, Konyak, and Jingpho (Kachin) languages, as well as the extinct Chairel language, shared distinctive roots for "sun" and "fire". proposed a grouping of the Bodo–Garo, Konyak (Northern Naga), and Jingpho languages, characterized by seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
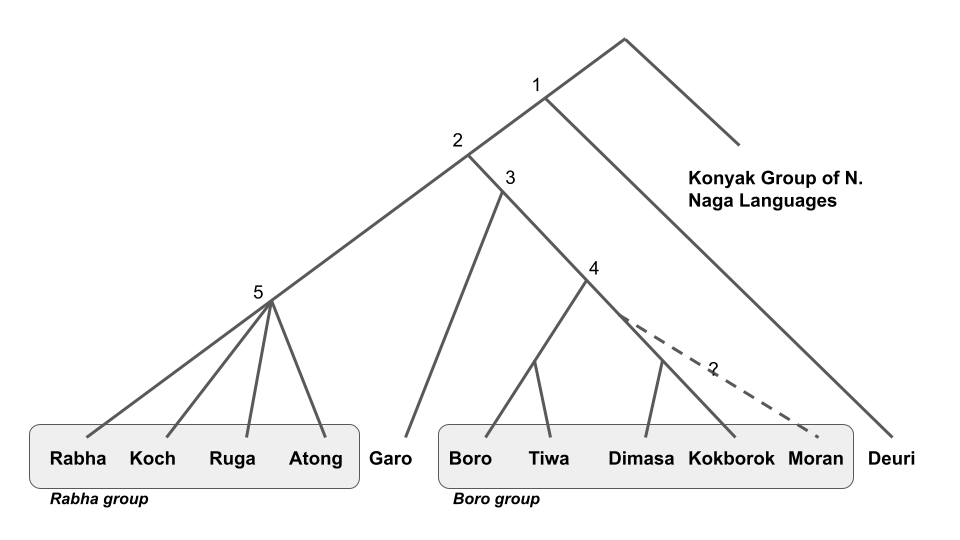
Boro–Garo Languages
The Boro–Garo languages are a branch of Sino-Tibetan languages, spoken primarily in Northeast India and parts of Bangladesh. The Boro–Garo languages form four groups: Boro, Garo, Koch and Deori. Boro–Garo languages were historically very widespread throughout the Brahmaputra Valley and in what are now the northern parts of Bangladesh, and it is speculated that the proto-Boro-Garo language was the lingua franca of the Brahmaputra valley before it was replaced by Assamese language, to which it has made major contributions. Branches The Boro-Garo languages were identified in the Grierson's Language Survey of India, and the names of the languages and their modern equivalents are given below in the table. Sub groups The Boro-Garo languages have been further divided into four subgroups by Burling. *Koch languages: Atong, Koch, Ruga, Rabha * Garo languages: Garo, Megam *Bodo languages: Bodo, Dimasa, Barman, Tiwa, Kokborok (Tripuri), Kachari, Moran * Deori language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sino-Tibetan Languages
Sino-Tibetan, also cited as Trans-Himalayan in a few sources, is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Chinese languages. Other Sino-Tibetan languages with large numbers of speakers include Burmese (33 million) and the Tibetic languages (6 million). Other languages of the family are spoken in the Himalayas, the Southeast Asian Massif, and the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Most of these have small speech communities in remote mountain areas, and as such are poorly documented. Several low-level subgroups have been securely reconstructed, but reconstruction of a proto-language for the family as a whole is still at an early stage, so the higher-level structure of Sino-Tibetan remains unclear. Although the family is traditionally presented as divided into Sinitic (i.e. Chinese) and Tibeto-Burman branches, a common origin of the non-Sinitic languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast India
, native_name_lang = mni , settlement_type = , image_skyline = , image_alt = , image_caption = , motto = , image_map = Northeast india.png , map_alt = Northeast india map.png , coordinates = , coordinates_footnotes = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = States , subdivision_name1 = , subdivision_type2 = Largest city , subdivision_name2 = Guwahati , subdivision_type3 = Major cities ( 2011 Census of India) , subdivision_name3 = [Baidu] |
Atong Language (Sino-Tibetan)
A.tong is one of the Garo dialect Sino-Tibetan (or Tibeto-Burman) language which is also related to Koch, Rabha, Bodo other than Garo language. It is spoken in the South Garo Hills and West Khasi Hills districts of Meghalaya state in Northeast India, southern Kamrup district in Assam, and adjacent areas in Bangladesh. The correct spelling "A.tong" is based on the way the speakers themselves pronounce the name of their language. There is no glottal stop in the name and it is not a tonal language. A reference grammar of the language has been published by Seino van Breugel.van Breugel, Seino. 2014. ''A grammar of Atong''. Leiden, Boston: Brill/ref> A dictionary with Atong–English and English-A.tong sections, as well as semantic word listsvan Breugel, Seino. 2021. ''A dictionary of Atong: A Tibeto-Burman language of Northeast India and Bangladesh''. Berlin, Boston: de Gruyter Mouton. was published in 2021, two years after the publication of an analysis of A.tong stories.van ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koch Language
Koch is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Koch people of Republic of India and Koch people in Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh. Geographical distribution Koch is spoken in: *Assam: **Baksa district - Hodi or Koch Mandai **Darrang district - Hodi or Koch Mandai **Dhemaji district - Hodi or Koch Mandai **Goalpara district - Madaci koch, kocha Rabha, Kocho koro, Hodi or Koch Mandai **Lakhimpur district - Hodi or Koch Mandai **Nagaon district - Hodi or Koch Mandai, Kocho koro ** Udalguri district - Hodi or Koch Mandai **Sonitpur district - Hodi or Koch Mandai *Bangladesh: Hodi or Koch Mandai and Kocho koro *Bihar: Rajbongshi koch *Meghalaya: **East Khasi hills - Hodi alias Koch Mandai **West Garo Hills district - Kocha rabha or Koch *Tripura: Hodi or Koch Mandai or koch *West Bengal West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruga Language
Ruga is a Garo dialect, an Sino-Tibetan language that spoken in the East Garo Hills district and West Garo Hills, Meghalaya, India. Today, people who identify themselves as Ruga have shifted to Garo Garo may refer to: People and languages * Garo people, a tribal people in India ** Garo language, the language spoken by the Garo tribe Places * Kingdom of Garo, a former kingdom in southern Ethiopia * Garo, Colorado * Garo Hills, part of the ... and only a few elderly native Ruga speakers remain. References Sal languages Extinct languages of Asia Languages of India Languages extinct in the 21st century {{st-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabha Language
Rabha is a Sino-Tibetan language of India. The two dialects, Maituri and Rongdani, are divergent enough to cause problems in communication. According to U.V. Joseph, there are three dialects, viz. Róngdani or Róngdania, Mayturi or Mayturia and Songga or Kocha (page ix). Joseph writes that "the Kocha dialect, spoken along the northern bank of the Brahmaputra, is highly divergent and is not intelligible to a Róngdani or Mayturi speaker" (page ix). Joseph also writes that " e dialect variations between Róngdani and Mayturi, both of which are spoken on the southern bank of the Brahmaputra, in the Goalpara district of Assam and belong to the northern slopes of Meghalaya, are minimal" (pages ix-x). He concludes the paragraph on dialectal variation with: "The Róngdani-Mayturi dialectal differences become gradually more marked as one moves further west" (page x). In 2007, U.V. Joseph published a grammar of Rabha with Brill in their series Languages of the Greater Himalayan Region.Jos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajbongshi People
The Rajbanshi, also Rajbongshi and Koch-Rajbongshi, are peoples from Lower Assam, North Bengal, eastern Bihar, Terai region of eastern Nepal, and Bhutan who have in the past sought an association with the Koch dynasty. Today, they speak various Indo-Aryan languages, though in the past they might have spoken Tibeto-Burman languages. In 2020, Kamatapur Autonomous Council has been created for socio-economic development and political rights of Koch-Rajbongshi community. They are related to the ethnic Koch people found in Meghalaya but are distinguished from them as well as from the Hindu caste called Koch in Upper Assam that receives converts from different tribes. Rajbanshi (''of royal lineage'') alludes to the community's claimed connection with the Koch dynasty. Etymology The Rajbanshi (literal meaning: ''of the royal lineage'') community gave itself this name after 1891 following a movement to distance itself from an ethnic identity and acquire the higher social status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Aryan Languages
The Indo-Aryan languages (or sometimes Indic languages) are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of the early 21st century, they have more than 800 million speakers, primarily concentrated in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Maldives. Moreover, apart from the Indian subcontinent, large immigrant and expatriate Indo-Aryan–speaking communities live in Northwestern Europe, Western Asia, North America, the Caribbean, Southeast Africa, Polynesia and Australia, along with several million speakers of Romani languages primarily concentrated in Southeastern Europe. There are over 200 known Indo-Aryan languages. Modern Indo-Aryan languages descend from Old Indo-Aryan languages such as early Vedic Sanskrit, through Middle Indo-Aryan languages (or Prakrits). The largest such languages in terms of first-speakers are Hindi–Urdu (),Standard Hindi first language: 260.3 million (2001), as second language: 120 million (199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |