|
Kaddare Script
The Kaddare script is a poorly known alphabetic script created to transcribe the Somali language. There are no known books written in the script. History The script was invented in 1952 by a Sufi Sheikh, named Hussein Sheikh Ahmed Kaddare. The Somali Language Committee, tasked in 1961 with deciding on a script for the nation after independence, recommended the Kaddare script, but had to settle for the Latin alphabet due to economic constraints. They appraised Kaddare as being the most accurate indigenous script for transcribing the Somali language. See also *Somali orthography *Borama alphabet, Borama *Osmanya alphabet, Osmanya References External links Kaddare alphabetat Omniglot * The report of the Somali Language Committee Writing systems of Africa Somali orthography Somali inventions Writing systems introduced in 1952 {{alphabet-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somali Language
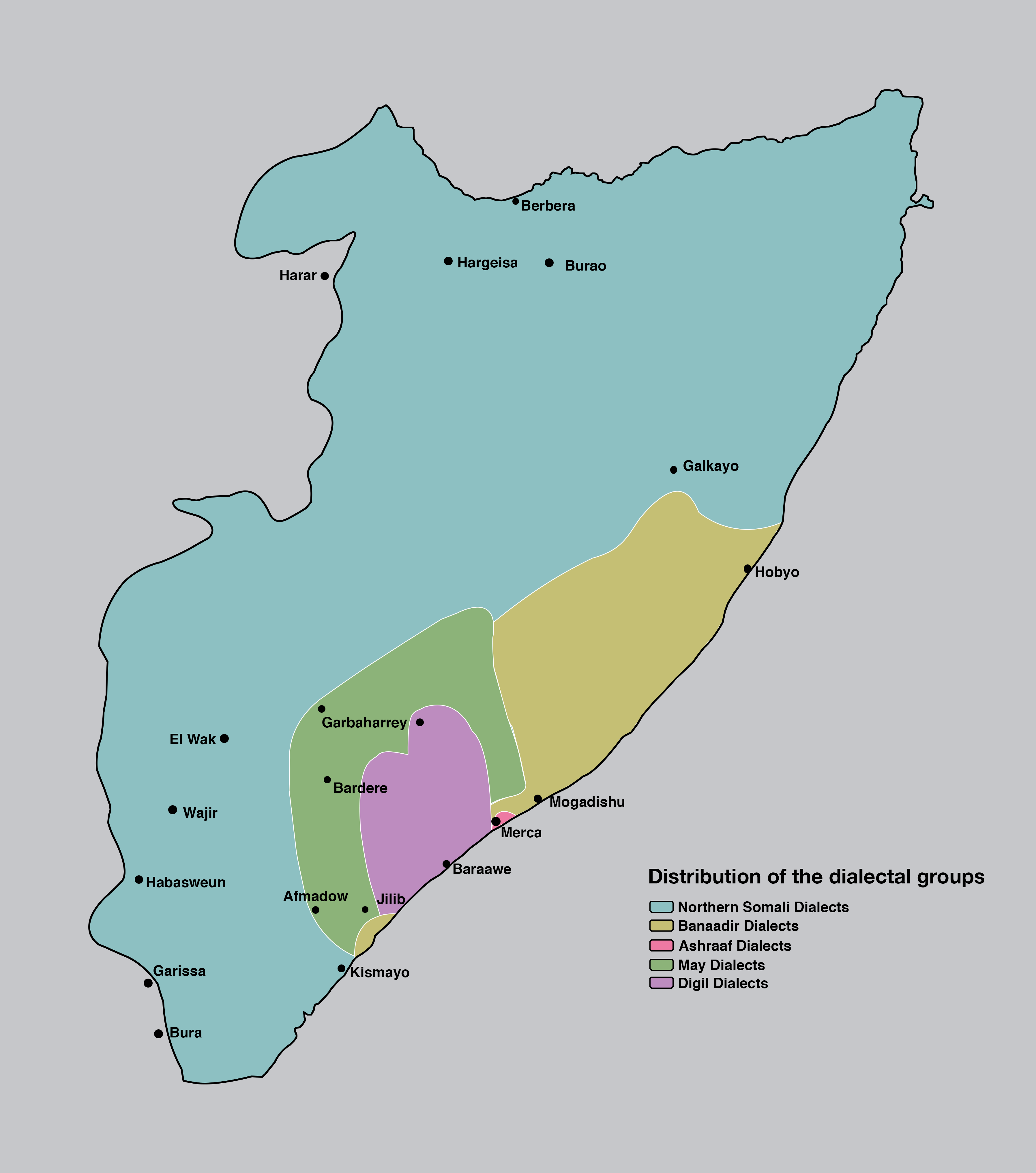
Somali is an Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic languages, Cushitic branch, primarily spoken by the Somalis, Somali people, native to Greater Somalia. It is an official language in Somalia, Somaliland, and Ethiopia; one of the two national languages in Djibouti; and a recognised minority language in Kenya. Somali is officially written in the Latin script (Somali Latin alphabet), with the Arabic script (Wadaad's writing) and several local scripts (Osmanya script, Osmanya, Kaddare script, Kaddare and Gadabuursi Somali Script, Borama scripts) being informally used.Lewis, I.M. (1958)The Gadabuursi Somali Script ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies'', University of London, Vol. 21, pp. 134–156. Classification Somali is classified within the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family, specifically, Lowland East Cushitic languages, Lowland East Cushitic in addition to Afar language, Afar and Saho language, Saho. Somali is the bes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letter (alphabet), letters written to represent particular sounds in a spoken language. Specifically, letters largely correspond to phonemes as the smallest sound segments that can distinguish one word from another in a given language. Not all writing systems represent language in this way: a syllabary assigns symbols to spoken syllables, while logographies assign symbols to words, morphemes, or other semantic units. The first letters were invented in Ancient Egypt to serve as an aid in writing Egyptian hieroglyphs; these are referred to as Egyptian uniliteral signs by lexicographers. This system was used until the 5th century AD, and fundamentally differed by adding pronunciation hints to existing hieroglyphs that had previously carried no pronunciation information. Later on, these phonemic symbols also became used to transcribe foreign words. The first fully phonemic script was the Proto-Sinaitic script, also descending from Egyptian hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabetic Script
An alphabet is a standard set of letters written to represent particular sounds in a spoken language. Specifically, letters largely correspond to phonemes as the smallest sound segments that can distinguish one word from another in a given language. Not all writing systems represent language in this way: a syllabary assigns symbols to spoken syllables, while logographies assign symbols to words, morphemes, or other semantic units. The first letters were invented in Ancient Egypt to serve as an aid in writing Egyptian hieroglyphs; these are referred to as Egyptian uniliteral signs by lexicographers. This system was used until the 5th century AD, and fundamentally differed by adding pronunciation hints to existing hieroglyphs that had previously carried no pronunciation information. Later on, these phonemic symbols also became used to transcribe foreign words. The first fully phonemic script was the Proto-Sinaitic script, also descending from Egyptian hieroglyphs, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hussein Sheikh Ahmed Kaddare
Hussein Sheikh Ahmed Kaddare (, ; 2 March 1934 – 1 February 2015) was a Somali people, Somali inventor, linguist, and researcher in Somali traditions and folklore. Kaddare contributed his linguistic expertise in Somalia's Ministry of information. Kaddare is widely known for creating the Kaddare script used in transcribing the Somali language. Biography Kaddare was born in the town of Adale in the Middle Shebelle region of Somalia in 1934. In 1953, he created the Kaddare script, an orthography named after him that was used to transcribe the Somali language He died on February 1, 2015, in Mogadishu after battling an unspecified illness. See also * Kaddare script * Osmanya script * Borama script * Wadaad's writing * Osman Yusuf Kenadid * Sheikh Abdurahman Sheikh Nuur Notes References * * External links Somali Language History and Vernaculars''The Gadabuursi Somali Script'' - qasidas in Gadabuursi/Borama 1934 births 2015 deaths Translators to Somali Ethnic Somali peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Chicago Press
The University of Chicago Press is the university press of the University of Chicago, a Private university, private research university in Chicago, Illinois. It is the largest and one of the oldest university presses in the United States. It publishes a wide range of academic titles, including ''The Chicago Manual of Style'', numerous academic journals, and advanced monographs in the academic fields. The press is located just south of the Midway Plaisance on the University of Chicago campus. One of its quasi-independent projects is the BiblioVault, a digital repository for scholarly books. History The University of Chicago Press was founded in 1890, making it one of the oldest continuously operating university presses in the United States. Its first published book was Robert F. Harper's ''Assyrian and Babylonian Letters Belonging to the Kouyunjik Collections of the British Museum''. The book sold five copies during its first two years, but by 1900, the University of Chicago Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cursive Writing Of Kaddare
Cursive (also known as joined-up writing) is any style of penmanship in which characters are written joined in a flowing manner, generally for the purpose of making writing faster, in contrast to block letters. It varies in functionality and modern-day usage across languages and regions; being used both publicly in artistic and formal documents as well as in private communication. Formal cursive is generally joined, but casual cursive is a combination of joins and pen lifts. The writing style can be further divided as "looped", " italic", or "connected". The cursive method is used with many alphabets due to infrequent pen lifting which allows increased writing speed. However, more elaborate or ornamental calligraphic styles of writing can be slower to reproduce. In some alphabets, many or all letters in a word are connected, sometimes making a word one single complex stroke. History Cursive is a style of penmanship in which the symbols of the language are written in a conjoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somali Orthography
A number of writing systems have been used to transcribe the Somali language. Of these, the Somali Latin alphabet is the most widely used. It has been the official writing script in Somalia since the Supreme Revolutionary Council (Somalia), Supreme Revolutionary Council formally introduced it in October 1972, and was disseminated through a nationwide Somali Rural Literacy Campaign, rural literacy campaign. Prior to the twentieth century, the Arabic script was used for writing Somali. An extensive literary and administrative corpus exists in Arabic script. It was the main script historically used by the various Somali sultans to keep records. Writing systems developed locally in the twentieth century include the Osmanya alphabet, Osmanya, Borama alphabet, Borama and Kaddare alphabet, Kaddare scripts. Latin script The Somali Latin script, or Somali Latin alphabet, was developed by a number of leading scholars of Somali language, Somali, including Musa Haji Ismail Galal, Bogumił An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borama Alphabet
The Gadabuursi script, also known as the Borama script (Borama: ), at is an for the . It was devised around 1933 by Sheikh Abdurahman Sheikh Nuur of the clan.
|
Osmanya Alphabet
Osmanya (, ), known in Somali as ''Far Soomaali'' (, "Somali writing") and in Arabic as ''al-kitābah al-ʿuthmānīyah'' (; "Osman writing"), is an alphabetic script created to transcribe the Somali language. It was invented by Osman Yusuf Kenadid, the son of Sultan Yusuf Ali Kenadid and brother of Sultan Ali Yusuf Kenadid of the Sultanate of Hobyo. Material written in the script is 'almost non-existent,' so it is difficult to describe its use with certainty. History While Osmanya gained reasonable acceptance for correspondence and bookkeeping at the local level, it met fierce resistance as a national script for several reasons: it was identified with the Majeerteen clan, who supported the Italian colonial government, rather than with the Somali nation as a whole view that has changed somewhat in the 21st century there was opposition to making Somali rather than Arabic the official language of the country, and in addition there was opposition to using any indigenous sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omniglot
Omniglot () is an online encyclopedia focused on languages and writing systems. Etymology The name "Omniglot" comes from the Latin prefix (meaning "all") and the Greek root (, meaning "tongue"). History The website was launched by British author Simon Ager in 1998, originally intended to be a web design and translation service. As Ager collected and added more information about languages and various writing systems, the project evolved into an encyclopedia. It provides reference materials for some 300 written scripts used in different languages, over 1,000 constructed, adapted and fictional scripts, and materials for learning languages. It also has reference materials in numerous languages. Its material was the source for a compendium of characters used for development of artificial intelligence, the Omniglot Challenge. The Omniglot compendium has been used widely since it was first released. As of November 2024, the number of languages detailed on the site is over 2,100 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadaad's Writing
''Wadaad's'' writing, also known as ''Wadaad's'' Arabic (), is either a mixture of Arabic and Somali in writing, or the non-standardized adaption of the Arabic script to write the Somali language. Originally, it referred to a non-grammatical Arabic featuring some words from the Somali language, with the proportion of Somali vocabulary varying depending on the context. The Somali people, Somalis were among the first people in Africa to embrace Islam. Alongside standard Arabic, ''Wadaad's'' writing was used by Somali religious men ''(Wadaado)'' to record ''xeer'' (customary law) petitions and to write ''qasidas.'' It was also used by merchants for business purposes and letter writing. Over the years, various Somali scholars improved and altered the use of the Arabic script for conveying Somali. This culminated in the 1930s with the work of Mahammad 'Abdi Makaahiil, standardizing Arabic diacritics, vowel diacritics and orthographic conventions, and in the 1950s with the controversi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osmanya Script
Osmanya (, ), known in Somali as ''Far Soomaali'' (, "Somali writing") and in Arabic as ''al-kitābah al-ʿuthmānīyah'' (; "Osman writing"), is an alphabetic script created to transcribe the Somali language. It was invented by Osman Yusuf Kenadid, the son of Sultan Yusuf Ali Kenadid and brother of Sultan Ali Yusuf Kenadid of the Sultanate of Hobyo. Material written in the script is 'almost non-existent,' so it is difficult to describe its use with certainty. History While Osmanya gained reasonable acceptance for correspondence and bookkeeping at the local level, it met fierce resistance as a national script for several reasons: it was identified with the Majeerteen clan, who supported the Italian colonial government, rather than with the Somali nation as a whole view that has changed somewhat in the 21st century there was opposition to making Somali rather than Arabic the official language of the country, and in addition there was opposition to using any indigenous script rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |