|
Juan De La Cruz Salvo
Juan José de la Cruz Salvo y Poblete (Santiago; 1842 — 1917) was a Chilean soldier who fought in the War of the Pacific as a Sergeant major. He is best known for being the envoy sent by the Chilean Army to the Casa Bolognesi, headquarters of Francisco Bolognesi's garrison in Arica to request his surrender after the allied defeat at the Battle of Tacna, to which Bolognesi replied by saying he would "fight until the last cartridge is spent" (). Painting A La respuesta (painting), painting by Peruvian painter Juan Lepiani illustrates the meeting between Salvo and Bolognesi. See also *Battle of Arica References {{reflist Chilean military personnel of the War of the Pacific Bernardo O'Higgins Military Academy alumni People from Santiago, Chile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santiago
Santiago (, ; ), also known as Santiago de Chile (), is the capital and largest city of Chile and one of the largest cities in the Americas. It is located in the country's central valley and is the center of the Santiago Metropolitan Region, which has a population of seven million, representing 40% of Chile's total population. Most of the city is situated between above sea level. Founded in 1541 by the Spanish conquistador Pedro de Valdivia, Santiago has served as the capital city of Chile since colonial times. The city features a downtown core characterized by 19th-century neoclassical architecture and winding side streets with a mix of Art Deco, Gothic Revival, and other styles. Santiago's cityscape is defined by several standalone hills and the fast-flowing Mapocho River, which is lined by parks such as Parque Bicentenario, Parque Forestal, and Parque de la Familia. The Andes Mountains are visible from most parts of the city and contribute to a smog problem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
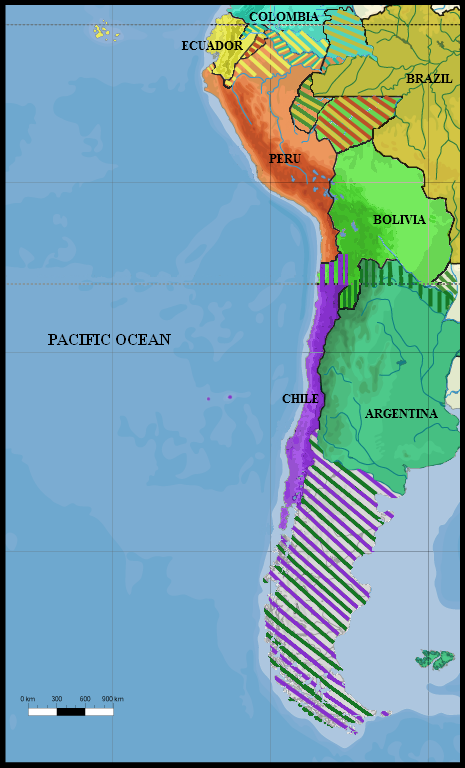
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Pacific Ocean. Chile had a population of 17.5 million as of the latest census in 2017 and has a territorial area of , sharing borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. The country also controls several Pacific islands, including Juan Fernández Islands, Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas Islands, Desventuradas, and Easter Island, and claims about of Antarctica as the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The capital and largest city of Chile is Santiago, and the national language is Spanish language, Spanish. Conquest of Chile, Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Incas in Central Chile, Inca rule; however, they Arauco War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Pacific
The War of the Pacific (), also known by War of the Pacific#Etymology, multiple other names, was a war between Chile and a Treaty of Defensive Alliance (Bolivia–Peru), Bolivian–Peruvian alliance from 1879 to 1884. Fought over Atacama Desert border dispute, Chilean claims on Litoral Department, coastal Bolivian territory in the Atacama Desert, the war ended with victory for Chile, which gained a significant amount of resource-rich territory from Peru and Bolivia. The direct cause of the war was a nitrate taxation dispute between Bolivia and Chile, with Peru being drawn in due to its secret alliance with Bolivia. Some historians have pointed to deeper origins of the war, such as the interest of Chile and Peru in the nitrate business, a long-standing rivalry between Chile and Peru for regional hegemony, as well as the political and economical disparities between the stability of Chile and the volatility of Peru and Bolivia. In February 1878, Bolivia increased taxes on the Chile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergeant Major
Sergeant major is a senior Non-commissioned officer, non-commissioned Military rank, rank or appointment in many militaries around the world. History In 16th century Spain, the ("sergeant major") was a general officer. He commanded an army's infantry, and ranked about third in the army's command structure; he also acted as a sort of Chief of staff (military), chief of staff to the army's commander. In the 17th century, sergeant majors appeared in individual regiments. These were field officers, third in command of their regiments (after their colonels and lieutenant colonels), with a role similar to the older, army-level sergeant major (although obviously on a smaller scale). The older position became known as "sergeant major general" to distinguish it. Over time, the term "sergeant" was dropped from both titles, giving rise to the modern ranks of Major (rank), major and major general. The full title of sergeant major fell out of use until the latter part of the 18th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilean Army
The Chilean Army () is the land arm of the Chilean Armed Forces. This 80,000-person army (9,200 of which are conscripts) is organized into six divisions, an army aviation brigade and a special operations brigade. In recent years, and after several major re-equipment programs, the Chilean Army has become the most technologically advanced and professional army in Latin America. The Chilean Army is mostly supplied with equipment from Germany, the Netherlands, Switzerland, Sweden, the United States, Israel, France, and Spain. History Colonial warfare 19th century Independence War The National Army of Chile was created on December 2, 1810, by order of the Government Junta of Chile (1810), First National Government Junta. The army was actively involved in the second Independence War, which was fought against Royalist (Spanish American Revolution), royalist troops in battles such as Battle of Chacabuco, Chacabuco and Battle of Maipú, Maipú or others. During this period, national f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casa Bolognesi
The Casa Bolognesi, also known as the Casa de la Respuesta (''House of the Reply''), is a historical building owned by the Peruvian State located in Arica, Chile. It is the site of a meeting that preceded the Battle of Arica during the War of the Pacific. History Its name comes from an event that preceded the battle of Arica during the War of the Pacific, being the site of the meeting between Francisco Bolognesi of the Peruvian Army and Juan de la Cruz Salvo of the Chilean Army, where the latter requested the Peruvian garrison's surrender after the defeat at Tacna, to which Bolognesi replied by saying he would "fight until the last cartridge is spent" (). From 1934 to 1987, it served as the Consulate General of Peru in the city, being the cultural section of the Consulate since 1996, having been restored the year prior. It is used by the Peruvian government The Republic of Peru is a unitary state with a multi-party semi-presidential system. The current government was es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francisco Bolognesi
Francisco Bolognesi Cervantes (4 November 1816 – 7 June 1880) was a Peruvian military colonel. He is considered a national hero in Peru and was declared patron of the Army of Peru by the government of Peru on 2 January 1951. Early life and education Francisco Bolognesi was born in Lima on 4 November 1816. He attended the Seminary of Arequipa until he was 16 and then entered into a career in commerce. His birthplace, known as the Casa de Bolognesi, later became a museum. His father, Andrés Bolognesi was of Italian-Peruvian background and was a violin player for the court of the Viceroy. Francisco Bolognesi had a son called Federico Pablo whose son was Federico Bolognesi Bolognesi (2nd Vice president of Peru). Federico Bolognesi Bolognesi had a daughter called Ana Maria Bolognesi who had two daughters called Ana Mamie and Selina Raguz Bolognesi. The Bolognesi family legacy lives on through Ana Mamie and Selina, who each have two children: Roberto and Emilia Abusada Raguz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arica
Arica ( ; ) is a commune and a port city with a population of 222,619 in the Arica Province of northern Chile's Arica y Parinacota Region. It is Chile's northernmost city, being located only south of the border with Peru. The city is the capital of both the Arica Province and the Arica and Parinacota Region. Arica is located at the bend of South America's western coast known as the Arica Bend or Arica Elbow. At the location of the city are two valleys that dissect the Atacama Desert converge: Azapa and Lluta. These valleys provide citrus and olives for export. Arica is an important port for a large inland region of South America. The city serves a free port for Bolivia and manages a substantial part of that country's trade. In addition it is the end station of the Bolivian oil pipeline beginning in Oruro. The city's strategic position is enhanced by being next to the Pan-American Highway, being connected to both Tacna in Peru and La Paz in Bolivia by railroad and being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Tacna
The Battle of Tacna, also known as the Battle of the Peak of the Alliance (Spanish: ''Batalla del Alto de la Alianza''), effectively destroyed the Peru-Bolivian alliance against Chile, forged by a secret treaty signed in 1873. On 26 May 1880, the Chilean Northern Operations Army led by General Manuel Baquedano González, conclusively defeated the combined armies of Peru and Bolivia commanded by Bolivian President, General Narciso Campero. The battle took place at the Inti Urqu ''( Intiorko)'' hill plateau, a few miles north of the Peruvian city of Tacna. As a result, Bolivia was knocked out of the war, leaving Peru to fight the rest of the war alone. Also, this victory consolidated the Chilean domain over the Tarapacá Department. The territory was definitively annexed to Chile after the signing of the ''Tratado de Ancón'', in 1884, which ended the war. Tacna itself remained under Chilean control until 1929. Prologue After their success in the Tarapacá campaign, the Chilea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Respuesta (painting)
''La respuesta'' (Spanish for "The response"), also known as ''La respuesta de Bolognesi'', is an 1891 oil painting by Peruvian painter Juan Lepiani. It forms part of the collection of the Combatants of the Morro de Arica Museum. Context The painting depicts a chapter of the War of the Pacific, where Chilean Major Juan de la Cruz Salvo arrived to Francisco Bolognesi's barracks in Arica, then part of Peru, to discuss the Peruvian group's surrender. Bolognesi replied to the request by saying "I have sacred dutes to fulfill, and I will carry them out until the last cartridge has been spent." Both armies subsequently fought in the violent battle two days later, where Bolognesi was killed in action. In 1994, a photograph showing what appeared to be Bolognesi and his army was found by journalist Alejandro Guerrero in Tacna. It was purchased by businessman Genaro Delgado Parker and subsequently restored in a Kodak laboratory in the United States, with historians concluding that it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Lepiani
José Juan de Dios Mateo Osbaldo Botaro Lepiani Toledo (20 September 1864, Lima – 28 November 1932, Rome) was a Peruvian painter. He is primarily known for historical and Patriotism, patriotic scenes; notably those related to the War of the Pacific. Biography As a young man he worked at a series of simple jobs, such as paymaster for the central railroad. He considered art to be his natural vocation, however, so he began studying with and Ramón Muñiz, a Spanish painter living in Lima, about whom little is known. In the 1890s, Lepiani began his series of historical scenes. In 1903, he went to Europe, where he visited museums and exhibitions. He eventually settled in Rome, where he lived a somewhat dissolute life and created few original works, preferring instead to copy the Old Masters, such as Raphael and Titian, and sell the reproductions to American tourists. His copies were highly regarded, however, and some of the best ones were even sent home to Peru. He returned home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |