|
Kaizen Costing
Kaizen costing is a cost reduction system used after a product's design has been completed and it is in production. Business professor Yasuhiro Monden defines kaizen costing as The Shogakukan Dictionary’s original definition of Kaizen is translated as ''“The act or making bad points better”.'' In English, the more popular definition of Kaizen is “Change for Better”. Many believe that the Kaizen meaning is “continuous improvement” but, Kaizen is a result of continuous improvement. It exists at the employee’s level. The employee’s goal is to reach their potential, challenge the status quo and achieve continual improvement. Prior to kaizen costing, when the products are under the development phase, target costing is applied. After targets have been set, they are continuously updated to display past improvements and the projected (expected) improvements. Monden has described two types of kaizen costing: * Asset and organization-specific kaizen costing activities pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cost Reduction
Cost reduction is the process used by companies to reduce their costs and increase their profits. Depending on a company’s services or products, the strategies can vary. Every decision in the product development process affects cost: design is typically considered to account for 70–80% of the final cost of a project such as an engineering project or the construction of a building. Companies typically launch a new product without focusing too much on cost. Cost becomes more important when competition increases and price becomes a differentiator in the market. The importance of cost reduction in relation to other strategic business goals is often debated. Cost reduction strategies * Supplier consolidation: see examples in the aerospace manufacturing industry * Component consolidation * Low-cost country sourcing * Request for quotations (RFQ) * Supplier cost breakdown analysis * Function cost analysis / Value analysis / Value engineering * Design for manufacture / Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yasuhiro Monden
Yasuhiro is a masculine Japanese given name. Possible writings Yasuhiro can be written using many different combinations of kanji characters. Here are some examples: *康弘, "healthy, vast" *康広, "healthy, wide" *康寛, "healthy, generosity" *康裕, "healthy, abundant" *康浩, "healthy, vast" *康洋, "healthy, ocean" *康博, "healthy, doctor" *康尋, "healthy, look for" *靖弘, "peaceful, vast" *靖広, "peaceful, wide" *靖寛, "peaceful, generosity" *靖裕, "peaceful, abundant" *靖浩, "peaceful, vast" *靖洋, "peaceful, ocean" *靖博, "peaceful, doctor" *靖尋, "peaceful, look for" *安弘, "tranquil, vast" *安広, "tranquil, wide" *安寛, "tranquil, generosity" *保弘, "preserve, vast" *保洋, "preserve,ocean" *保博, "preserve, doctor" *泰洋, "peaceful, ocean" *泰弘, "peaceful,vast" *泰博, "peaceful, doctor" *易尋, "divination, look for" *易大, "divination,big" *恭大, "respectful, big" The name can also be written in hiragana やすひろ o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaizen
is concept referring to business activities that continuously improve all functions and involve all employees from the CEO to the assembly line workers. ''Kaizen'' also applies to processes, such as purchasing and logistics, that cross organizational boundaries into the supply chain. It has been applied in healthcare, psychotherapy, life coaching, government, and banking. By improving standardized programs and processes, kaizen aims to eliminate waste and redundancies ( lean manufacturing). Kaizen was first practiced in Japanese businesses after World War II, influenced in part by American business and quality-management teachers, and most notably as part of The Toyota Way. It has since spread throughout the world and has been applied to environments outside of business and productivity. Overview The Japanese word means 'change for better', with the inherent meaning of either 'continuous' or 'philosophy' in Japanese dictionaries and in everyday use. The word refers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
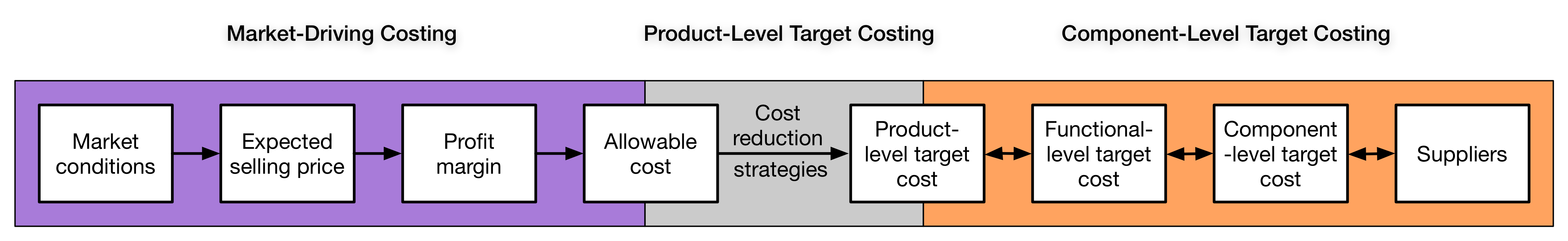
Target Costing
Target costing is an approach to determine a product's life-cycle cost which should be sufficient to develop specified functionality and quality, while ensuring its desired profit. It involves setting a target cost by subtracting a desired profit margin from a competitive market price. A target cost is the maximum amount of cost that can be incurred on a product, however, the firm can still earn the required profit margin from that product at a particular selling price. Target costing decomposes the target cost from product level to component level. Through this decomposition, target costing spreads the competitive pressure faced by the company to product's designers and suppliers. Target costing consists of cost planning in the design phase of production as well as cost control throughout the resulting product life cycle. The cardinal rule of target costing is to never exceed the target cost. However, the focus of target costing is not to minimize costs, but to achieve a desired lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costing
Cost accounting is defined as "a systematic set of procedures for recording and reporting measurements of the cost of manufacturing goods and performing services in the aggregate and in detail. It includes methods for recognizing, classifying, allocating, aggregating and reporting such costs and comparing them with standard costs." (IMA) Often considered a subset of managerial accounting, its end goal is to advise the management on how to optimize business practices and processes based on cost efficiency and capability. Cost accounting provides the detailed cost information that management needs to control current operations and plan for the future. Cost accounting information is also commonly used in financial accounting, but its primary function is for use by managers to facilitate their decision-making. Origins of Cost Accounting All types of businesses, whether manufacturing, trading or producing services, require cost accounting to track their activities. Cost accounting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value Analysis
Value engineering (VE) is a systematic analysis of the functions of various components and materials to lower the cost of goods, products and services with a tolerable loss of performance or functionality. Value, as defined, is the ratio of function to cost. Value can therefore be manipulated by either improving the function or reducing the cost. It is a primary tenet of value engineering that basic functions be preserved and not be reduced as a consequence of pursuing value improvements. The term "value management" is sometimes used as a synonym of "value engineering", and both promote the planning and delivery of projects with improved performance The reasoning behind value engineering is as follows: if marketers expect a product to become practically or stylistically obsolete within a specific length of time, they can design it to only last for that specific lifetime. The products could be built with higher-grade components, but with value engineering they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supply Chain
In commerce, a supply chain is a network of facilities that procure raw materials, transform them into intermediate goods and then final products to customers through a distribution system. It refers to the network of organizations, people, activities, information, and resources involved in delivering a product or service to a consumer. Supply chain activities involve the transformation of natural resources, raw materials, and components into a finished product and delivering the same to the end customer. In sophisticated supply chain systems, used products may re-enter the supply chain at any point where residual value is recyclable. Supply chains link value chains. Suppliers in a supply chain are often ranked by "tier", with first-tier suppliers supplying directly to the client, second-tier suppliers supplying to the first tier, and so on. Overview A typical supply chain begins with the ecological, biological, and political regulation of natural resources, followed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waste
Waste (or wastes) are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use. A by-product, by contrast is a joint product of relatively minor economic value. A waste product may become a by-product, joint product or resource through an invention that raises a waste product's value above zero. Examples include municipal solid waste (household trash/refuse), hazardous waste, wastewater (such as sewage, which contains bodily wastes ( feces and urine) and surface runoff), radioactive waste, and others. Definitions What constitutes waste depends on the eye of the beholder; one person's waste can be a resource for another person. Though waste is a physical object, its generation is a physical and psychological process. The definitions used by various agencies are as below. United Nations Environment Program According to the Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costs
In production, research, retail, and accounting, a cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something or deliver a service, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it is counted as cost. In this case, money is the input that is gone in order to acquire the thing. This acquisition cost may be the sum of the cost of production as incurred by the original producer, and further costs of transaction as incurred by the acquirer over and above the price paid to the producer. Usually, the price also includes a mark-up for profit over the cost of production. More generalized in the field of economics, cost is a metric that is totaling up as a result of a process or as a differential for the result of a decision. Hence cost is the metric used in the standard modeling paradigm applied to economic processes. Costs (pl.) are often further described based on thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |