|
Klonimir Strojimirović
Klonimir ( sr-cyr, Клонимир, , fl. 896) was a Serbs, Serbian prince of the Vlastimirović dynasty, and List of Serbian monarchs, pretender to the throne of the Principality of Serbia (early medieval), Serbian Principality. His father and uncle, co-princes Strojimir and Gojnik, had been exiled to Bulgaria with their families after their eldest brother Mutimir had ousted them and taken the Serbian throne. Klonimir married a Bulgarian noblewoman chosen by Khan Boris I himself. She later gave birth to a son named Časlav. The descendants of the three Vlastimirović branches continued the feud over the Serbian throne which spanned over the century, and Klonimir returned to Serbia in ca. 896 and attempted to take the country from his cousin Petar, who had ruled since 891. He managed to take over the Serbian city of Destinikon, but the much more powerful Petar defeated him, and it is presumed that Klonimir died in battle. His son Časlav later became the most powerful of the Vlast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petar Of Serbia
Petar Gojniković or Peter of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Петар Гојниковић, ; ca. 870 – 917) was List of Serbian monarchs, Prince of the Serbs from 892 to 917. He ruled and expanded the Principality of Serbia (early medieval), First Serbian Principality and won several wars against other family members that sought the crown. He was the first Serbian monarch with a Christian (non-Slavic) name. Petar was the son of Gojnik, the youngest son of Vlastimir (r. 831–851) of House of Vlastimirović, the first Serbian dynasty (ruling since the early 7th century). Early life Petar was born between 870 and 874, as the son of Prince Gojnik, the youngest son of dynastic founding father Vlastimir of Serbia, Vlastimir. His Byzantine Christian name, in relation to the previous generation of pagan names, shows the spread of Christianization among the Serbs.''The entry of the Slavs into Christendom''p. 209/ref> At the time of his birth, Serbia was ruled as an oligarchy consisting o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boyar
A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Bulgaria, Kievan Rus' (and later Russia), Moldavia and Wallachia (and later Romania), Lithuania and among Baltic Germans. Comparable to Dukes/Grand Dukes, Boyars were second only to the ruling princes, grand princes or tsars from the 10th to the 17th centuries. Etymology Also known as ''bolyar''; variants in other languages include or ; , , ; , ; and . The title Boila is predecessor or old form of the title Bolyar (the Bulgarian word for Boyar). Boila was a title worn by some of the Bulgar aristocrats (mostly of regional governors and noble warriors) in the First Bulgarian Empire (681–1018). The plural form of boila ("noble"), ''bolyare'' is attested in Bulgar inscriptions and rendered as ''boilades'' or ''boliades'' in the Greek of Byzantine documents. Multiple different derivation theories of the word have been suggested by scholars and linguists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seal Of Strojimir
Seal may refer to any of the following: Common uses * Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly: ** Earless seal, also called "true seal" ** Fur seal ** Eared seal * Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of authentication, on paper, wax, clay or another medium (the impression is also called a seal) * Seal (mechanical), a device which helps prevent leakage, contain pressure, or exclude contamination where two systems join ** Hermetic seal, an airtight mechanical seal * Security seals such as labels, tapes, bands, or ties affixed onto a container in order to prevent and detect tampering Arts, entertainment and media * ''Seal'' (1991 album), by Seal * ''Seal'' (1994 album), sometimes referred to as ''Seal II'', by Seal * '' Seal IV'', a 2003 album by Seal * ''Seal Online'', a 2003 massively multiplayer online role-playing game Law * Seal (contract law), a legal formality for contracts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
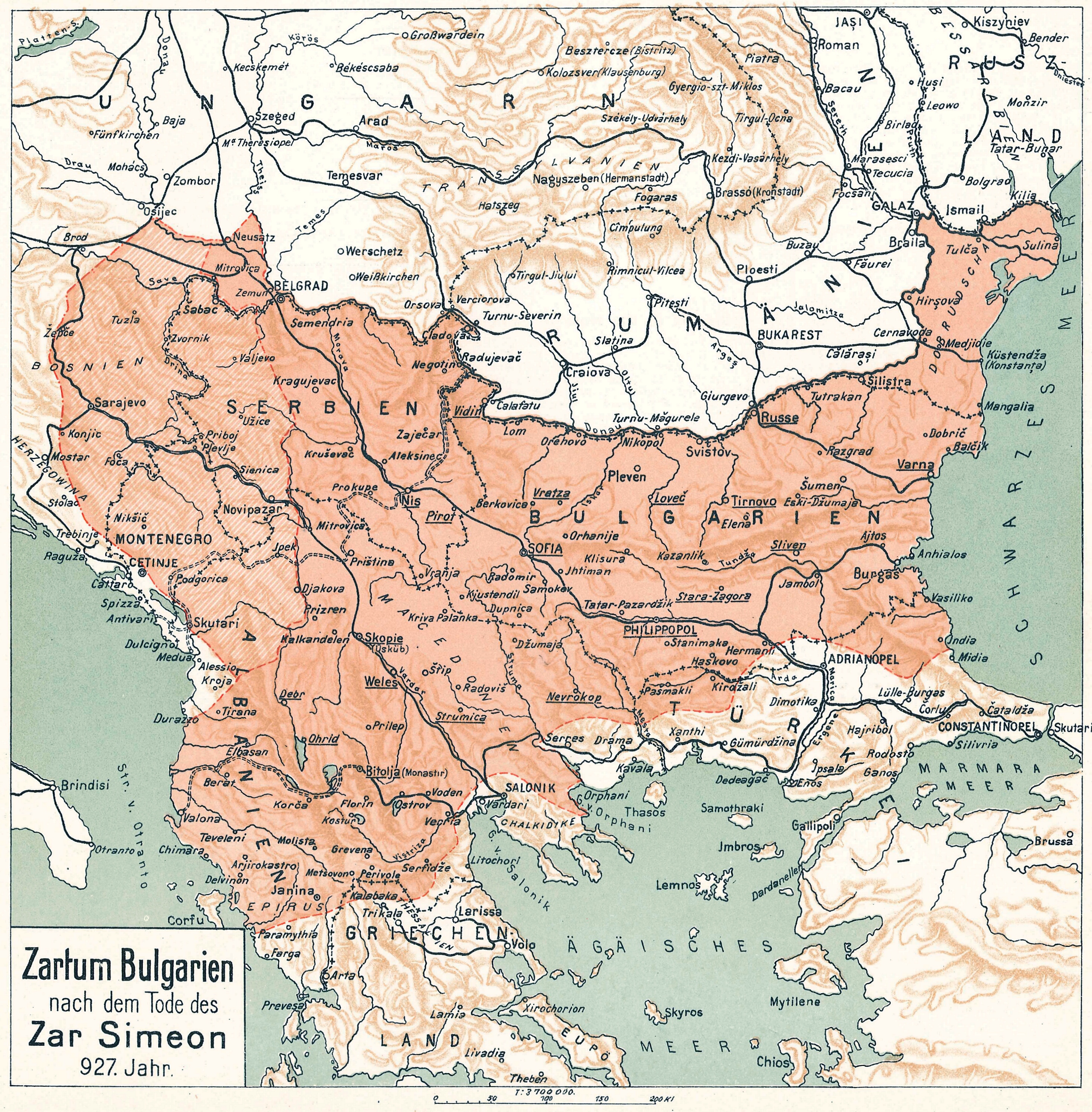
Symeon I Of Bulgaria
Simeon I the Great (; ; ) ruled over Bulgaria from 893 to 927,Lalkov, ''Rulers of Bulgaria'', pp. 23–25. during the First Bulgarian Empire. Simeon's successful campaigns against the Byzantines, Magyars and Serbs led Bulgaria to its greatest territorial expansion ever, making it the most powerful state in contemporary Eastern and Southeast Europe. His reign was also a period of unmatched cultural prosperity and enlightenment later deemed the Golden Age of Bulgarian culture. During Simeon's rule, Bulgaria spread over a territory between the Aegean, the Adriatic and the Black seas.Bakalov, ''Istorija na Bǎlgarija'', "Simeon I Veliki". The newly independent Bulgarian Orthodox Church became the first new patriarchate besides the Pentarchy, and Bulgarian Glagolitic and Cyrillic translations of Christian texts spread all over the Slavic world of the time. It was at the Preslav Literary School in the 890s that the Cyrillic alphabet was developed. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomorje
Pomorje ( sr-Cyrl, Поморје), also known (in plural) as the Lands of Pomorje (), is a medieval term, used in Byzantine title, and at end of the 12th century, during the reign of Stefan Nemanja (1166–1196), inherited by Serbian monarchs, thus becoming part of the Serbian title, whose rulers were styled with the title: "''crowned king and autocrat of all Serbian and coastal lands''". Use in royal titles The term was used in royal and religious titles both by Bosnian and Serbian monarchs and their heirs (Uroš I, styled himself "King in Christ, God faithful, King of Serbia and Maritime Lands", and Patriarchs ( Saint Sava III, "Archbishop of All Serbian and Maritime Lands"). * Desa, styled himself "Prince of Pomorje (Maritime Lands)" * Vladislav, styled himself "King of all the Serbian and Maritime Lands" * Uroš I, styled himself "King in Christ, God faithful, King of Serbia and Maritime Lands" * Uroš IV Dušan, "King of all the Serbian and Maritime Lands" * 1329 Steph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Mutilation In Byzantine Culture
Mutilation was a common method of punishment for criminals in the Byzantine Empire, but it also had a role in the empire's political life. By blinding a rival, one would not only restrict his mobility but also make it almost impossible for him to lead an army into battle, then an important part of taking control of the empire. Castration was also used to eliminate potential opponents. In the Byzantine Empire, for a man to be castrated meant that he was no longer a man—half-dead, "life that was half death". Castration also eliminated any chance of heirs being born to threaten either the emperor's or the emperor's children's place at the throne. Other mutilations were the severing of the nose ( rhinotomy), or the amputating of limbs. Rationale The mutilation of political rivals by the emperor was deemed an effective way of side-lining from the line of succession a person who was seen as a threat. Castrated men were not seen as a threat, as no matter how much power they gained t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stefan Mutimirović
Stefan Mutimirović (, ) was a 9th-century Serbian royal member of the ruling dynasty, the Vlastimirović. He was the younger son of Mutimir of the ruling Serbian dynasty, the Vlastimirovići. His father had with his brothers Strojimir and Gojnik, defeated the Bulgar Army sent by Tsar Boris, led by his son Vladimir. They were captured with 12 boyar A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Bulgaria, Kievan Rus' (and later Russia), Moldavia and Wallachia (and later Romania), Lithuania and among Baltic Germans. C ...s, but were soon freed in exchange for good relations between the peoples. Peace was agreed upon and Stefan and his older brother, Pribislav, escorted the prisoners towards the border at Ras. There, Boris gave them rich gifts and received 2 slaves, 2 falcons, two dogs, and 80 furs from Mutimir. References Sources * * * *Ferjančić, B. 1997, "Basile I et la restauration du pou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bran Mutimirović
Bran Mutimirović () was a Serbian prince, son of Serbian ruler Mutimir. He and Stefan escorted Khan Boris I of Bulgaria to the Serbian-Bulgarian border at Ras after the Serbs successfully fought off the Khan's army in an attempted revenge to the defeat of Presian years earlier by their grandfather Vlastimir. Bran and Stefan were given presents for the escort, and in turn gifted 2 slaves, 2 falcons, 2 dogs, and 80 furs as a symbol of friendship, the Bulgars were pleased with the tribute. After the death of his father Mutimir, his elder brother Pribislav took the Serbian crown, but was deposed after a year by their cousin Petar Gojniković Petar Gojniković or Peter of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Петар Гојниковић, ; ca. 870 – 917) was Prince of the Serbs from 892 to 917. He ruled and expanded the First Serbian Principality and won several wars against other family mem ... and fled with Bran and Stefan to Croatia. Three years after the accession of Petar, Bran r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pribislav Of Serbia
Pribislav (, ) was Prince of the Serbs for a year, in 891–892, before being deposed by his cousin Petar. He was the eldest son of Mutimir (r. 851–891) of the Vlastimirović dynasty, who ruled during the expanding and Christianization of Serbia. Life His father had with his brothers Strojimir and Gojnik, defeated the Bulgar Army sent by ''Tsar'' Boris I of Bulgaria and led by his son Vladimir.''The early medieval Balkans''p. 141/ref> Vladimir was captured together with 12 boyars. Boris I and Mutimir agreed on peace (and perhaps an alliance), and Mutimir sent his sons Bran and Stefan beyond the border to escort the prisoners, where they exchanged items as a sign of peace: Boris himself gave them "rich gifts", while he was given "two slaves, two falcons, two dogs, and eighty furs". In the 880s, Mutimir seized the throne, exiling his younger brothers and Klonimir, Strojimir's son, to the court of Boris I in the Bulgar Khanate. This was most likely due to treachery.Đe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petar Gojniković
Petar Gojniković or Peter of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Петар Гојниковић, ; ca. 870 – 917) was Prince of the Serbs from 892 to 917. He ruled and expanded the First Serbian Principality and won several wars against other family members that sought the crown. He was the first Serbian monarch with a Christian (non-Slavic) name. Petar was the son of Gojnik, the youngest son of Vlastimir (r. 831–851) of the first Serbian dynasty (ruling since the early 7th century). Early life Petar was born between 870 and 874, as the son of Prince Gojnik, the youngest son of dynastic founding father Vlastimir. His Byzantine Christian name, in relation to the previous generation of pagan names, shows the spread of Christianization among the Serbs.''The entry of the Slavs into Christendom''p. 209/ref> At the time of his birth, Serbia was ruled as an oligarchy consisting of the three brothers Mutimir, Gojnik and Strojimir, although Mutimir, the oldest, had supreme rule.Đeki� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliska
Pliska ( , ) was the first capital of the First Bulgarian Empire during the Middle Ages and is now List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, a small town in Shumen Province, on the Ludogorie plateau of the Danubian Plain (Bulgaria), Danubian Plain, 20 km northeast of the provincial capital, Shumen. Pliska was the first capital of Bulgaria. According to legend, it was founded by Asparuh of Bulgaria in the late 7th century; this legend is archaeologically unsubstantiated. The site was originally an encampment, with the first tent-shaped buildings at Pliska of uncertain date. No evidence exists of a settlement before the 9th century, and claims that the site dates from Late Antiquity have been contested. By the early 9th century, Pliska was surrounded by a defensive wall and of land was further enclosed by an outer earthwork with stone revetment long. After the Byzantine army sacked and burned Pliska in 811, led by the emperor Nikephoros I (), Pliska was rebuilt by Omurtag of Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Leader
A supreme leader or supreme ruler typically refers to powerful figures with an unchallenged authority, such as autocrats, dictators to spiritual and revolutionary leaders. Historic examples are Adolf Hitler () of Nazi Germany, Francisco Franco () of Francoist Spain, Benito Mussolini () of Fascist Italy and Joseph Stalin, the leader of the Soviet Union. List of titles Listed by date of establishment. Interwar period * Alexander Kolchak, White leader in the Russian Civil War as " Supreme Ruler of Russia". * Benito Mussolini, dictator of Italy from 1922 to 1943 and of Italian Social Republic from 1943 to 1945, was known as ''Duce'' ("leader"). * Antanas Smetona, the authoritarian president of Lithuania (1926–1940), adopted the title of ''Tautos Vadas'' ("Leader of the Nation"). * Hirohito, emperor of Imperial Japan under the Meiji Constitution from 1926 to 1947, sometimes known as ("August Gate"). * Chiang Kai-shek, ''de facto'' leader of the Kuomintang Republic of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |