|
Jules Louis Bolé, Marquis De Chamlay
Jules-Louis Bolé de Chamlay (1650–1719) was a French soldier and diplomat. He was born in a noble family; his father was procureur of the Paris Parlement. Chamlay had a classical education, and the fought in the French army during the Franco-Dutch War (1672–1678). He received the title of ''maréchal général des logis aux camps et armées du Roi''. He had a meteoric rise, and some years later, he was generally appreciated by the most important generals of his time, like Condé and Turenne. He also became one of the most important aides to Louvois. Very appreciated and listened to by King Louis XIV, he played an important role in determining the "stratégie de cabinet." When Louvois died, the King offered him the Ministry of War, but he had the modesty to refuse and leave the function for Barbezieux, son of Louvois, under whose orders he continued to work. The King entrusted him with several diplomatic missions. Chamlay also seemed to have played an important role in creat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
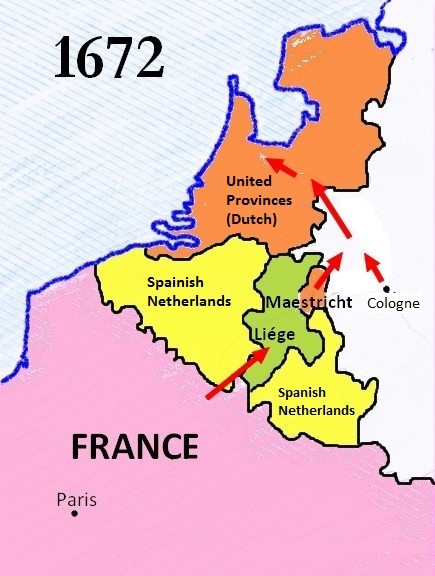
Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, 1672 to 1678, was primarily fought by Kingdom of France, France and the Dutch Republic, with both sides backed at different times by a variety of allies. Related conflicts include the 1672 to 1674 Third Anglo-Dutch War and 1675 to 1679 Scanian War. In May 1672, France nearly overran the Netherlands, an event remembered in Dutch history as the ''Rampjaar'', or "Disaster Year". However, by late July the position had stabilised, while concern over French gains brought the Dutch support from Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor Leopold I, Habsburg Spain, Spain and Brandenburg-Prussia. Previously an ally of France, Kingdom of England, England Treaty of Westminster (1674), exited the war in February 1674. Now facing a war of attrition on several fronts, Louis XIV of France instead focused on strengthening French borders with the Spanish Netherlands and Rhineland, while a coalition led by William III of England, William of Orange sought to minimise any losses. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis, Prince Of Condé (1621–1686)
Louis, Prince of Condé may refer to: * Louis, Prince of Condé (1530–1569) Louis, Prince of Condé may refer to: * Louis, Prince of Condé (1530–1569), Huguenot leader and general * Louis, Prince of Condé (1621–1686) * Louis, Prince of Condé (1668–1710) {{disambiguation, tndis ..., Huguenot leader and general * Louis, Prince of Condé (1621–1686) * Louis, Prince of Condé (1668–1710) {{disambiguation, tndis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri De La Tour D'Auvergne, Vicomte De Turenne
Henri de La Tour d'Auvergne, vicomte de Turenne (11 September 161127 July 1675), commonly known as Turenne (), was a French general and one of only six Marshal of France, marshals to have been promoted Marshal General of France. The most illustrious member of the La Tour d'Auvergne family, his military exploits over his five-decade career earned him a reputation as one of the greatest military commanders in history. Born to a Huguenot family, the son of a Henri de La Tour d'Auvergne, Duke of Bouillon, Marshal of France, he was introduced to the art of war at a young age. He first served as a volunteer in the Dutch States Army under the orders of his maternal uncles Maurice of Nassau and Frederick Henry, Prince of Orange, Frederick Henry before pursuing his career in the service of France, where his noble origins and proven qualities soon saw him rise to the top of the military hierarchy. He rose to prominence during the Thirty Years' War by Battle of Breisach, capturing the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Michel Le Tellier De Louvois
François () is a French masculine given name and surname, equivalent to the English name Francis. People with the given name * François Amoudruz (1926–2020), French resistance fighter * François-Marie Arouet (better known as Voltaire; 1694–1778), French Enlightenment writer, historian, and philosopher * François Beauchemin (born 1980), Canadian ice hockey player for the Anaheim Ducks * François Blanc (1806–1877), French entrepreneur and operator of casinos * François Bonlieu (1937–1973), French alpine skier * François Cevert (1944–1973), French racing driver * François Chau (born 1959), Cambodian American actor * François Clemmons (born 1945), American singer and actor * François Corbier (1944–2018), French television presenter and songwriter * François Coty (1874–1934), French perfumer * François Coulomb the Elder (1654–1717), French naval architect * François Coulomb the Younger (1691–1751), French naval architect * François Couperin (1668� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis François Marie Le Tellier
Louis François Marie Le Tellier, Marquis of Barbezieux (23 June 1668 – 5 January 1701) was a French statesman. Biography Born in Barbezieux-Saint-Hilaire (Charente), he was the third son of the François-Michel le Tellier, Marquis de Louvois, Marquis de Louvois, War Minister to Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV. After the death of Louvois, Louis XIV appointed Barbezieux to succeed his father and grandfather, becoming the third Le Tellier to serve Louis XIV at the War Ministry. Although talented, the 23-year-old neglected his office in favour of his pleasures. The King complained to Barbezieux's uncle, Charles-Maurice Le Tellier, Archbishop of Reims that:''Your nephew has talents, but he does not make good use of them. He prefers to dine with princes rather than work. He neglected his affairs for his pleasures. He leaves officers waiting too long in his antechamber; he speaks to them disdainfully and sometimes harshly.'' Marriage and Children Barbezieux was twice married: *firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Per Head
A poll tax, also known as head tax or capitation, is a lump-sum tax, tax levied as a fixed sum on every liable individual (typically every adult), without reference to income or resources. ''Poll'' is an archaic term for "head" or "top of the head". The sense of "counting heads" is found in phrases like polling place and opinion poll. Head taxes were important sources of revenue for many governments from ancient times until the 19th century. In the United Kingdom, poll taxes were levied by the governments of John of Gaunt in the 14th century, Charles II of England, Charles II in the 17th and Margaret Thatcher in the 20th century. In the United States, voting poll taxes (whose payment was a precondition to voting in an election) have been used to Disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction Era, disenfranchise impoverished and minority voters (especially after Reconstruction Era, Reconstruction). Poll taxes are Regressive tax, regressive, meaning the higher someone's income is, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean De La Bruyère
Jean de La Bruyère (, , ; 16 August 1645 – 11 May 1696) was a French philosopher and moralist, who was noted for his satire. Early years Jean de La Bruyère was born in Paris, in today's Essonne ''département'', in 1645. His family was middle class, and his reference to a certain "Geoffroy de La Bruyère", a crusader, is only a satirical illustration of a method of self-ennoblement then common in France, as in some other countries. As such, he signed his surname as Delabruyère in one word, as evidence of this disdain. La Bruyère could trace his family back on his father's side at least as far as his great-grandfather, who along with his grandfather had been dedicated members of the Catholic League. His great-grandfather had been exiled from France when Henry IV came to the throne and Catholics fell into disfavor. La Bruyère's father also had been active in the league under the Duke of Guise in 1584. His father was controller general of finance to the Hôtel de Vill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis De Rouvroy, Duc De Saint-Simon
Louis de Rouvroy, duc de Saint-Simon, Grandee of Spain, GE (; 16 January 16752 March 1755), was a French soldier, diplomat, and memoirist. He was born in Paris at the Hôtel Selvois, 6 rue Taranne (demolished in 1876 to make way for the Boulevard Saint-Germain). The family's ducal peerage (''duché-pairie''), granted in 1635 to his father Claude de Rouvroy, duc de Saint-Simon, Claude de Rouvroy (1608–1693), served as both perspective and theme in Saint-Simon's life and writings. He was the second and last Duke of Saint-Simon. His enormous memoirs are a classic of French literature, giving the fullest and most lively account of the court at Palace of Versailles, Versailles of Louis XIV and the ''Régence'' at the start of Louis XV's reign. Peerage of France Men of the nobility, noblest blood (in Saint-Simon's view) might not be, and in most cases were not, peers in France. Derived at least traditionally and imaginatively from the ''douze pairs'' (twelve peers) of Charlemagne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Cross
Grand Cross is the highest class in many orders, and manifested in its insignia. Exceptionally, the highest class may be referred to as Grand Cordon or equivalent. In other cases, there may exist a rank even higher than Grand Cross, e.g. Grand Collar. In rare cases, the insignia itself is referred to as the "grand cross".Burke, B. ''The Book of Orders of Knighthood and Decorations of Honour of All Nations.'' Uckfield: Naval & Military Press, 2016. In international relations, many times the class of Grand Cross is typically reserved for royalty, heads of state and equivalent. Sometimes a holder of the highest class or grade are referred to as "Commander Grand Cross", "Knight Grand Cross", or just "Grand Cross". In the United Kingdom, the rank of "Knight Grand Cross" or "Dame Grand Cross" allows the recipient to continue to use the honorific " Sir" (male) or "Dame" (female) as a style before his or her name. The knighthood is initially conferred, as in other countries, at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Saint Louis
The Royal and Military Order of Saint Louis () is a dynastic order of chivalry founded 5 April 1693 by King Louis XIV, named after Saint Louis (King Louis IX of France). It was intended as a reward for exceptional officers, notable as the first decoration that could be granted to non-nobles. By the authorities of the French Republic, it is considered a predecessor of the Legion of Honour, with which it shares the red ribbon (though the Legion of Honour is awarded to military personnel and civilians alike). Although officially abolished by the government authorities of the July Revolution in 1830 following the French Revolution, its activities carried on as a dynastic order of the formerly sovereign royal family. As such, it is still recognised by the International Commission on Orders of Chivalry. (PDF) Members |
Diplomats For France
A diplomat (from ; romanized ''diploma'') is a person appointed by a state, intergovernmental, or nongovernmental institution to conduct diplomacy with one or more other states or international organizations. The main functions of diplomats are representation and protection of the interests and nationals of the sending state; initiation and facilitation of strategic agreements, treaties and conventions; and promotion of information, trade and commerce, technology, and friendly relations. Seasoned diplomats of international repute are used in international organizations (for example, the United Nations, the world's largest diplomatic forum) as well as multinational companies for their experience in management and negotiating skills. Diplomats are members of foreign services and diplomatic corps of various nations of the world. The sending state is required to get the consent of the receiving state for a person proposed to serve in key diplomatic positions such as an ambassado ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1650 Births
Events January–March * January 7 – Louis I, Prince of Anhalt-Köthen, dies after a reign of more than 63 years. The area is now part of the northeastern German state of Saxony-Anhalt. * January 18 – Cardinal Mazarin, Cardinal Jules Mazarin, the Chief Minister of France and head of its government since 1642, learns of a plot against him and has the Louis II de Bourbon, Prince de Condé, Prince de Condé, the Armand de Bourbon, prince de Conti, Prince de Conti and the Henri II d'Orléans, Duke of Longueville, Duc de Longueville arrested, prompting The Fronde, a rebellion by parliament against the Crown. * January 28 – The Sultan bin Saif of Oman expels the Portuguese colonial government from Muscat, forcing the surrender of the port of Muttrah and of Fort Capitan, and captures two warships, ending 35 years of Portuguese occupation. * February 1 – The French verse play ''Andromède'', commissioned by Cardinal Mazarin, written by Pierre Corneille ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |