|
Juniper Berries
A juniper berry is the female seed cone produced by the various species of junipers. It is not a true berry but a cone with unusually fleshy and merged scales called a galbulus, which gives it a berry-like appearance. The cones from a handful of species, especially ''Juniperus communis'', are used as a spice, particularly in European cuisine, and also give gin its distinctive flavour. Juniper berries are among the only spices derived from conifers, along with spruce buds. Description Unlike the separated and woody scales of a typical pine cone, those in a juniper berry remain fleshy and merge into a unified covering surrounding the seeds. Juniper berries are sometimes regarded as arils, like the berry-like cones of yews. ''Juniperus communis'' berries vary from to in diameter; other species are mostly similar in size, though some are larger, notably '' J. drupacea'' (). The berries are green when young and mature to purple-black over about 18 months in most species, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juniperus Communis Fruits - Keila
Junipers are coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Juniperus'' ( ) of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending on the taxonomy, between 50 and 67 species of junipers are widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere as far south as tropical Africa, including the Arctic, parts of Asia, and Central America. The highest-known juniper forest occurs at an altitude of in southeastern Tibet and the northern Himalayas, creating one of the highest tree lines on earth. Description Junipers vary in size and shape from tall trees, tall, to columnar or low-spreading shrubs with long, trailing branches. They are evergreen with needle-like and/or scale-like leaves. They can be either monoecious or dioecious. The female seed cones are very distinctive, with fleshy, fruit-like coalescing scales which fuse together to form a berrylike structure (galbulus), long, with one to 12 unwinged, hard-shelled seeds. In some species, these "berries" are red-brown or orange, but in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essential Oil
An essential oil is a concentrated hydrophobic liquid containing volatile (easily evaporated at normal temperatures) chemical compounds from plants. Essential oils are also known as volatile oils, ethereal oils, aetheroleum, or simply as the oil of the plant from which they were extracted, such as oil of clove. An essential oil is essential in the sense that it contains the essence of the plant's fragrance—the characteristic fragrance of the plant from which it is derived. The term "essential" used here does ''not'' mean required or usable by the human body, as with the terms essential amino acid or essential fatty acid, which are so called because they are nutritionally required by a living organism. Essential oils are generally extracted by distillation, often by using steam. Other processes include expression, solvent extraction, '' sfumatura'', absolute oil extraction, resin tapping, wax embedding, and cold pressing. They are used in perfumes, cosmetics, soaps, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
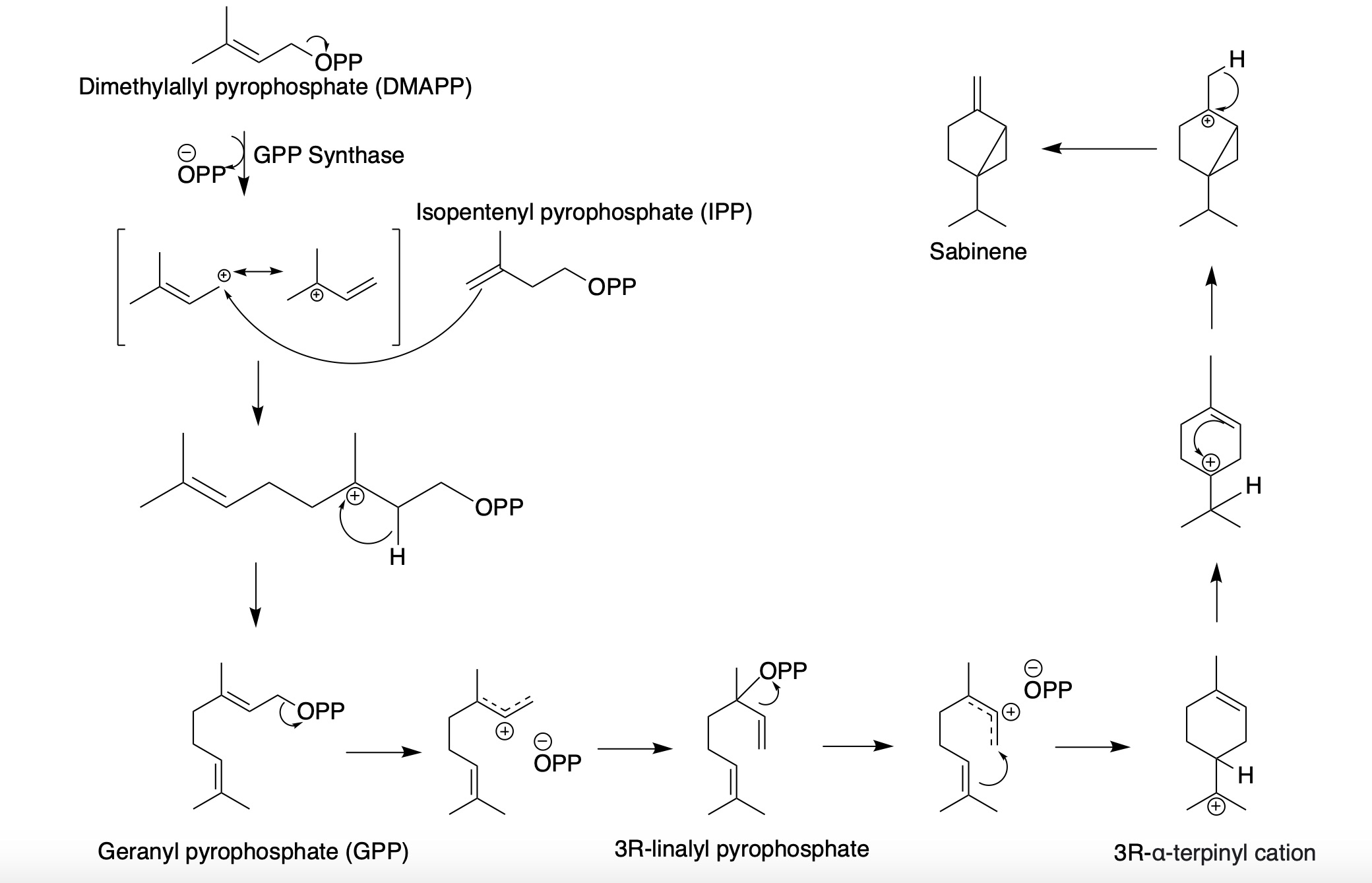
Sabinene
Sabinene is a natural bicyclic monoterpene with the molecular formula C10H16. It is isolated from the essential oils of a variety of plants including Marjoram, holm oak (''Quercus ilex'') and Norway spruce (''Picea abies''). It has a strained ring system with a cyclopentane ring fused to a cyclopropane ring. Sabinene is one of the chemical compounds that contributes to the spiciness of black pepper and is a major constituent of carrot seed oil. It also occurs in tea tree oil at a low concentration. It is also present in the essential oil obtained from nutmeg, '' Laurus nobilis'', and '' Clausena anisata''. Biosynthesis Sabinene, a bicyclic monoterpene, is present in the (+) and (-) enantiomer In chemistry, an enantiomer (Help:IPA/English, /ɪˈnænti.əmər, ɛ-, -oʊ-/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''ih-NAN-tee-ə-mər''), also known as an optical isomer, antipode, or optical antipode, is one of a pair of molecular entities whi ...s. It is biosynthesized from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinene
Pinene is a collection of unsaturated bicyclic monoterpenes. Two geometric isomers of pinene are found in nature, α-pinene and β-pinene. Both are chiral. As the name suggests, pinenes are found in pines. Specifically, pinene is the major component of the liquid extracts of conifers. Pinenes are also found in many non-coniferous plants such as camphorweed ('' Heterotheca'') and big sagebrush ('' Artemisia tridentata''). Isomers Biosynthesis α-Pinene and β-pinene are both produced from geranyl pyrophosphate, via cyclisation of linaloyl pyrophosphate followed by loss of a proton from the carbocation equivalent. Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology and the Joint BioEnergy Institute have been able to synthetically produce pinene with a bacterium. Plants Alpha-pinene is the most widely encountered terpenoid in nature and is highly repellent to insects. Alpha-pinene appears in conifers and numerous other plants. Pinene is a major component of the essent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually faint, and may be similar to that of gasoline or Naphtha, lighter fluid. They occur in a diverse range of molecular structures and phases: they can be gases (such as methane and propane), liquids (such as hexane and benzene), low melting solids (such as paraffin wax and naphthalene) or polymers (such as polyethylene and polystyrene). In the fossil fuel industries, ''hydrocarbon'' refers to naturally occurring petroleum, natural gas and coal, or their hydrocarbon derivatives and purified forms. Combustion of hydrocarbons is the main source of the world's energy. Petroleum is the dominant raw-material source for organic commodity chemicals such as solvents and polymers. Most anthropogenic (human-generated) emissions of greenhouse gases are eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic Compound
Aromatic compounds or arenes are organic compounds "with a chemistry typified by benzene" and "cyclically conjugated." The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on odor, before their general chemical properties were understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation to their odor. Aromatic compounds are now defined as cyclic compounds satisfying Hückel's rule. Aromatic compounds have the following general properties: * Typically unreactive * Often non polar and hydrophobic * High carbon-hydrogen ratio * Burn with a strong sooty yellow flame, due to high C:H ratio * Undergo electrophilic substitution reactions and nucleophilic aromatic substitutions Arenes are typically split into two categories - benzoids, that contain a benzene derivative and follow the benzene ring model, and non-benzoids that contain other aromatic cyclic derivatives. Aromatic compounds are commonly used in organic synthesis and are involved in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terpene
Terpenes () are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n ≥ 2. Terpenes are major biosynthetic building blocks. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predominantly by plants, particularly Pinophyta, conifers. In plants, terpenes and terpenoids are important mediators of ecological biological interaction, interactions, while some insects use some terpenes as a form of defense. Other functions of terpenoids include cell growth modulation and plant elongation, light harvesting and photoprotection, and membrane permeability and fluidity control. Terpenes are classified by the number of carbons: monoterpenes (C10), sesquiterpenes (C15), diterpenes (C20), as examples. The terpene alpha-pinene is a major component of the common solvent, turpentine. The one terpene that has major applications is natural rubber (i.e., polyisoprene). The possibility that other terpenes could be used as precursors to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an Branched chain fatty acids, unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important diet (nutrition), dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cell (biology), cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extract
An extract (essence) is a substance made by extracting a part of a raw material, often by using a solvent such as ethanol, oil or water. Extracts may be sold as tinctures or absolutes or dried and powdered. The aromatic principles of many spices, nuts, herbs, fruits, etc., and some flowers, are marketed as extracts, among the best known of true extracts being almond, cinnamon, cloves, ginger, lemon, nutmeg, orange, peppermint, pistachio, rose, spearmint, vanilla, violet, rum, and wintergreen. Extraction techniques Most natural essences are obtained by extracting the essential oil from the feedstock, such as blossoms, fruit, and roots, or from intact plants through multiple techniques and methods: * Expression ( juicing, pressing) involves physical extraction material from feedstock, used when the oil is plentiful and easily obtained from materials such as citrus peels, olives, and grapes. * Absorption (steeping, decoction). Extraction is done by soak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formic Acid
Formic acid (), systematically named methanoic acid, is the simplest carboxylic acid. It has the chemical formula HCOOH and structure . This acid is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in some ants. Esters, salts, and the anion derived from formic acid are called formates. Industrially, formic acid is produced from methanol. Natural occurrence Formic acid, which has a pungent, penetrating odor, is found naturally in insects, weeds, fruits and vegetables, and forest emissions. It appears in most ants and in stingless bees of the genus '' Oxytrigona''. Wood ants from the genus ''Formica'' can spray formic acid on their prey or to defend the nest. The puss moth caterpillar (''Cerura vinula'') will spray it as well when threatened by predators. It is also found in the trichomes of stinging nettle (''Urtica dioica''). Apart from that, this acid is incorporated in many fruits such as pineapple (0.21 mg per 100 g), apple (2 mg per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malic Acid
Malic acid is an organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a dicarboxylic acid that is made by all living organisms, contributes to the sour taste of fruits, and is used as a food additive. Malic acid has two stereoisomeric forms (L- and D-enantiomers), though only the L-isomer exists naturally. The salts and esters of malic acid are known as malates. The malate anion is a metabolic intermediate in the citric acid cycle. Etymology The word 'malic' is derived from Latin , meaning 'apple'. The related Latin word , meaning 'apple tree', is used as the name of the genus ''Malus'', which includes all apples and crabapples; and is the origin of other taxonomic classifications such as Maloideae, Malinae, and Maleae. Biochemistry L-Malic acid is the naturally occurring form, whereas a mixture of L- and D-malic acid is produced synthetically. File:L-Äpfelsäure.svg, L-Malic acid (''S'') File:D-Äpfelsäure.svg, D-Malic acid (''R'') Malate plays an important role i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. Historically, vinegar was produced from the third century BC and was likely the first acid to be produced in large quantities. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important Reagent, chemical reagent and industrial chemical across various fields, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood Adhesive, glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the E number, food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is funda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |