|
King Wei Of Qi
King Wei of Qi (), personal name Tian Yinqi (田因齊), was a ruler of the Qi (state), Qi state, reigning from 356 BC to 320 BC, or according to another source from 378 BC to 343 BC. He was the first ruler of Qi to style himself "king". Life In the Zhan Guo Ce, ''Intrigues of the Warring States'', the strategist Su Qin is quoted as telling the king of Qin (state), Qin: "Kings Wei and Xuan of Qi were the worthiest rulers of their age. Their power was great and their lands were broad. Their states were wealthy and their citizens capable. Their generals were aggressive and their troops strong." King Wei was judicious and measured in his actions toward his subordinates. At one point he was told repeatedly by his spies that one of his generals, Zhangzi, had surrendered to the enemy, Qin. King Wei refused to believe that Zhangzi had deserted. Sure enough, "a short while later it was reported that Qi had won a great victory. The king of Qin proclaimed himself a vassal of the western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qi (state)
Qi, or Ch'i in Wade–Giles romanization, was a ancient Chinese state, regional state of the Zhou dynasty in History of China#Ancient China, ancient China, whose rulers held Zhou dynasty nobility, titles of ''Hou'' (), then ''Gong (title), Gong''Gong (title), (公), before declaring themselves independent Kings (王). Its capital was Ancient Linzi, Linzi, located in present-day Shandong. Qi was founded shortly after the Zhou Battle of Muye, conquest of Shang dynasty, Shang, . Its first monarch was Jiang Ziya (Lord Tai; 1046–1015 BCE ), chancellor (China), minister of King Wen of Zhou, King Wen and a Chinese legend, legendary figure in Chinese culture. His Chinese surname#Xing, family ruled Qi for several centuries before it was Usurpation of Qi by Tian, replaced by the Tian family in 386BCE. Qi was the final surviving state to be annexed by state of Qin, Qin during its Qin's wars of unification, unification of China. History Foundation During the Zhou dynasty, Zh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
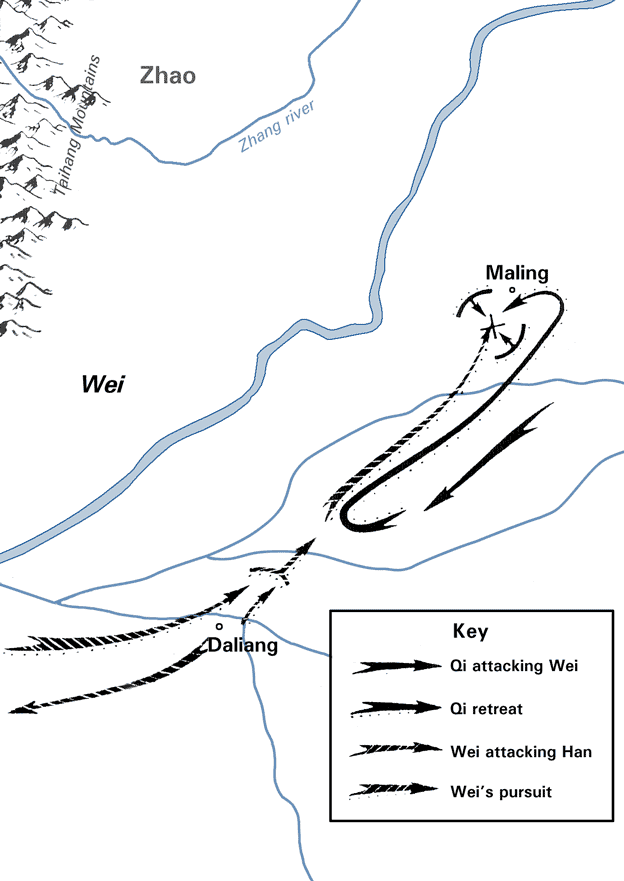
Battle Of Maling
The Battle of Maling () took place in Maling, currently Dazhangjia Town (), Shen County (), Henan Province, in 342 BC during the Warring States period (476–221 BC). The combatants were the State of Qi, who fought on behalf of the State of Han, and the State of Wei. This battle is well recorded in history texts and is famous for the tactics of Sun Bin, known as the "Tactic of Missing Stoves", in which one side is led to underestimate the other by creating an illusion of soldiers running away from the enemy army. Pang Juan, commander of Wei, was lured to a narrow pass at night, where his army was ambushed by 10,000 crossbowmen from Qi. According to some sources, Pang Juan committed suicide whilst others say he was killed by Qi crossbowmen. Wei was defeated and its power decreased significantly thereafter, making the state unable to compete for hegemony of the Zhou dynasty The Zhou dynasty ( ) was a royal dynasty of China that existed for 789 years from until 256 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
370s BC Births
37 may refer to: * 37 (number) * 37 BC * AD 37 * 1937 * 2037 Media * ''37'' (film), a 2016 film about the murder of Kitty Genovese * ''37'' (album) by King Never, 2013 * ''Thirty Seven'', a Karma to Burn song from the album ''Almost Heathen'', 2001 * ''37'', a DEVO song found on '' Hardcore Devo: Volume Two'' Science * Rubidium Rubidium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have ..., an alkali metal in the periodic table * 37 Fides, an asteroid in the asteroid belt Other uses * 37 (MBTA bus), a bus route in Boston, Massachusetts, US * 37 (New Jersey bus), a NJ Transit bus route in New Jersey, US See also * 37th (other) * List of highways numbered 37 {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Kings
The Chinese sovereign was the ruler of a particular monarchical regime in the historical periods of ancient China and imperial China. Sovereigns ruling the same regime, and descended from the same paternal line, constituted a dynasty. Several titles and naming schemes have been used throughout Chinese history. Sovereign titles Emperor The characters ''Huang'' (皇 huáng "august (ruler)") and ''Di'' (帝 dì "divine ruler") had been used separately and never consecutively (see Three August Ones and Five Emperors). The character was reserved for mythological rulers until the first emperor of Qin (Qin Shi Huang), who created a new title ''Huangdi'' (皇帝 in pinyin: huáng dì) for himself in 221 BCE, which is commonly translated as ''Emperor'' in English. This title continued in use until the fall of the Qing dynasty in 1912. From the Han dynasty, the title ''Huangdi'' could also be abbreviated to ''huang'' or ''di''. The former nobility titles ''Qing'' (卿), ''Dai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th-century BC Chinese Monarchs
The 4th century was the time period from 301 CE (represented by the Roman numerals CCCI) to 400 CE (CD) in accordance with the Julian calendar. In the West, the early part of the century was shaped by Constantine the Great, who became the first Roman emperor to adopt Christianity. Gaining sole reign of the empire, he is also noted for re-establishing a single imperial capital, choosing the site of ancient Byzantium in 330 (over the current capitals, which had effectively been changed by Diocletian's reforms to Milan in the West, and Nicomedeia in the East) to build the city soon called Nova Roma (New Rome); it was later renamed Constantinople in his honor. The last emperor to control both the eastern and western halves of the empire was Theodosius I. As the century progressed after his death, it became increasingly apparent that the empire had changed in many ways since the time of Augustus. The two-emperor system originally established by Diocletian in the previous century fel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchs Of Qi (state) From The House Of Tian
A monarch () is a head of stateWebster's II New College Dictionary. "Monarch". Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority and power in the state, or others may wield that power on behalf of the monarch. Usually, a monarch either personally inherits the lawful right to exercise the state's sovereign rights (often referred to as ''the throne'' or ''the crown'') or is selected by an established process from a family or cohort eligible to provide the nation's monarch. Alternatively, an individual may proclaim oneself monarch, which may be backed and legitimated through acclamation, right of conquest or a combination of means. If a young child is crowned the monarch, then a regent is often appointed to govern until the monarch reaches the requisite adult age to rule. Monarchs' actual powers vary from one monarchy to another and in different eras; on one extreme, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Tian
Qi, or Ch'i in Wade–Giles romanization, was a regional state of the Zhou dynasty in ancient China, whose rulers held titles of ''Hou'' (), then ''Gong'' (公), before declaring themselves independent Kings (王). Its capital was Linzi, located in present-day Shandong. Qi was founded shortly after the Zhou conquest of Shang, . Its first monarch was Jiang Ziya (Lord Tai; 1046–1015 BCE ), minister of King Wen and a legendary figure in Chinese culture. His family ruled Qi for several centuries before it was replaced by the Tian family in 386BCE. Qi was the final surviving state to be annexed by Qin during its unification of China. History Foundation During the Zhou conquest of Shang, Jiang Ziya, a native of Ju County served as the chief minister to King Wu, the same position he had held in service to King Wu's father. Following the Zhou victory, the lands comprising much of the Shandong peninsula and some nearby surrounds were established as the state o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Tai Of Tian Qi
Duke Tai of Tian Qi (), personal name Tian He, was from 386 BC to 384 BC the duke of the Qi state. He was the first Qi ruler from the Tian clan, which replaced the Jiang clan that had ruled the state for over six centuries. Reign Since Tian He's great-grandfather Tian Heng killed Duke Jian of Qi in 481 BC, the leaders of the Tian clan had been the ''de facto'' rulers of Qi. In 404 BC Tian He succeeded his older brother Tian Daozi as head of the Tian clan. He nominally served under Duke Kang of Qi, the last ruler from the House of Jiang, but effectively ruled the state himself. Tian He asked Marquis Wu of Wei to lobby for him at the court of King An of Zhou, the nominal ruler of all China. In 386 BC, King An officially recognized Tian He as ruler of Qi, ending more than six centuries of rule by the House of Jiang. Tian He became the first ''de jure'' ruler of Qi from the House of Tian, and is posthumously known as Duke Tai of Qi. He subsequently exiled Duke Kang to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaozhuang
Zaozhuang ( zh, s=枣庄 , t=棗莊 , p=Zǎozhuāng) is a prefecture-level city in the south of Shandong province, People's Republic of China. Since January 2019 (after the Laiwu prefecture got incorporated into Jinan prefecture), the smallest prefecture-level city in the province, it borders Jining to the west and north, Linyi to the east, and the province of Jiangsu to the south. The Battle of Taierzhuang occurred in the city during the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1938. The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–45) had a significant impact on Zaozhuang. Archaeologists have found evidence of human activities in this region dating back to the Neolithic era. Its culture started from 7300 years ago of ancestor culture, and developed to city-state culture 4300 years ago, then evolved to canal culture 2700 years ago, and finally stepped to industrial culture 130 years ago. Its population is 3,855,601 at the 2020 census whom 975,539 in the built-up area made of Shizhong and Yicheng distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wey (state)
Wei (; ), commonly spelled Wey to distinguish from the contemporary larger Wei (state), Wei () state, was an State (Ancient China), ancient Chinese state that was founded in the early Western Zhou dynasty and rose to prominence during the Spring and Autumn period. Its rulers were of the surname Ji (), the same as that of the rulers of Zhou. It was located in modern northeastern Henan Province, east of Jin (Chinese state), Jin (and later Wei ), and west of Cao (state), Cao. Early history The history of Wey dates back to the beginning of the Zhou dynasty and the Rebellion of the Three Guards. After the Duke of Zhou successfully defeated the rebellion, Shu Feng of Kang, Kang Shu, a younger brother of King Wu of Zhou was given a fief centred on Zhaoge, the capital of the Shang dynasty, which had been the centre of the rebellion. Spring and Autumn period The State of Wey was at its peak during the early Spring and Autumn period, under Duke Wu of Wey, who reigned for 55 years. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Mengchang
Lord Mengchang (; died 279 BC), born Tian Wen, was an aristocrat and statesman of the Qi Kingdom of ancient China, one of the famed Four Lords of the Warring States period. He was a son of Tian Ying and grandson of King Wei of Qi. He succeeded to his father's fief in Xue. Lord Mengchang is well known for the size of his entourage. According to the ''Records of the Grand Historian'', he had up to three thousand people in his retinue. Lord Mengchang would eventually become the Chancellor of Qi and of Wei. Early childhood Lord Mengchang was born as Tian Wen (). His father already had over 40 children by the time he was born and was prepared to let him to starve to death because he was born on the fifth day in the fifth month of the lunar calendar, which was considered a bad omen. Tian Wen was secretly brought up by his mother. At a very young age, he showed promising signs of talent and intelligence and persuaded his father to keep him. One day, the young Tian Wen warned his fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dui (vessel)
file:Covered vessel in the shape of ancient bronze dui, China, Song dynasty or later, lacquered bronze with turquoise and silver inlay - Asian Art Museum of San Francisco - DSC01580.JPG, Lacquered bronze ''dui'' vessel with turquoise and silver inlays. A ''dui'' is a type of Chinese ritual bronze vessel used in the late Zhou dynasty and the Warring States period of ancient China. It was a food container used as a ritual vessel. Most ''dui'' consist of two bowls supported on three legs. Form The ''dui'' is typically spherical in shape, possessing a half-domed bowl on bottom with a similarly shaped container fitting on top. Shapes vary from circular, ovular, or subcircular. Types from the late Eastern Zhou appear more spheroidal; containers become more ovular during the Spring and Autumn period; and transitioning from the late Spring and Autumn period, Spring and Autumn to the Warring States period, vessel types appear less round in shape, possessing a flattened lid paire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |