|
Kithãulhu Language
Nambikwara (also called ''Nambiquara'' and ''Southern Nambiquara'', to distinguish it from '' Mamaindê'') is an indigenous language spoken by the Nambikwara, who reside on federal reserves covering approximately 50,000 square kilometres of land in Mato Grosso and neighbouring parts of Rondônia in Brazil. Due to the fact that the Nambikwara language has such a high proportion of speakers (and, one can infer, a high rate of transmission), and the fact that the community has a positive attitude towards the language, it is not considered to be endangered despite the fact that its speakers constitute a small minority of the Brazilian population. For these reasons, UNESCO instead classifies Nambikwara as vulnerable. History According to David Price (1983), a reference to the Nambikwara people was made as early as 1671 in a report by Padre Gonçalo de Veras. However, in another account from the ''Povos Indígenas do Brasil'', the Nambikwara people are said to have been first contacted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mato Grosso
Mato Grosso ( – ) is one of the states of Brazil, the List of Brazilian states by area, third largest by area, located in the Central-West Region, Brazil, Central-West region. The state has 1.66% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 1.9% of the Brazilian GDP. Neighboring states (from west clockwise) are: Rondônia, Amazonas State, Brazil, Amazonas, Pará, Tocantins, Goiás and Mato Grosso do Sul. It is divided into 142 municipalities and covers an area of 903,357 square kilometers, consequently the state is roughly 82.2% of the size of its southwest neighbor, the nation of Bolivia. A state with a flat landscape that alternates between vast ''chapadas'' and plain areas, Mato Grosso contains three main ecosystems: the Cerrado, the Pantanal and the Amazon rainforest. The Chapada dos Guimarães National Park, with its caves, grottoes, tracks, and waterfalls, is one of its tourist attractions. The extreme northwest of the state has a small part of the Amazonian fores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vilhena
Vilhena () is the easternmost municipality in the Brazilian state of Rondônia. Its population was 102,211 (IBGE-2020) and its area is 11,519 km2. – IBGE It is the fifth-largest city in Rondônia and has the best HDI in the state (0,771 – UNDP/2000). According to IBGE-2015, Vilhena also had a GDP of R$1.824.367,69(approximately US$460 million), which represented a GDP per capita of R$23.055,20 (around US$6.000,00) History In common with many other municipalities of Rondônia, Vilhena was started in the early twentieth century, around 1910, when Cândido Mariano da Silva Rondon built telegraph posts in the fields of the Plateau Parecis, linking several cities between Cuiabá and Porto Velho. Towns often would rise around these posts, Vilhena included. Population growth Migration from southern and southeastern regions caused the population to increase in 1959 after the construction of highway BR-364, which connects the north with the rest of the country and was paved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Tense
In grammar, tense is a grammatical category, category that expresses time reference. Tenses are usually manifested by the use of specific forms of verbs, particularly in their grammatical conjugation, conjugation patterns. The main tenses found in many languages include the past tense, past, present tense, present, and future tense, future. Some languages have only two distinct tenses, such as past and nonpast, or future and Nonfuture tense, nonfuture. There are also tenseless languages, like most of the Varieties of Chinese, Chinese languages, though they can possess a future and Nonfuture tense, nonfuture system typical of Sino-Tibetan languages. In recent work Maria Bittner and Judith Tonhauser have described the different ways in which tenseless languages nonetheless mark time. On the other hand, some languages make finer tense distinctions, such as remote vs recent past, or near vs remote future. Tenses generally express time relative to the TUTT (linguistics), moment of spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how languages employ different orders. Correlations between orders found in different syntactic sub-domains are also of interest. The primary word orders that are of interest are * the ''constituent order'' of a clause, namely the relative order of subject, object, and verb; * the order of modifiers (adjectives, numerals, demonstratives, possessives, and adjuncts) in a noun phrase; * the order of adverbials. Some languages use relatively fixed word order, often relying on the order of constituents to convey grammatical information. Other languages—often those that convey grammatical information through inflection—allow more flexible word order, which can be used to encode pragmatic information, such as topicalisation or focus. However, even languages with flexible word order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
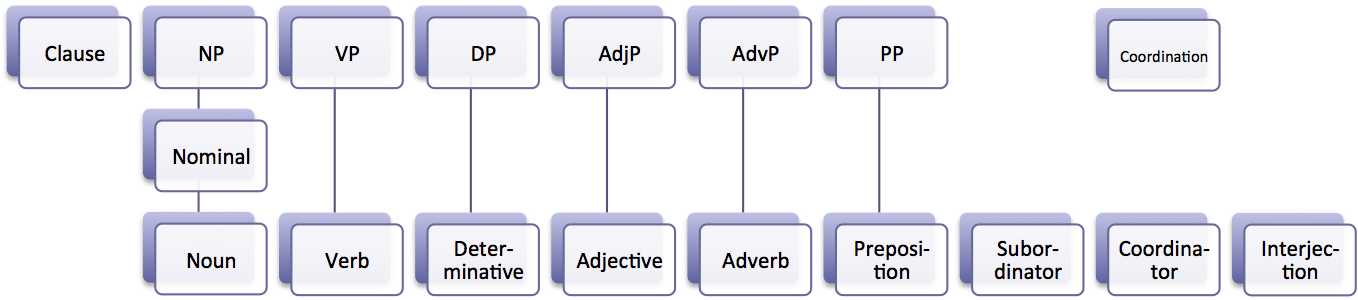
Parts Of Speech
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech (abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner. Other terms than ''part of speech''—particularly in modern linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional scheme does—include word class, lexical class, and lexical category. Some authors restrict the term ''lexical category'' to refer only to a particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantics
Semantics is the study of linguistic Meaning (philosophy), meaning. It examines what meaning is, how words get their meaning, and how the meaning of a complex expression depends on its parts. Part of this process involves the distinction between sense and reference. Sense is given by the ideas and concepts associated with an expression while reference is the object to which an expression points. Semantics contrasts with syntax, which studies the rules that dictate how to create grammatically correct sentences, and pragmatics, which investigates how people use language in communication. Lexical semantics is the branch of semantics that studies word meaning. It examines whether words have one or several meanings and in what lexical relations they stand to one another. Phrasal semantics studies the meaning of sentences by exploring the phenomenon of compositionality or how new meanings can be created by arranging words. Formal semantics (natural language), Formal semantics relies o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax ( ) is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). Diverse approaches, such as generative grammar and functional grammar, offer unique perspectives on syntax, reflecting its complexity and centrality to understanding human language. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from the ancient Greek word , meaning an orderly or systematic arrangement, which consists of (''syn-'', "together" or "alike"), and (''táxis'', "arrangement"). In Hellenistic Greek, this also specifically developed a use referring to the grammatical order of words, with a slightly altered spelling: . The English term, which first appeared in 1548, is partly borrowed from Latin () and Greek, though the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphophonology
Morphophonology (also morphophonemics or morphonology) is the branch of linguistics that studies the interaction between morphological and phonological or phonetic processes. Its chief focus is the sound changes that take place in morphemes (minimal meaningful units) when they combine to form words. The origins of morphophonology trace back to the early 20th century with foundational works in structural linguistics. Notable contributions include Roman Jakobson's insights into phonological alternations and Chomsky and Halle's ''The Sound Pattern of English'' (1968), which formalized the relationship between phonology and morphology within generative grammar. Subsequent theories, such as Autosegmental Phonology and Optimality Theory, have refined the analysis of morphophonological patterns Morphophonological analysis often involves an attempt to give a series of formal rules or constraints that successfully predict the regular sound changes occurring in the morphemes of a given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonology
Phonology (formerly also phonemics or phonematics: "phonemics ''n.'' [''obsolescent''] 1. Any procedure for identifying the phonemes of a language from a corpus of data. 2. (formerly also phonematics) A former synonym for phonology, often preferred by the American Structuralists and reflecting the importance in structuralist work of phonemics in sense 1.": "phonematics ''n.'' 1. [''obsolete''] An old synonym for phonemics (sense 2).") is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages systematically organize their phonemes or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a particular language variety. At one time, the study of phonology related only to the study of the systems of phonemes in spoken languages, but now it may relate to any Linguistic description, linguistic analysis either: Sign languages have a phonological system equivalent to the system of sounds in spoken languages. The buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Intelligibility
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between different but related language varieties in which speakers of the different varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. Mutual intelligibility is sometimes used to distinguish languages from dialects, although sociolinguistic factors are often also used. Intelligibility between varieties can be asymmetric; that is, speakers of one variety may be able to better understand another than vice versa. An example of this is the case between Afrikaans and Dutch. It is generally easier for Dutch speakers to understand Afrikaans than for Afrikaans speakers to understand Dutch. In a dialect continuum, neighbouring varieties are mutually intelligible, but differences mount with distance, so that more widely separated varieties may not be mutually intelligible. Intelligibility can be partial, as is the case with Azerbaijani and Turkish, or significant, as is the case with Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarare
Sarare is a town in the Venezuelan state of Lara. It is the seat of the Simón Planas Municipality. The town and surroundings have about 12535 inhabitants. It is located on the shores of the Sarare River, which flows into the Orinoco The Orinoco () is one of the longest rivers in South America at . Its drainage basin, sometimes known as the Orinoquia, covers approximately 1 million km2, with 65% of it in Venezuela and 35% in Colombia. It is the List of rivers by discharge, f .... History {{Unreferenced section, date=January 2023 Fray Pedro de Alcalá founded the town in 1716 as Indian missionary town. The first inhabitants were 73 families from the Atures tribe. There were also Indians from the Cherrecheres, Guamonteyes, Guamos, Colorados, Achaguas, Guáricos, Gayones and Otomaco and Taparita groups. A year after the foundation most settlers died from an epidemic. Fray Diego de Urbique founded Sarare in 1754 as the Mission of Saint Nicolas of Sarare. References Ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guaporé River
Guaporé River (, ) is a river in western Brazil and northeastern Bolivia. It is long; of the river forms the border between Brazil and Bolivia. The Guaporé is part of the Madeira River basin, which eventually empties into the Amazon River. The Guaporé crosses the eastern part of the Beni savanna region. It forms the border of the Guaporé Biological Reserve, and is fed by rivers originating in the reserve, the São Miguel, Branco, São Simão, Massaco and Colorado. About 260 fish species are known from the Guaporé River basin, and about 25 of these are endemic.Hales, J., and P. Petry (2013). Guapore - Itenez'. Freshwater Ecoregions of the World. Retrieved 28 February 2013 While many fish species in the river essentially are Amazonian, the fauna in the Guaporé also has a connection with the Paraguay River (part of the Río de la Plata Basin The Río de la Plata basin (, ), more often called the River Plate basin in scholarly writings, sometimes called the Platine basi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |