|
Kinship Terminology
Kinship terminology is the system used in languages to refer to the persons to whom an individual is related through kinship. Different societies classify kinship relations differently and therefore use different systems of kinship terminology; for example, some languages distinguish between consanguine and Affinal kin, affinal uncles (i.e. the brothers of one's parents and the husbands of the sisters of one's parents, respectively), whereas others have only one word to refer to both a father and his brothers. Kinship terminologies include the terms of address used in different languages or communities for different relatives and the terms of reference used to identify the relationship of these relatives to ego or to each other. Historical view Anthropologist Lewis H. Morgan, Lewis Henry Morgan (1818–1881) performed the first survey of kinship terminologies in use around the world. Though much of his work is now considered dated, he argued that kinship terminologies reflect di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing system, writing. Human language is characterized by its cultural and historical diversity, with significant variations observed between cultures and across time. Human languages possess the properties of Productivity (linguistics), productivity and Displacement (linguistics), displacement, which enable the creation of an infinite number of sentences, and the ability to refer to objects, events, and ideas that are not immediately present in the discourse. The use of human language relies on social convention and is acquired through learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crow Kinship
Crow kinship is a kinship system used to define family. Identified by Lewis Henry Morgan in his 1871 work '' Systems of Consanguinity and Affinity of the Human Family'', the Crow system is one of the six major kinship systems (Eskimo, Hawaiian, Iroquois, Crow, Omaha, and Sudanese). Kinship system The system is somewhat similar to the Iroquois system, but distinguishes between the mother's side and the father's side. Relatives on the mother's side of the family have more descriptive terms, and relatives on the father's side have more classificatory terms. The Crow system is distinctive because unlike most other kinship systems, it chooses not to distinguish between certain generations. The relatives of the subject's father's matrilineage are distinguished only by their sex, regardless of their age or generation. In contrast, within Ego's own matrilineage, differences of generation are noted. The system is associated with groups that have a strong tradition of matrilineal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Language
Tamil (, , , also written as ''Tamizhil'' according to linguistic pronunciation) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. It is one of the longest-surviving classical languages in the world,. "Tamil is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India" (p. 7). attested since 300 BC, 300 BCE.: "...the most acceptable periodisation which has so far been suggested for the development of Tamil writing seems to me to be that of A Chidambaranatha Chettiar (1907–1967): 1. Sangam Literature – 200BC to AD 200; 2. Post Sangam literature – AD 200 – AD 600; 3. Early Medieval literature – AD 600 to AD 1200; 4. Later Medieval literature – AD 1200 to AD 1800; 5. Pre-Modern literature – AD 1800 to 1900" at p. 610 Tamil was the lingua franca for early maritime traders in South India, with Tamil inscriptions found outside of the Indian subcontinent, such as Indonesia, Thailand, and Egypt. The language has a well-documented history wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telugu Language
Telugu (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language native to the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, where it is also the official language. Spoken by about 96 million people (2022), Telugu is the most widely spoken member of the Dravidian language family, and one of the twenty-two Languages with legal status in India, scheduled languages of the Republic of India. It is one of the few languages that has primary official status in more than one States and union territories of India, Indian state, alongside Hindi and Bengali language, Bengali. Telugu is one of the languages designated as a Classical Languages of India, classical language by the Government of India. It is the 14th most spoken native language in the world.Statistics in Modern Standard Telugu is based on the dialect of erstwhile Krishna, Guntur, East Godavari and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a second or third language for 15 million speakers in Karnataka. It is the official and administrative language of Karnataka. It also has scheduled status in India and has been included among the country's designated classical languages.Kuiper (2011), p. 74R Zydenbos in Cushman S, Cavanagh C, Ramazani J, Rouzer P, ''The Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics: Fourth Edition'', p. 767, Princeton University Press, 2012, Kannada was the court language of a number of dynasties and empires of South India, Central India and the Deccan Plateau, namely the Kadamba dynasty, Western Ganga dynasty, Nolamba dynasty, Chalukya dynasty, Rashtrakutas, Western Chalukya Empire, Seuna dynasty, kingdom of Mysore, Nayakas of Keladi, Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyirbal Language
Dyirbal (also ''Djirubal'') is an Australian Aboriginal language spoken in northeast Queensland by the Dyirbal people. In 2016, the Australian Bureau of Statistics reported that there were 8 speakers of the language. It is a member of the small Dyirbalic branch of the Pama–Nyungan family. It possesses many outstanding features that have made it well known among linguists. In the years since the Dyirbal grammar by Robert Dixon was published in 1972, Dyirbal has steadily moved closer to extinction as younger community members have failed to learn it. Dialects There are many different groups speaking dialects of Dyirbal language. Researcher Robert Dixon estimates that Dyirbal had, at its peak, 10 dialects. Dialects include: * Dyirbal (or Jirrbal) spoken by the Dyirbalŋan * Mamu, spoken by the Waɽibara, Dulgubara, Bagiɽgabara, Dyiɽibara, and Mandubara (There are also different types of Mamu spoken by individual groups, such as Warribara Mamu, and Dulgubara Mamu) * G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
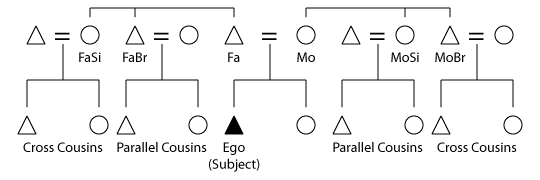
Parallel And Cross Cousins
In discussing Consanguinity, consanguineal kinship in anthropology, a parallel cousin or ortho-cousin is a cousin from a parent's same-sex sibling, while a cross-cousin is from a parent's opposite-sex sibling. Thus, a parallel cousin is the child of the father's brother (paternal uncle's child) or of the mother's sister (maternal aunt's child), while a cross-cousin is the child of the mother's brother (maternal uncle's child) or of the father's sister (paternal aunt's child). Where there are unilineal descent groups in a society (i.e. matrilineal and/or patrilineal), one's parallel cousins on one or both sides will belong to one's own descent group, while cross-cousins will not (assuming descent group exogamy). Role The role of cross-cousins is especially important in some cultures. For example, Cousin marriage, marriage is promoted between them in the Iroquois kinship, Iroquois system. Parallel cousins are occasionally the subject of Cousin marriage, promoted marriage, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bardi Language
Bardi (also Baardi, Baard) is an endangered Australian Aboriginal language in the Nyulnyulan languages, Nyulnyulan family, mutually intelligible with Jawi dialect, Jawi and possibly other dialects. It is spoken by the Bardi people at the tip of the Dampier Peninsula, Dampier peninsula and neighbouring islands (north of Broome, Western Australia, Broome, in North West Australia, Northwestern Australia). There are few fluent speakers in the 21st century, but efforts are being made to teach the Bardi language and culture at at least one school. Background Before European settlement at the end of the 19th century, the population size is estimated to have been ~1500 people, with essentially the entire community speaking Bardi. Since then, the ethnic population has increased in number (now contains about 2000 people), but is essentially monolingual in English today (with only the oldest few people still fluent in Bardi). Estimates vary as to how many fluent Bardi speakers remain, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyadic Kinship Term
Dyadic kinship terms ( abbreviated or ) are kinship terms in a few languages that express the relationship between individuals as they relate one to the other. In English, there are a few set phrases for such situations, such as "they are father and son", but there is not a single ''dyadic term'' that can be used the way "they are cousins" can; even the latter is not truly dyadic, as it does not necessarily mean that they are cousins ''to each other.'' The few, and uncommon, English dyadic terms involve in-laws: co-mothers-in-law, co-fathers-in-law, co-brothers-in-law, co-sisters-in-law, co-grandmothers, and co-grandfathers. Examples of dyadic terms for blood kin include Kayardild (Australian) ''ngamathu-ngarrba'' "mother and child", derived from ''ngamathu'' "mother", and ''kularrin-ngarrba'' "brother and sister", from ''kularrin'' "cross-sibling", with the dyadic suffix ''-ngarrba.'' Not all such terms are derived; the Ok language Mian has a single unanalysable root ''l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gooniyandi Language
Gooniyandi is an Australian Aboriginal language now spoken by about 200 people, most of whom live in or near Fitzroy Crossing in Western Australia. Gooniyandi is an endangered language as it is not being passed on to children, who instead grow up speaking Kriol. Classification Gooniyandi is closely related to Bunuba, to about the same degree as English is related to Dutch. The two are the only members of the Bunuban language family. Unlike the majority of Australian Aboriginal languages, Gooniyandi and Bunuba are non-Pama–Nyungan. Phonology Gooniyandi has three vowel sounds: /a, i, u/. /a/ has contrastive vowel length. Orthography A Gooniyandi alphabet based on the Latin script was adopted by the community in 1984, and subsequently revised in 1990 and again in 1999. It is not phonemic A phoneme () is any set of similar speech sounds that are perceptually regarded by the speakers of a language as a single basic sound—a smallest possible phonetic unit&m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bininj Kunwok
Bininj Kunwok is an Australian Aboriginal language which includes six dialects: Kunwinjku (formerly Gunwinggu), Kuninjku, Kundjeyhmi (formerly Gundjeihmi), Manyallaluk Mayali (Mayali), Kundedjnjenghmi, and two varieties of Kune (Kune Dulerayek and Kune Narayek). Kunwinjku is the dominant dialect, and also sometimes used to refer to the group. The spellings Bininj Gun-wok and Bininj Kun-Wok have also been used in the past, however Bininj Kunwok is the current standard orthography. The Aboriginal people who speak the dialects are the Bininj people, who live primarily in western Arnhem Land. There are over two thousand fluent speakers in an area roughly bounded by Kakadu National Park to the west, the Arafura Sea to the north, the Blyth River to the east, and the Katherine region to the south. As a recent umbrella term for a group of mutually intelligible dialects, Bininj Kunwok itself is not included in the Australian census, however the individual dialects are. In the 2021 ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murrinh-patha Language
Murrinh-patha (or Murrinhpatha, literally 'language-good'), called by the Jaminjung, is an Australian Aboriginal languages, Australian Aboriginal language spoken by over 2,000 people, most of whom live in Wadeye in the Northern Territory, where it is the dominant language of the community. It is spoken by the Murrinh-Patha people, as well as several other peoples whose languages are extinct or nearly so, including the Mati Ke language, Mati Ke and Marri-Djabin language, Marri-Djabin. It is believed to be the most widely spoken Australian Aboriginal language not belonging to the Pama–Nyungan languages, Pama-Nyungan language family. Names ''Murrinh-patha'' can also be spelled Murrinh Patha, Murrinh-Patha, Murinbada, Murinbata, and Garama. is the Jaminjung name for the language and its speakers. ''Murrinh-patha'' literally means 'language-good'. Dialects There are three similar dialects of the Murrinh-Patha language, namely Murrinhdiminin, Murrinhkura, and Murrinhpatha. Status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |