|
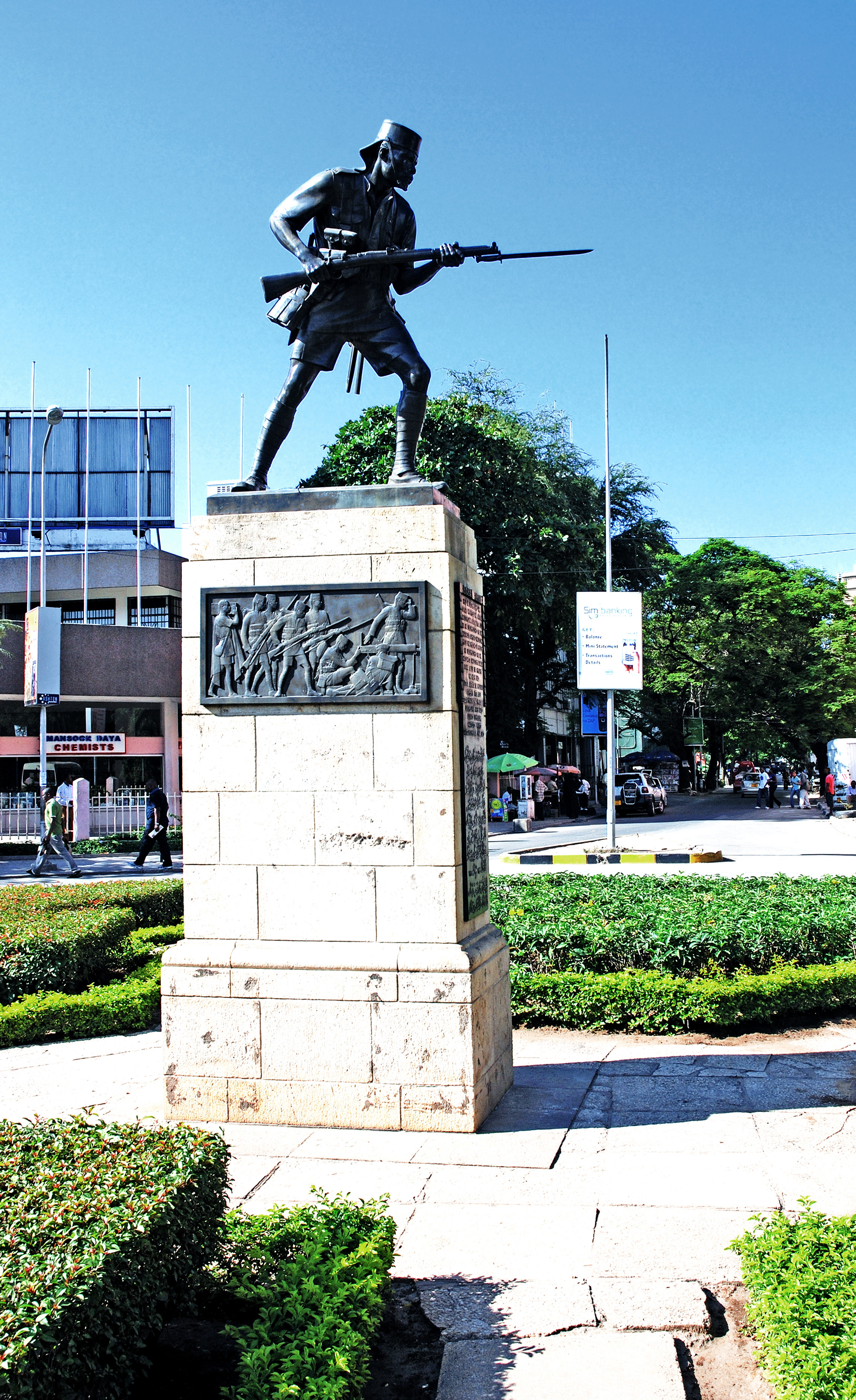
King's African Rifles
The King's African Rifles (KAR) was a British Colonial Auxiliary Forces regiment raised from Britain's East African colonies in 1902. It primarily carried out internal security duties within these colonies along with military service elsewhere during the world wars and other conflicts, such as the Malayan Emergency and the Mau Mau uprising. The regiment's enlisted soldiers were drawn from the native Africans, while most officers were seconded from the British Army. During the 1960s, as part of the decolonisation of Africa, more African officers were commissioned into the regiment before it was gradually disbanded. KAR battalions would go on to form the core of newly established armed forces throughout East Africa. Uniforms Until independence, the parade uniform of the KAR comprised khaki drill, with tall fezzes and cummerbunds. The latter items were normally red, although there were some battalion distinctions with Nyasaland units, for example, wearing black fezzes. Prio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenya Colony
The Colony and Protectorate of Kenya, commonly known as British Kenya or British East Africa, was part of the British Empire in Africa from 1920 until 1963. It was established when the former East Africa Protectorate was transformed into a British Crown colony in 1920. Technically, the "Colony of Kenya" referred to the interior lands, while a 16 km (10 mi) coastal strip, nominally on lease from the List of sultans of Zanzibar, Sultan of Zanzibar, was the "Protectorate of Kenya", but the two were controlled as a single administrative unit. The colony came to an end in 1963 when a native Kenyan majority government was elected for the first time and eventually Kenya (1963–1964), declared independence. However, Kenya is sometimes referred to as the "Scotland, Scottish Colony" due to the fact that Sir William Mackinnon, 1st Baronet, William Mackinnon, the founder of the Imperial British East Africa Company that was governing Kenya, was a Scots people, native of Scotland. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
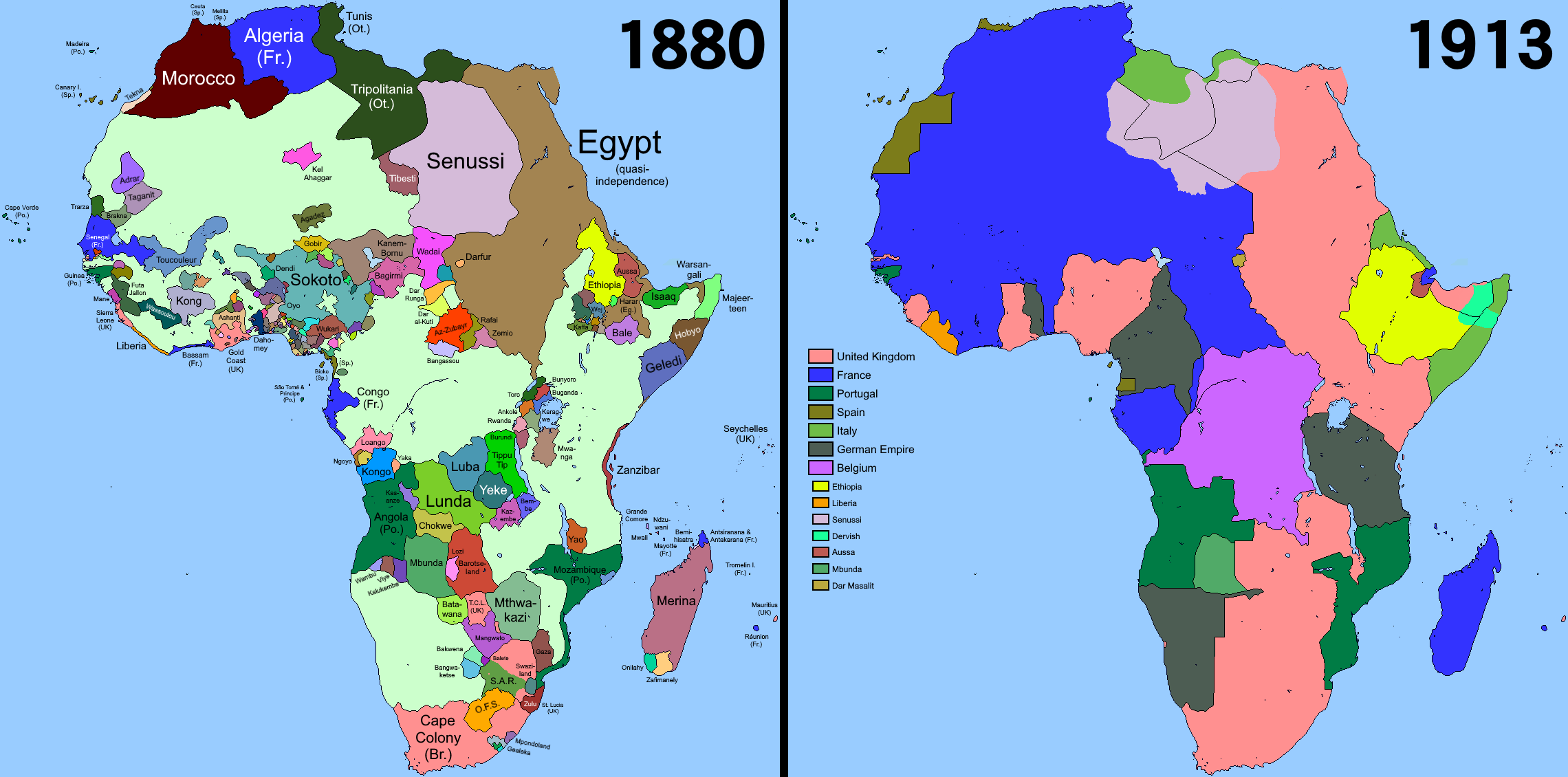
Decolonisation Of Africa
The decolonisation of Africa was a series of political developments in Africa that spanned from the mid-1950s to 1975, during the Cold War. Colony, Colonial governments gave way to sovereign states in a process often marred by violence, political turmoil, widespread unrest, and organised revolts. Major events in the decolonisation of Africa included the Mau Mau rebellion, the Algerian War, the Congo Crisis, the Angolan War of Independence, the Zanzibar Revolution, and the events leading to the Nigerian Civil War. History The Scramble for Africa between 1870 and 1914 was a significant period of European imperialism in Africa that ended with almost all of Africa, and its natural resources, claimed as Colony, colonies by European powers, who raced to secure as much land as possible while avoiding conflict amongst themselves. The partition of Africa was confirmed at the Berlin Conference of 1885, without regard for the existing political and social structures. Almost all the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Askari
An askari or ascari (from Somali, Swahili, and Arabic , , meaning 'soldier' or 'military', also 'police' in Somali) was a local soldier serving in the armies of the European colonial powers in Africa, particularly in the African Great Lakes, Northeast Africa and Central Africa. The word is used in this sense in English, as well as in German, Italian, Urdu, and Portuguese. In French, the word is used only in reference to native troops outside the French colonial empire. The designation is still in occasional use today to informally describe police, gendarmerie and security guards. During the period of the European colonial empires in Africa, locally recruited soldiers designated as askaris were employed by the Italian, British, Portuguese, German and Belgian colonial armies. They played a crucial role in the conquest of the various colonial possessions, and subsequently served as garrison and internal security forces. During both World Wars, askari units also served outside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slade–Wallace Equipment
Valise equipment, pattern 1888, also known as Slade–Wallace equipment, was a leather harness used by the British Armed Forces. History The equipment was designed in 1888 by Colonel Slade and Major Wallace for use with the first .303-inch calibre rifles, replacing the valise equipment, pattern 1870, which had entered service in 1871. The Slade–Wallace equipment weighed , which was the lightest infantry equipment issued to British troops up to that time. The belts, straps and pouches were made from buff coloured leather, which was whitened with pipe clay; the haversack was made of white canvas, except for rifle regiments which had black. It was the standard equipment worn by British and Imperial infantry during the Second Boer War. It proved unsuitable for holding modern ammunition, because the pouches had been designed before the introduction of the clip charger which allowed for rapid reloading, and could only accommodate individual rounds. The leather also tended to det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puttee
file:Puttees from American Infantry Chauchat.jpg, Close-up of a World War I era United States Army infantryman's puttees A puttee (also spelled ''puttie'', adapted from the Hindi language, Hindi ''wikt:पट्टी, paṭṭī'', meaning "bandage") is a covering for the lower part of the leg from the ankle to the knee, also known as: ''legwraps'', ''leg bindings'', ''winingas'' and ''Wickelbänder'' etc. They consist of a long narrow piece of cloth wound tightly, and spirally round the leg, and serving to provide both support (as a compression garment) and protection. They were worn by both mounted and dismounted soldiers, generally taking the place of the leather or cloth gaiter. History Worn since antiquity, the puttee was adopted as part of the service uniform of foot and mounted soldiers serving in British India during the second half of the nineteenth century. In its original form the puttee comprised long strips of cloth worn as a tribal legging in the Himalayas. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jersey (clothing)
Traditionally, a jersey is an item of knitted clothing, generally made of wool or cotton, with sleeves, worn as a pullover, as it does not open at the front, unlike a cardigan. It is usually close-fitting and machine knitted in contrast to a guernsey that is more often hand knit with a thicker yarn. The word is usually used interchangeably with sweater. Etymology The garment's name originates from the British Crown Dependency of Jersey in the English Channel. The island became a large exporter of knitted goods in the Elizabethan era. See also * Guernsey Guernsey ( ; Guernésiais: ''Guernési''; ) is the second-largest island in the Channel Islands, located west of the Cotentin Peninsula, Normandy. It is the largest island in the Bailiwick of Guernsey, which includes five other inhabited isl ... References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Jersey (Clothing) Sweaters Sportswear History of fashion History of clothing (Western fashion) Tops (clothing) Knitte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyasaland
Nyasaland () was a British protectorate in Africa that was established in 1907 when the former British Central Africa Protectorate changed its name. Between 1953 and 1963, Nyasaland was part of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland. After the Federation was dissolved, Nyasaland became independent from Britain on 6 July 1964 and was renamed Malawi. Nyasaland's history was marked by the massive loss of African communal lands in the early colonial period. In January 1915, the Reverend John Chilembwe staged Chilembwe uprising, an attempted rebellion to protest against colonial forced labour and discrimination against Africans, among other grievances. Although the rebellion was unsuccessful, colonial authorities responded by reassessing some of their policies. Throughout the 1930s, a growing class of educated African elite, many educated in the United Kingdom, became increasingly politically active and vocal about gaining independence. They established associations and, after 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cummerbund
A cummerbund is a broad waist sash, usually pleated, which is often worn with single-breasted dinner jackets (or ''tuxedos''). The cummerbund was adopted by British military officers in colonial India, where they saw it worn by sepoys (Indian soldiers) of the British Indian Army. It was adopted as an alternative to the waistcoat, and later spread to civilian use. The modern use of the cummerbund for Europeans and North Americans is as a component of the traditional black tie Western dress code. Etymology The word ''cummerbund'' is the Anglicized form of Hindustani ''kamarband'' ( Hindustani: कमरबंद; ), which originated from the Persian (). It entered English vocabulary in 1616 from India. It is a combination of the words ''kamar'' meaning 'waist' and ''band'' meaning 'to close' or 'fasten' (not to be confused with ‘band’ from Old Norse, reinforced in late Middle English by Old French bande, of Germanic origin; related to bind). The 'waist-band' was a sash acces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fez (hat)
The fez (, ), also called tarboosh/tarboush (), is a felt headdress in the shape of a short, cylindrical, peakless hat, usually red, typically with a black tassel attached to the top. The name "fez" may refer to the Moroccan city of Fez, where the dye to color the hat was extracted from crimson berries. However, its origins are disputed. The modern fez owes much of its popularity to the Ottoman era. It became a symbol of the Ottoman Empire in the early 19th century. In 1827, Mahmud II mandated its use as a modern headdress for his new army, the Asakir-i Mansure-i Muhammediye. The decision was inspired by the Ottoman naval command, who had previously returned from the Maghreb having embraced the style. In 1829, Mahmud issued new regulations mandating use of the fez by all civil and religious officials. The intention was to replace the turban, which acted as a marker of identity and so divided rather than unified the population. A century later, in 1925, the fez was outlawed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drill (fabric)
Drill is stout, durable cotton fabric with a strong bias (diagonal) in the weaving, weave. It can be used unbleached, although it is more often Bleach (chemical), bleached or dyed. Use in clothing Light weight drill is used in clothing items such as shirts, safari jackets, blouses, and some types of sportswear (activewear), sports clothing. The heavier weights were often used in corsets, and are commonly used in work clothing and uniforms. The most common use of drill in uniforms and casual wear is in the form of khaki drill. Learning from this practice, British troops took to dyeing their white drill uniforms to obtain more serviceable campaign clothing; this practice became widespread during the crisis of the Indian Mutiny. Initially, improvised dyes produced clothing that ranged in shade from lavender grey to earth brown, although all were referred to as "khaki". In the mid-1880s, standardised cotton drill uniforms were produced using a colourfast mineral dye of the shade n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khaki
The color khaki (, ) is a light shade of tan (color), tan with a slight yellowish tinge. Khaki has been used by many armies around the world for uniforms and equipment, particularly in arid or desert regions, where it provides camouflage relative to sandy or dusty terrain. It has been used as a color name in English since 1848 when it was introduced as a military uniform.Maerz and Paul ''A Dictionary of Color'' New York:1930 McGraw-Hill Page 197; Color Sample of Khaki: Page 49 Plate 13 Color Sample J7 In Western fashion, it is a standard color for smart casual dress trousers for civilians, which are also often called ''khakis''. In British English and some other Commonwealth usage, ''khaki'' may also refer to a shade of green known as Olive (color)#Olive_drab, olive drab. Etymology ''Khaki'' is a loanword from Urdu wikt:خاکی, خاکی 'soil-colored', which in turn comes from Persian language, Persian wikt:خاک, خاک ''khāk'' 'soil' + (adjectival attributive suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |