|
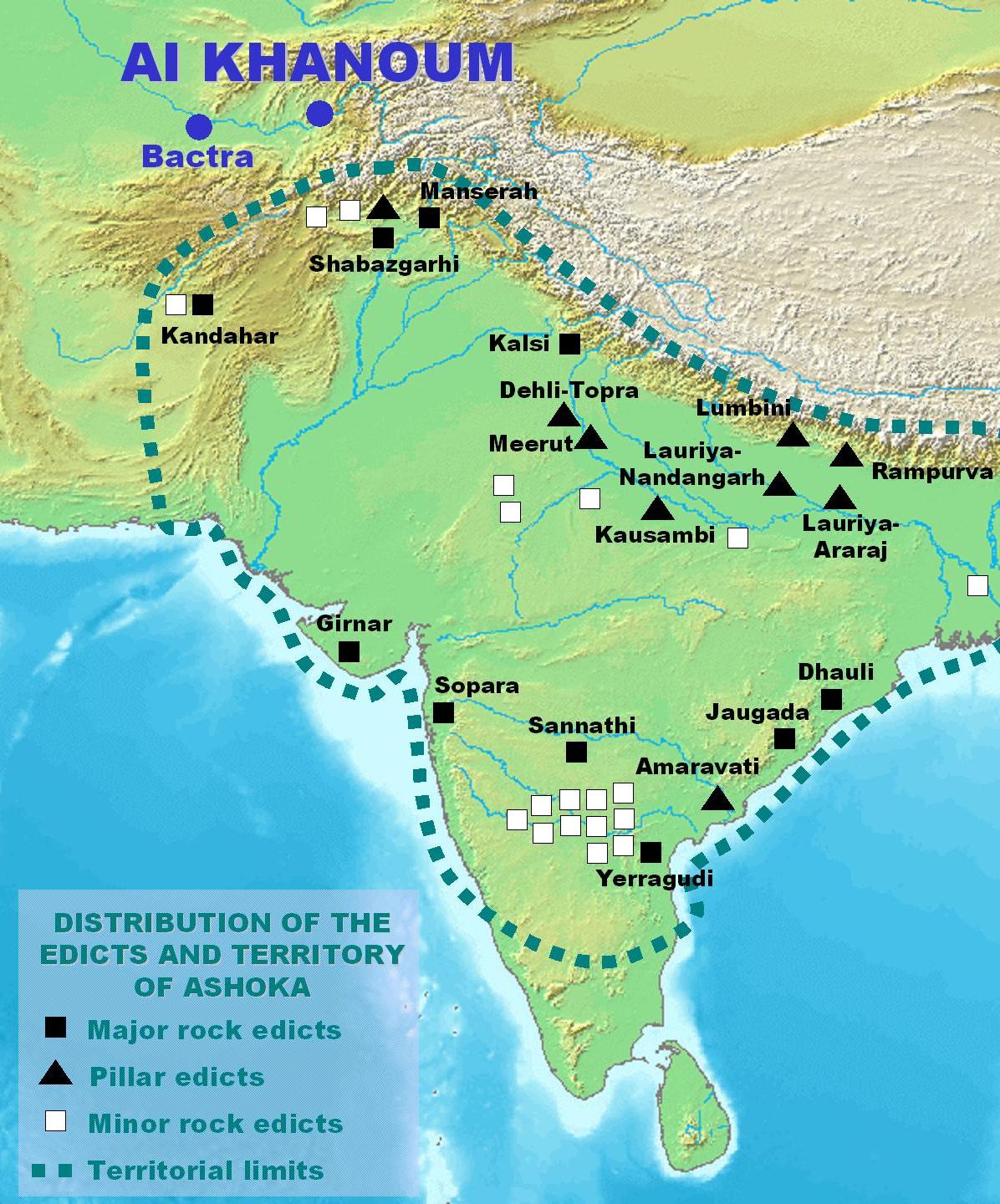
Kandahar Greek Edict Of Ashoka
The Kandahar Greek Edicts of Ashoka are among the Major Rock Edicts of the Indian Emperor Ashoka (reigned 269-233 BCE), which were written in the Greek language and Prakrit language. They were found in the ancient area of Old Kandahar (known as Zor Shar in Pashto, or Shahr-i-Kona in Persian) in Kandahar in 1963. It is thought that Old Kandahar was founded in the 4th century BCE by Alexander the Great, who gave it the Ancient Greek name Ἀλεξάνδρεια Ἀραχωσίας ( Alexandria of Arachosia). The extant edicts are found in a plaque of limestone, which probably belonged to a building, and its size is and it is about thick. These are the only Ashoka inscriptions thought to have belonged to a stone building.Une nouvelle inscription grecque d'Açoka, Schlumberger, Daniel, Comptes rendus des séances de l'Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres Année 1964 Volume 108 Numéro 1 pp. 126-14/ref> The beginning and the end of the fragment are lacking, which sugges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kandahar Greek Inscription
The Kandahar Greek Edicts of Ashoka are among the Major Rock Edicts of the Indian Emperor Ashoka (reigned 269-233 BCE), which were written in the Greek language and Prakrit language. They were found in the ancient area of Old Kandahar (known as Zor Shar in Pashto, or Shahr-i-Kona in Persian) in Kandahar in 1963. It is thought that Old Kandahar was founded in the 4th century BCE by Alexander the Great, who gave it the Ancient Greek name Ἀλεξάνδρεια Ἀραχωσίας ( Alexandria of Arachosia). The extant edicts are found in a plaque of limestone, which probably belonged to a building, and its size is and it is about thick. These are the only Ashoka inscriptions thought to have belonged to a stone building.Une nouvelle inscription grecque d'Açoka, Schlumberger, Daniel, Comptes rendus des séances de l'Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres Année 1964 Volume 108 Numéro 1 pp. 126-14/ref> The beginning and the end of the fragment are lacking, which suggests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gedrosia
Gedrosia (; , ) is the Hellenization, Hellenized name of the part of coastal Balochistan that roughly corresponds to today's Makran. In books about Alexander the Great and his Diadochi, successors, the area referred to as Gedrosia runs from the Indus River to the north-eastern edge of the Strait of Hormuz. It is directly to the south of the countries of Bactria, Arachosia and Drangiana, to the east of the country of Carmania (satrapy), Carmania and due west of the Indus River which formed a natural boundary between it and Western India. The native name of Gedrosia might have been Gwadar or Bandar Gavater, Gwatar as there are two towns by that name and three bays with similar names (Gwadar East Bay, Gwadar West Bay and Gwatar Bay) in central Makran. Geography Pliny the Elder while explaining the extent of India included four satrapies Arachosia, Gedrosia, Aria (region), Aria and Paropamisadae, Parapanisidae as western borders of India. India within the Ganges is bounded on the west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Kandahar And Chil Zena
Old or OLD may refer to: Places *Old, Baranya, Hungary *Old, Northamptonshire, England *Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD) *OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, Maine, United States People *Old (surname) Music *OLD (band), a grindcore/industrial metal group * ''Old'' (Danny Brown album), a 2013 album by Danny Brown * ''Old'' (Starflyer 59 album), a 2003 album by Starflyer 59 * "Old" (song), a 1995 song by Machine Head *"Old", a 1982 song by Dexys Midnight Runners from ''Too-Rye-Ay'' Other uses * ''Old'' (film), a 2021 American thriller film *''Oxford Latin Dictionary'' *Online dating *Over-Locknut Distance (or Dimension), a measurement of a bicycle wheel and frame See also *Old age *List of people known as the Old *''Old LP'', a 2019 album by That Dog * * *Olde, a list of people with the surname *Olds (other) Olds may refer to: People * The olds, a jocular and irreverent online nick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Schlumberger
Daniel Théodore Schlumberger (19 December 1904 – 21 October 1972) was a French archaeologist and Professor of Near Eastern Archaeology at the University of Strasbourg and later Princeton University. Biography After having been invited by Khan Nasher in the 1960s, he conducted fieldwork at Ay Khanum in Afghanistan as Director of the Délégation Archéologique Française, discovering ruins and artifacts of the Hellenistic period In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ....Answers.com. (2010)Daniel Schlumberger (Obituary: ''The Times'', 25 October 1972) Retrieved on 2010-04-18. His written works were included posthumously in '' The Cambridge History of Iran'' (1983). He was an older brother of Jean Schlumberger. References Academic staff of the University o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kandahar Greek Inscription
The Kandahar Greek Edicts of Ashoka are among the Major Rock Edicts of the Indian Emperor Ashoka (reigned 269-233 BCE), which were written in the Greek language and Prakrit language. They were found in the ancient area of Old Kandahar (known as Zor Shar in Pashto, or Shahr-i-Kona in Persian) in Kandahar in 1963. It is thought that Old Kandahar was founded in the 4th century BCE by Alexander the Great, who gave it the Ancient Greek name Ἀλεξάνδρεια Ἀραχωσίας ( Alexandria of Arachosia). The extant edicts are found in a plaque of limestone, which probably belonged to a building, and its size is and it is about thick. These are the only Ashoka inscriptions thought to have belonged to a stone building.Une nouvelle inscription grecque d'Açoka, Schlumberger, Daniel, Comptes rendus des séances de l'Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres Année 1964 Volume 108 Numéro 1 pp. 126-14/ref> The beginning and the end of the fragment are lacking, which suggests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piodasses
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was Emperor of Magadha from until his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynasty. His empire covered a large part of the Indian subcontinent, stretching from present-day Afghanistan in the west to present-day Bangladesh in the east, with its capital at Pataliputra. A patron of Buddhism, he is credited with playing an important role in the spread of Buddhism across ancient Asia. The Edicts of Ashoka state that during his eighth regnal year (), he conquered Kalinga after a brutal war. Ashoka subsequently devoted himself to the propagation of "dhamma" or righteous conduct, the major theme of the edicts. Ashoka's edicts suggest that a few years after the Kalinga War, he was gradually drawn towards Buddhism. The Buddhist legends credit Ashoka with establishing a large number of stupas, patronising the Third Buddhist council, supporting Buddhist missiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ai-Khanoum
Ai-Khanoum (, meaning 'Lady Moon'; ) is the archaeological site of a Hellenistic city in Takhar Province, Afghanistan. The city, whose original name is unknown, was likely founded by an early ruler of the Seleucid Empire and served as a military and economic centre for the rulers of the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom until its destruction BC. Rediscovered in 1961, the ruins of the city were excavated by a French team of archaeologists until the outbreak of conflict in Afghanistan in the late 1970s. The city was probably founded between 300 and 285 BC by an official acting on the orders of Seleucus I Nicator or his son Antiochus I Soter, the first two rulers of the Seleucid dynasty. There is a possibility that the site was known to the earlier Achaemenid Empire, who established a small fort nearby. Ai-Khanoum was originally thought to have been a foundation of Alexander the Great, perhaps as Alexandria Oxiana, but this theory is now considered unlikely. Loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greco-Bactrian Kingdom
The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom () was a Ancient Greece, Greek state of the Hellenistic period located in Central Asia, Central-South Asia. The kingdom was founded by the Seleucid Empire, Seleucid satrap Diodotus I, Diodotus I Soter in about 256 BC, and continued to dominate Central Asia until its fall around 120 BC. At its peak the kingdom consisted of present-day Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan, and for a short time, small parts of Kazakhstan, Pakistan and Iran. An extension further east, with military campaigns and settlements, may have reached the borders of the Qin (state), Qin State in China by about 230 BC. Although a Greek population was already present in Bactria by the 5th century BC, Alexander the Great conquered the region by 327 BC and founded many cities, most of them named List of cities founded by Alexander the Great, Alexandria, and further settled with Ancient Macedonians, Macedonians and other Ancient Greece, Greeks. After the death of Alexande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya (Sanskrit: [Help:IPA/Sanskrit, t̪͡ɕɐn̪d̪ɾɐgupt̪ɐ mɐʊɾjɐ]) (reigned 320 BCE – c. 298 BCE) was the founder and the first emperor of the Maurya Empire, based in Magadha (present-day Bihar) in the Indian subcontinent. His rise to power began in the period of unrest and local warfare that arose after Alexander the Great's Indian campaign of Alexander the Great, Indian campaign and early death in 323 BCE, although the exact chronology and sequence of events remains subject to debate among historians. He started a war against the unpopular Nanda dynasty in Magadha on the Ganges, Ganges Valley, defeated them and established his own dynasty. In addition, he raised an army to resist the Greeks, defeated them, and took control of the eastern Indus Valley. His conquest of Magadha is generally dated to ca. 322–319 BCE, and his expansion to Punjab subsequently at ca. 317–312 BCE, but some scholars have speculated that he might have initially con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; Ancient Greek, Greek: Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ, ''Séleukos Nikátōr'', "Seleucus the Victorious"; ) was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general, officer and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to found the eponymous Seleucid Empire, led by the Seleucid dynasty. Initially a secondary player in the power struggles following Alexander's death, Seleucus rose to become the total ruler of Asia Minor, Syria (region), Syria, Mesopotamia, and the Iranian plateau, assuming the title of ''basileus'' (king). The Seleucid Empire was one of the major powers of the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic world, until it was overcome by the Roman Republic and Parthian Empire in the late second and early first centuries BC. While serving under Alexander, Seleucus was commander of the ''Hypaspists, Hypaspistai,'' an elite Macedonian infantry unit. After the death of Alexander in June 323 BC, Seleucus initially supported Perdiccas, the regent of Alexander's em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription
The Kandahar Bilingual Rock Inscription, also known as the Kandahar Edict of Ashoka and less commonly as the Chehel Zina Edict, is an inscription in the Ancient Greek, Greek and Aramaic languages that dates back to 260 BCE and was carved by the Maurya Empire, Mauryan emperor Ashoka () at Chil Zena, Chehel Zina, a mountainous outcrop near Kandahar, Afghanistan. It is among the earliest-known edicts of Ashoka, having been inscribed around the 8th year of his reign (), and precedes all of his other inscriptions, including the Minor Rock Edicts and Barabar Caves in India and the Major Rock Edicts.Valeri P. Yailenk''Les maximes delphiques d'Aï Khanoum et la formation de la doctrine du dharma d'Asoka''. Dialogues d'histoire ancienne vol.16 n°1, 1990, pp. 243. This early inscription was written exclusively in the Greek and Aramaic languages. It was discovered below a layer of rubble in 1958 during an excavation project around Kandahar, and is designated as Kanaanäische und Aram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalinga (historical Kingdom)
Kalinga is a historical region of India. It is generally defined as the eastern coastal region between the Ganges and the Godavari rivers, although its boundaries have fluctuated with the territory of its rulers. The core territory of Kalinga now encompasses all of Odisha and some part of northern Andhra Pradesh. At its widest extent, the Kalinga region also included parts of present-day Chhattisgarh, extending up to Amarkantak in the west. In the ancient period it extended until the bank of the Ganges river. The Kalingas have been mentioned as a major tribe in the legendary text '' Mahabharata''. In the 3rd century BCE, the region came under Mauryan control as a result of the Kalinga War. It was subsequently ruled by several regional dynasties whose rulers bore the title ''Kalingādhipati'' ("Lord of Kalinga"); these dynasties included Mahameghavahana, Vasishtha, Mathara, Pitrbhakta, Shailodbhava, Bhaumkara, Somavamshi, and Eastern Ganga. The medieval era ruler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |