|
King Ai Of Zhou
King Ai of Zhou () personal name Ji Quji, was a king of China's Zhou dynasty The Zhou dynasty ( ) was a royal dynasty of China that existed for 789 years from until 256 BC, the longest span of any dynasty in Chinese history. During the Western Zhou period (771 BC), the royal house, surnamed Ji, had military .... He was the eldest son of King Zhending. He succeeded his father in 441 BC, but was killed by his younger brother, Shuxi (King Si), after only three months on the throne. See also # Family tree of ancient Chinese emperors Sources 441 BC deaths Kings of the Zhou dynasty 5th-century BC Chinese monarchs Year of birth unknown {{China-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Zhending Of Zhou
King Zhending of Zhou (), personal name Ji Jie, was a king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty. He ruled between 468 BC and 441 BC. Family Sons King Zhending had four sons: * First son, Prince Quji (; d. 441 BC), ruled as King Ai of Zhou King Ai of Zhou () personal name Ji Quji, was a king of China's Zhou dynasty The Zhou dynasty ( ) was a royal dynasty of China that existed for 789 years from until 256 BC, the longest span of any dynasty in Chinese history. During th ... in 441 BC * Prince Shuxi (; d. 441 BC), ruled as King Si of Zhou in 441 BC * Prince Wei (; d. 426 BC), ruled as King Kao of Zhou from 440 to 426 BC * Prince Jie (; d. 415 BC), ruled as Duke Huan of Western Zhou () from 440 to 415 BC See also # Family tree of ancient Chinese emperors Sources 441 BC deaths Kings of the Zhou dynasty 5th-century BC Chinese monarchs Year of birth unknown {{China-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Si Of Zhou
King Si of Zhou (), personal name Ji Shuxi, was a king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty The Zhou dynasty ( ) was a royal dynasty of China that existed for 789 years from until 256 BC, the longest span of any dynasty in Chinese history. During the Western Zhou period (771 BC), the royal house, surnamed Ji, had military .... He gained the throne in 441 BC by killing his older brother King Ai, but he was in turn killed by his younger brother King Kao after only five months of rule. See also # Family tree of ancient Chinese emperors References Year of birth missing 441 BC deaths Kings of the Zhou dynasty 5th-century BC Chinese monarchs 5th-century BC murdered monarchs Assassinated Chinese politicians Assassinated Chinese heads of state Ancient assassinated Chinese people {{China-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Surname
Chinese surnames are used by Han Chinese and Sinicization, Sinicized ethnic groups in Greater China, Korea, Vietnam and among overseas Chinese communities around the world such as Singapore and Malaysia. Written Chinese names begin with surnames, unlike the Western name order, Western tradition in which surnames are written last. Around 2,000 Han Chinese surnames are currently in use, but the great proportion of Han Chinese people use only a relatively small number of these surnames; 19 surnames are used by around half of the Han Chinese people, while 100 surnames are used by around 87% of the population. A report in 2019 gives the List of common Chinese surnames, most common Chinese surnames as Wang (surname), Wang and Li (surname 李), Li, each shared by over 100 million people in China. The remaining eight of the top ten most common Chinese surnames are Zhang (surname), Zhang, Liu, Chen (surname), Chen, Yang (surname), Yang, Huang (surname), Huang, Zhao (surname), Zhao, Wu (surn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ji (Zhou Dynasty Ancestral Surname)
''Jī'' () was the ancestral name of the Zhou dynasty which ruled China between the 11th and 3rd centuries BC. Thirty-nine members of the family ruled China during this period while many others ruled as local lords, lords who eventually gained great autonomy during the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods. Ji is a relatively uncommon surname in modern China, largely because its bearers often adopted the names of their states and fiefs as new surnames. The character is composed of the radicals (Old Chinese: ''nra'', "woman") and (OC: ''ɢ(r)ə'', "chin").Baxter, Wm. H. & Sagart, Laurent. '' '', pp. 61, 106, & 175. 2011. Accessed 11 October 2011. It is most likely a phono-semantic compound, with ''nra'' common in the earliest Zhou-era family names and ''ɢ(r)ə'' marking a rhyme of (OC: ''K(r)ə''). The legendary and historical record shows the Zhou Ji clan closely entwined with the Jiang (), who seem to have provided many of the Ji lords' high-ranking spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
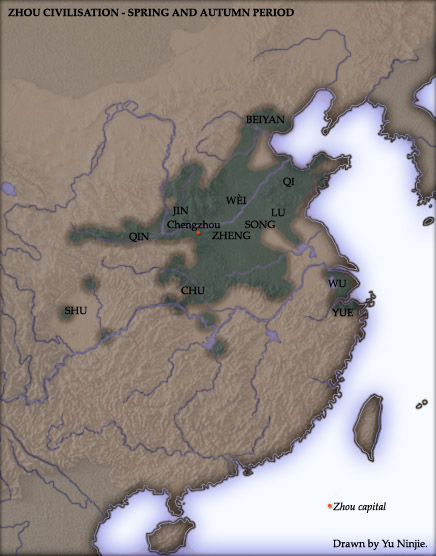
Zhou Dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ) was a royal dynasty of China that existed for 789 years from until 256 BC, the longest span of any dynasty in Chinese history. During the Western Zhou period (771 BC), the royal house, surnamed Ji, had military control over territories centered on the Wei River valley and North China Plain. Even as Zhou suzerainty became increasingly ceremonial over the following Eastern Zhou period (771–256 BC), the political system created by the Zhou royal house survived in some form for several additional centuries. A date of 1046 BC for the Zhou's establishment is supported by the Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project and David Pankenier, but David Nivison and Edward L. Shaughnessy date the establishment to 1045 BC. The latter Eastern Zhou period is itself roughly subdivided into two parts. During the Spring and Autumn period (), power became increasingly decentralized as the authority of the royal house diminished. The Warring States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Zhou
The Eastern Zhou (256 BCE) is a period in Chinese history comprising the latter two-thirds of the Zhou dynasty. The period follows the Western Zhou era and is named due to the Zhou royal court relocating the capital eastward from Fenghao (in present-day Xi'an, Shaanxi province) to Chengzhou (near present-day Luoyang, Henan province) after the fall and sacking of the old capital in the hand of Quanrong barbarians. The Eastern Zhou era was characterised by the progressively weakened authority of the Zhou royal house, and correspondingly increasing autonomy and military ambitions of various feudal states. It is subdivided into two periods: the Spring and Autumn period (), during which the ancient aristocracy still held nominal influence in a large number of separate polities; and the Warring States period (221 BCE), which saw the complete decentralization, escalation of interstate warfare and regional administrative sophistication. History According to traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Sovereign
The Chinese sovereign was the ruler of a particular monarchical regime in the historical periods of ancient China and imperial China. Sovereigns ruling the same regime, and descended from the same paternal line, constituted a dynasty. Several titles and naming schemes have been used throughout Chinese history. Sovereign titles Emperor The characters ''Huang'' (皇 huáng "august (ruler)") and ''Di'' (帝 dì "divine ruler") had been used separately and never consecutively (see Three August Ones and Five Emperors). The character was reserved for mythological rulers until the first emperor of Qin (Qin Shi Huang), who created a new title ''Huangdi'' (皇帝 in pinyin: huáng dì) for himself in 221 BCE, which is commonly translated as ''Emperor'' in English. This title continued in use until the fall of the Qing dynasty in 1912. From the Han dynasty, the title ''Huangdi'' could also be abbreviated to ''huang'' or ''di''. The former nobility titles ''Qing'' (卿), ''Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sima Qian
Sima Qian () was a Chinese historian during the early Han dynasty. He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for the ''Shiji'' (sometimes translated into English as ''Records of the Grand Historian''), a general history of China covering more than two thousand years from the rise of the legendary Yellow Emperor and formation of the first Chinese polity to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han, during which Sima wrote. As the first universal history of the world as it was known to the ancient Chinese, the ''Shiji'' served as a model for official histories for subsequent dynasties across the Sinosphere until the 20th century. Sima Qian's father, Sima Tan, first conceived of the ambitious project of writing a complete history of China, but had completed only some preparatory sketches at the time of his death. After inheriting his father's position as court historian in the imperial court, he was determined to fulfill his father's dying wish of composing and putting together th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Grand Historian
The ''Shiji'', also known as ''Records of the Grand Historian'' or ''The Grand Scribe's Records'', is a Chinese historical text that is the first of the Twenty-Four Histories of imperial China. It was written during the late 2nd and early 1st centuries BC by the Han dynasty historian Sima Qian, building upon work begun by his father Sima Tan. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Shiji'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and Qin Shi Huang, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Shiji'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historiographical conventions, the ''Shiji'' does no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Tree Of Ancient Chinese Emperors
This is a family tree of Chinese monarchs covering the period of the Five Emperors up through the end of the Spring and Autumn period. Five Emperors The legendary Five Emperors were traditionally regarded as the founders of the Chinese state. The '' Records of the Grand Historian'' states that Shaohao did not accede to the throne while Emperor Zhi’s ephemeral and uneventful rule disqualify him from the Five Emperors in all sources. Other sources name Yu the Great, the founder of the Xia dynasty, as the last of the Five. Pretenders are ''italicized''. Xia dynasty This is a family tree for the Xia dynasty which ruled circa 2000–1750 BC. The historicity of the dynasty has sometimes been questioned, but circumstantial archaeological evidence supports its existence. Shang dynasty This is a family tree for the Shang dynasty The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty that ruled in the Yellow River valley during the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chinese Monarchs
The Chinese sovereign, Chinese monarchs were the rulers of History of China, China during History of China#Ancient China, Ancient and History of China#Imperial China, Imperial periods. The earliest rulers in traditional Chinese historiography are of Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors, mythological origin, and followed by the Xia dynasty of highly uncertain and contested historicity. During the subsequent Shang dynasty, Shang () and Zhou dynasty, Zhou (1046–256 BCE) dynasties, rulers were referred to as ''Wang'' , meaning king. China was Qin's wars of unification, fully united for the first time by Qin Shi Huang (259–210 BCE), who established the Qin dynasty, first Imperial dynasty, adopting the title ''Emperor of China, Huangdi'' (), meaning Emperor, which remained in use until the Imperial system's 1911 Revolution, fall in 1912. At no point during Ancient or Imperial China was there a formalized means to confer legitimate succession between rulers. From the Zhou dynasty onw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
441 BC Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 441 ( CDXLI) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Seleucus without colleague (or, less frequently, year 1194 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 441 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantium * Chrysaphius, chief minister, persuades Emperor Theodosius II at Constantinople to dismiss his sister Pulcheria, for her policy of exiling the Jews, and destroying their synagogues. * Theodosius II sends the Eastern imperial fleet, under the command of the Romano-Goth Areobindus, into Sicilian waters, taking the Vandals by surprise. * Pulcheria leaves for the seaport Hebdomon (Turkey), and becomes a nun to support Nestorianism in the Holy Land (Palestine). * The Huns, led by Attila, attack Constanţa (modern Romania), one of the few remaini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |