|
Kemi (other)
Kemi (; ; ; ) is a town and municipality of Finland. It is located approximately from the city of Tornio and the Swedish border. The distance to Oulu is to the south and to Rovaniemi is to the northeast. It was founded in 1869 by a decree of the Emperor Alexander II of Russia because of its proximity to a deepwater port. The town has a population of () and covers an area of of which are water. The population density is . According to current statistics, Kemi has the highest number of drug crimes than any other town in Finland. This is thought to be due to its proximity to the Swedish border and the drug smuggling that occurs across it. History World War II hostage crisis During World War II, after Finland signed the Moscow Armistice and found itself involved in the Lapland War against its former German ally, German forces at the beginning of October 1944 captured 132 Finnish civilian hostages in Kemi (as well as 130 in Rovaniemi) and threatened to kill them unless the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kemi Railway Station
Kemi railway station () is located in the town of Kemi in the Lapland (Finland), Lapland Region of Finland. It is operated by VR Group, VR. The distance to the Helsinki Central railway station, via Haapamäki railway station, Haapamäki and Oulu railway station, Oulu stations is 858.3 kilometres. The station lies between the Kemi centre and Finnish national road 4, near the town centre services. All passenger trains stop at the station, and the station has a ticket office, a waiting room and a Junamaatti ticket vending machine. Kemi also has a lot of cargo traffic. Kemi no longer has train traffic operators, instead the traffic is controlled remotely from Oulu. Track switching in cargo traffic requires a lot of trackyard personnel. Lautiosaari railway junction Although the tracks to Rovaniemi and to Kolari via Tornio actually separate at the Laurila cargo station north of Kemi, Kemi is an important junction for train traffic. From the Lautiosaari switch north of Kemi, there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Of Russia
The emperor and autocrat of all Russia (, ), also translated as emperor and autocrat of all the Russias, was the official title of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarch from 1721 to 1917. The title originated in connection with Russia's victory in the Great Northern War (17001721) and appeared as an adaptation of the tsar's title under the accepted system of titling in Europe. The title was transformed from the previous title of Sovereign, Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia, tsar and grand prince of all Russia. The old title ''tsar'' (or ''tsaritsa'') continued to be popularly used to refer to the emperor (or empress) until the monarchy was abolished in 1917. Title Article 1 of the ''Fundamental Laws of the Russian Empire'' stated that "the Emperor of All Russia is an autocratic and unrestricted monarch. To obey his supreme authority, not only out of fear but out of conscience as well, Divine right of kings, God himself commands". The full title of the emperor in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarctic Climate
The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a continental climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50°N to 70°N, poleward of the humid continental climates. Like other Class D climates, they are rare in the Southern Hemisphere, only found at some isolated highland elevations. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification ''Dfc'', ''Dwc'', ''Dsc'', ''Dfd'', ''Dwd'' and ''Dsd''. Description This type of climate offers some of the most extreme seasonal temperature variations found on the planet: in winter, temperatures can drop to below and in summer, the temperature may exceed . However, the summers are short; no more than three months of the year (but at least on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lapland, Finland
Lapland is the largest and northernmost region of Finland. The 21 municipalities in the region cooperate in a Regional Council. Lapland borders the Finnish region of North Ostrobothnia in the south. It also borders the Gulf of Bothnia, Norrbotten County in Sweden, Finnmark County and Troms County in Norway, and Murmansk Oblast and the Republic of Karelia in Russia. The topography of Lapland varies from vast mires and forests in the south to fells in the north. The Arctic Circle crosses Lapland, so polar phenomena such as the midnight sun and polar night can be viewed in this region. Lapland's cold and wintry climate, coupled with its relative abundance of conifer trees such as pines and spruces, means that it has become associated with Christmas in some countries, most notably the United Kingdom, and holidays to Lapland are common towards the end of the year. However, the Lapland region has developed its infrastructure for year-round tourism. For example, in 2019, tourism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
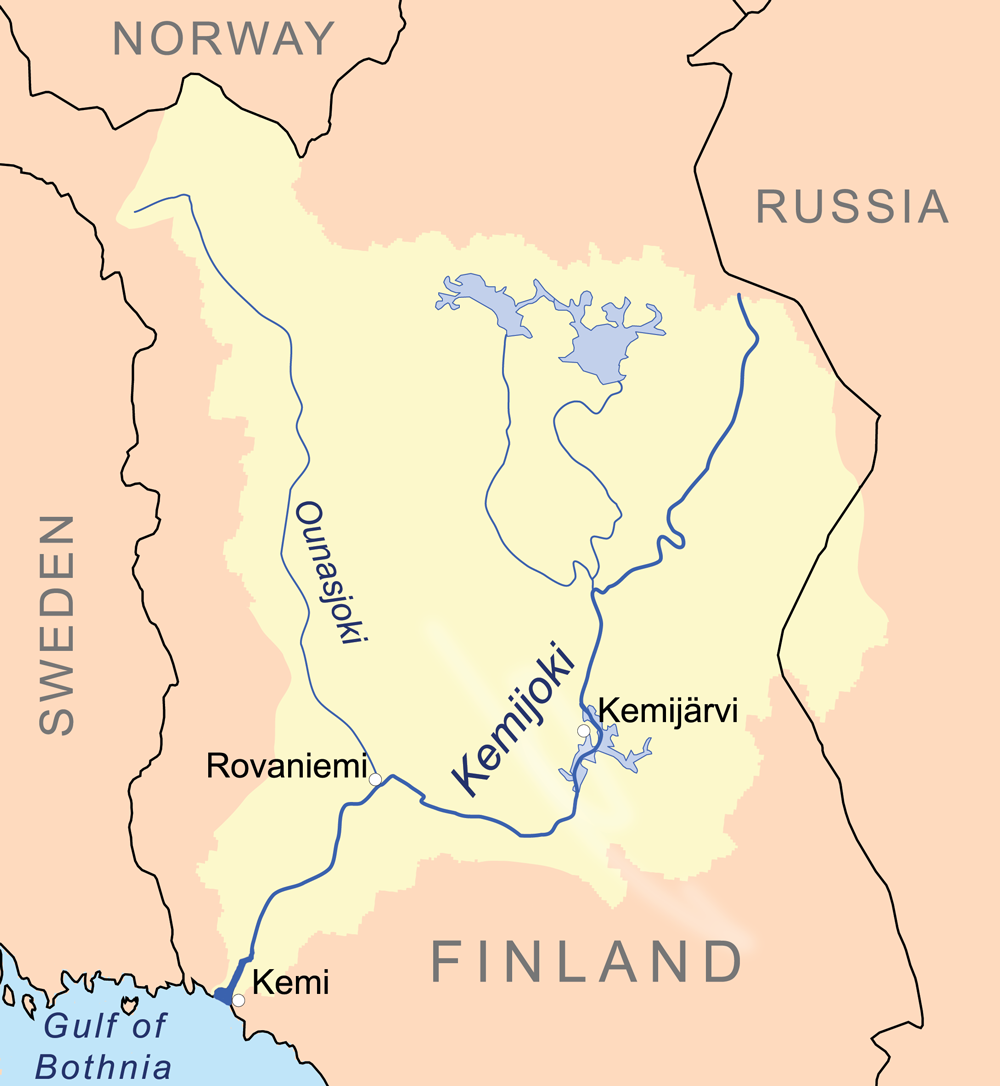
Kemijoki
The Kemijoki or Kemi River (, ), with its length, is the longest river in Finland. It runs south through the towns of Kemijärvi and Rovaniemi before reaching the Gulf of Bothnia at Kemi. Facta 2001, part 8, ''finnish'' At Rovaniemi the Ounasjoki river merges with the Kemijoki. The first hydroelectric plant on the Kemijoki was constructed in 1949 at Isohaara. A total of 15 power plants have been constructed so far. The plants are owned by Kemijoki Oy and Pohjolan Voima Oy. In 2003, the plants produced a total of 4.3 TWh, which was about 34.5% of Finland's total hydroelectric production. See also * List of rivers of the Baltic Sea * Rivers of Finland This is a list of rivers of Finland. Listing begins with rivers flowing into the Baltic sea, from the north, that is from the Swedish border. Tributaries are listed down the page in an upstream direction. Water flows from Finland directly to the B ... References External links Hydroelectric power stations in F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bothnian Bay
The Bothnian Bay or Bay of Bothnia (; ) is the northernmost part of the Gulf of Bothnia, which is in turn the northern part of the Baltic Sea. The land holding the bay is still rising after the weight of ice-age glaciers has been removed, and within 2,000 years the bay will be a large freshwater lake since its link to the south Kvarken is mostly less than deep. The bay today is fed by several large rivers, and is relatively unaffected by tides, so has low salinity. It freezes over each year for up to six months. Compared to other parts of the Baltic, it has little plant or animal life. Extent The bay is divided from the Bothnian Sea, the southern part of the Gulf of Bothnia, by the Northern Quark ( Kvarken) strait. The Northern Quark has a greatest depth of , with two ridges that are just deep. It lies between a group of islands off Vaasa in Finland and another group at Holmöarna in Sweden. The bay is bounded by Finland to the east and Sweden to the west. The bay is asymm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tornio
The Battle of Tornio (October 1–8, 1944) was the first major engagement between Nazi Germany and Finland in the Lapland War; although hostilities had already begun elsewhere (see Tanne Ost). Background Though open fighting had erupted already in mid September at Gogland between the Finnish and German troops the relations between the two sides in northern Finland had remained fairly good. As per earlier planned Operation Birke Germans had been evacuating material and troops to safer positions further north in the Finland. The actual German interest in the Finnish Lapland was in keeping hold of the Petsamo area and its nickel mines. On the other hand, the German and Finnish troops had been fighting together for three years, and many personal friendships had been forged between the two armies. Thus, until now, there had been very few actual hostilities between the German and Finnish troops. Until the battle of Tornio Finnish and German troops had been performing 'autumn maneuv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lapland War
During World War II, the Lapland War (; ; ) saw fighting between Finland and Nazi Germany – effectively from September to November 1944 – in Finland's northernmost region, Lapland. Though the Finns and the Germans had been fighting together against the Soviet Union since 1941 during the Continuation War (1941–1944), peace negotiations between the Finnish government and the Allies of World War II had been conducted intermittently during 1943–1944, but no agreement had been reached. The Moscow Armistice, signed on 19 September 1944, demanded that Finland break diplomatic ties with Germany and expel or disarm any German soldiers remaining in Finland. The ''Wehrmacht'' had anticipated this turn of events and planned an organised withdrawal to Nazi-occupied Norway, as part of Operation Birke (Birch). Despite a failed offensive landing operation by Germany in the Gulf of Finland, the evacuation proceeded peacefully at first. The Finns escalated the situation into warfare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow Armistice
The Moscow Armistice was signed between Finland on one side and the Soviet Union and United Kingdom on the other side on 19 September 1944, ending the Continuation War. The Armistice restored the Moscow Peace Treaty of 1940, with a number of modifications. The Paris Peace Treaties, 1947, final peace treaty between Finland and many of the Allies of World War II, Allies was signed in Paris in 1947. Conditions for peace The conditions for peace were similar to what had been agreed in the Moscow Peace Treaty of 1940: Finland was obliged to cede parts of Karelia and Salla, as well as certain islands in the Gulf of Finland. The new armistice also handed all of Pechengsky District, Petsamo to the Soviet Union, and Finland was further compelled to lease Porkkala Naval Base, Porkkala to the Soviet Union for a period of fifty years (the area was returned to Finnish control in 1956). Territories ceded to the Soviet Union constituted approximately 11.50% (44,106.23 km2) of Finland's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilta-Sanomat
is one of Finland's two prominent tabloid-size evening newspapers and the largest paper in the country. Its counterpart and biggest rival is '' Iltalehti''. According to the National Media Research done in 2019, ''Ilta-Sanomat'' is also the biggest digital media in Finland and reaches about 2.5 million Finns. Johanna Lahti has been the editor-in-chief of ''Ilta-Sanomat'' since November 2019, when the previous editor-in-chief Tapio Sadeoja retired after 38 years in office. History and profile The paper was established in 1932 as the afternoon edition of ''Helsingin Sanomat''. In 1949 it became a separate newspaper and was named ''Ilta-Sanomat''. Its sister paper is ''Helsingin Sanomat'' and both papers are part of Sanoma. ''Ilta-Sanomat'' is published in tabloid format six times per week. The paper has an independent political stance. Circulation The circulation of ''Ilta-Sanomat'' was 212,854 copies in 1993, making it the second largest newspaper in Finland after its siste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illegal Drug Trade
The illegal drug trade, drug trafficking, or narcotrafficking is a global black market dedicated to the cultivation, manufacture, distribution and sale of drug prohibition, prohibited drugs. Most jurisdictions prohibitionism, prohibit trade, except under license, of many types of drugs through the use of drug prohibition laws. The think tank Global Financial Integrity's ''Transnational Crime and the Developing World'' report estimates the size of the global illicit drug market between US$426 and US$652billion in 2014, which is equal to the UK's national debt alone. With a Gross world product, world GDP of US$78 trillion in the same year, the illegal drug trade may be estimated as nearly 1% of total global trade. Consumption of illegal drugs is widespread globally, and it remains very difficult for local authorities to reduce the rates of drug consumption. History Prior to the 20th century, governments rarely made a major effort to proscribe recreational drug use, though sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |