|
José Manuel De Álava
José Manuel Álava y Sáenz de Navarrete (Vitoria, 19 January 1743 – Guanajuato, 3 June 1795) was a Spanish officer, Colonel of the regiment posted in Puebla and brigadier of the Royal Armies, interim Spanish governor of Acapulco, explorer of the North Pacific, brother of Ignacio María de Álava and uncle of Miguel Ricardo de Álava. Biography The son of Gaspar Álava Aranguren and Joaquina Sáenz Navarrete, he was born in Vitoria on 19 January 1743. He studied at the Vergara Aristocrats' Seminary, entered the army as a cadet and was sent into the Seville Infantry Regiment, where he was successively promoted to second lieutenant (1762), lieutenant (1767), captain and adjutant (1771) and colonel. As a captain, he took part in the thwarted blockade and Siege of Gibraltar. He was named director of La Luisiana and Punto Mochales in the New Villages of Sierra Morena, the most ambitious project of the Spanish Enlightenment. In 1776 he sailed to North America and in Mexico he wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitoria-Gasteiz
Vitoria-Gasteiz (; ; also historically spelled Vittoria in English) is the seat of government and the capital city of the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country and of the provinces of Spain, province of Álava in northern Spain. It holds the autonomous community's Basque Parliament, House of Parliament, the headquarters of the Government, and the Lehendakari, Lehendakari's (Prime Minister's) official residency. The municipality—which comprises not only the city but also the mainly agricultural lands of 63 villages around—is the largest in the Basque Country, with a total area of , and it has a population of 261,494 (January 2025). The dwellers of Vitoria-Gasteiz are called ''vitorianos'' or ''gasteiztarrak'', while traditionally they are dubbed ''babazorros'' (Basque language, Basque for 'bean sacks'). Vitoria-Gasteiz is a dynamic city with strengths in healthcare, aeronautics, the automotive industry, and viticulture. It is the first Spanish municipality to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strait Of Juan De Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca (officially named Juan de Fuca Strait in Canada) is a body of water about long that is the Salish Sea's main outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The Canada–United States border, international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre of the Strait. It was named in 1787 by the maritime fur trader Charles William Barkley, captain of ''Imperial Eagle (ship), Imperial Eagle'', for Juan de Fuca, the Greek navigator who sailed in a Spanish expedition in 1592 to seek the fabled Strait of Anián. Barkley was the first recorded person to find the strait, unless Juan de Fuca's story was true. Samuel Bawlf posited in 2003 that "Fuca's story was nothing more than a fabrication designed to extract money from the English government". The story would have been based on Francis Drake 1579 exploration of the Northwest Passage at its western end. Drake would therefore have been more than the first European to ever sight the entry of the strait but wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Vitoria-Gasteiz
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contiguous United States
The contiguous United States, also known as the U.S. mainland, officially referred to as the conterminous United States, consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the District of Columbia of the United States in central North America. The term excludes the only two non- contiguous states and the last two to be admitted to the Union, which are Alaska and Hawaii, and all other offshore insular areas, such as the U.S. territories of American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. The colloquial term ''Lower48'' is also used, especially in relation to Alaska. The term The Mainland is used in Hawaii. The related but distinct term ''continental United States'' includes Alaska, which is also on North America, but separated from the 48 states by British Columbia in Canada, but excludes Hawaii and all the insular areas in the Caribbean and the Pacific. The greatest distance on a great-circle route entirely within the contiguous U.S. i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
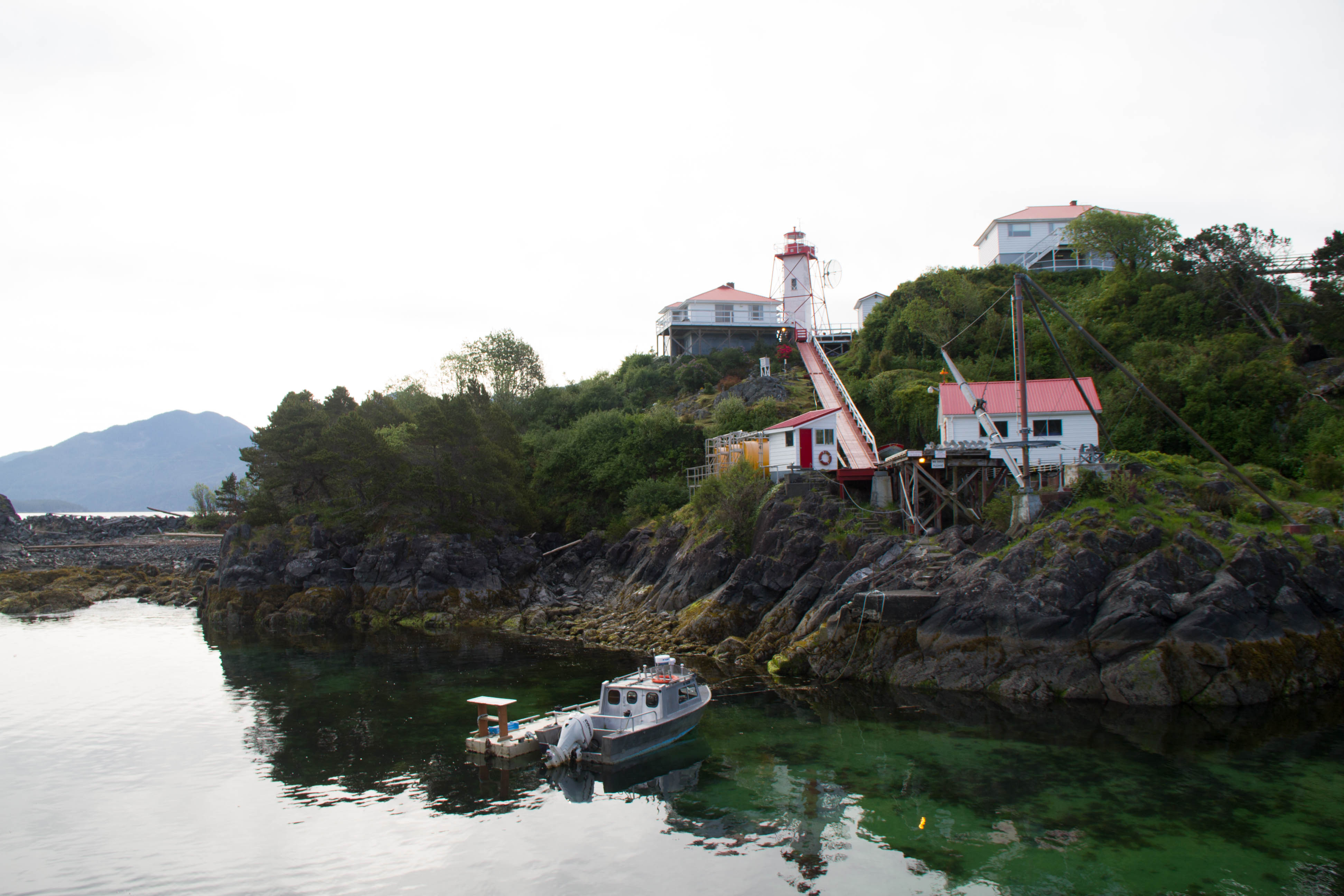
Cape Alava
Cape Alava is a cape in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. Located in Clallam County, Washington, the cape is situated within Olympic National Park and the Makah Indian Reservation, and is accessible via a 3-mile boardwalk hike from a ranger station in the park. Cape Alava Trail was designated a National Recreation Trail in 1981. Name The cape was named after the Basque Don José Manuel de Álava (born in Vitoria, Álava, January 1, 1743) for his role as commissioner during the solution of the conflict of Nootka in 1794. Westernmost location Cape Alava is the westernmost point in the contiguous United States, with a longitude of (during low tide and walking out to the west side of Tskawahyah Island). Nearby Cape Flattery and Cape Blanco in southern Oregon are also very close longitudinally to being the westernmost points in the contiguous 48 states, which are at and respectively. History In early 1834, a mastless and rudderless Japanese rice tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nootka Island
Nootka Island (; ) is the largest island off the west coast of Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. It is in area. It is separated from Vancouver Island by Nootka Sound and its side-inlets, and is located within Electoral Area A of the Strathcona Regional District. Europeans named the island after a Nuu-chah-nulth language word meaning "go around, go around". They likely thought the natives were referring to the island itself. The Spanish and later English applied the word to the island and the sound, thinking they were naming both after the people. In the 1980s, the First Nations peoples in the region created the collective autonym of ''Nuu-chah-nulth'', a term that means "along the outside (of Vancouver Island)". An older term for this group of peoples was "Aht", which means "people" in their language and is a component in all the names of their subgroups, and of some locations (e.g. Yuquot, Mowachaht, Kyuquot, Opitsaht etc.). Climate See also *Nootka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Francisco De La Bodega Y Quadra
Juan Francisco de la Bodega y Quadra (22 May 1743 – 26 March 1794) was a Hispano-Peruvian naval officer operating in the Americas. Assigned to the Pacific coast Spanish Naval Department base at San Blas, in Viceroyalty of New Spain (present-day Mexico), he explored the Northwest Coast of North America as far north as present day Alaska. Bodega Bay in California is named for him. Juan Francisco de la Bodega y Quadra joined the Spanish Naval Academy in Cádiz at 19, and four years later, in 1767 was commissioned as an officer of the rank Frigate Ensign (''alférez de fragata''). In 1773 he was promoted to Ship Ensign (''alférez de navío''), and in 1774 to Ship Lieutenant (''teniente de navío''). Parentage Bodega y Quadra was born in Lima, Peru, to Tomás de la Bodega y de las Llanas of Biscay, Spain and Francisca de Mollinedo y Losada of Lima, Peru (her parents were from Bilbao in Spain). His family was of Basque origin. He studied at the National University of San Marco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academy Of San Carlos
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of tertiary education. The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 386 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. The Royal Spanish Academy defines academy as scientific, literary or artistic society established with public authority and as a teaching establishment, public or private, of a professional, artistic, technical or simply practical nature. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, '' Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his ses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cayetano Valdés Y Flores
Cayetano Valdés y Flores Bazán (28 September 1767 – 6 February 1835) was a Spanish Navy officer and explorer who served in the American Revolutionary War and the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, fighting on opposing sides at different times due to the changing fortunes of Spain. He took part in a number of battles, including the Battle of Cape Spartel, the Battle of Cape St Vincent and the Battle of Trafalgar. He was an explorer, most notable in the Pacific Northwest, where he and Dionisio Alcalá Galiano conducted the first circumnavigation of Vancouver Island, in partial cooperation with George Vancouver. Over his long career he achieved the highest ranks in the Spanish navy, eventually being named Captain General of Cadiz and Captain General of the Navy. Early career He was born in Seville in 1767, and was the nephew of Antonio Valdés y Fernández Bazán. Cayetano Valdés joined the Naval Academy in Cadiz as a ''guardiamarina'' (midshipman) in 1781. After f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Álava
Álava () or Araba (), officially Araba/Álava, is a Provinces of Spain, province of Spain and a historical territory of the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country, heir of the ancient Basque señoríos#Lords of Álava, Lordship of Álava, former medieval Catholic bishopric and now Latin titular see. Its capital city, Vitoria-Gasteiz, is also the seat of the political main institutions of the Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Autonomous Community. It borders the Basque provinces of Biscay and Gipuzkoa to the north, the community of La Rioja (Spain), La Rioja to the south, the province of Burgos (in the community of Castile and León) to the west and the community of Navarre to the east. The Treviño enclave, Enclave of Treviño, surrounded by Alavese territory, is however part of the province of Burgos, thus belonging to the autonomous community of Castile and León, not Álava. It is the largest of the three provinces in the Basque Autonomous Communi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonio Alcalá Galiano
Antonio Alcalá Galiano y Fernández de Villavicencio, (22 July 1789, Cádiz – 11 April 1865, Madrid) was a Spanish politician and writer who served as Minister of the Navy (1836) and Ministry of Public Works and Transport (Spain), Minister of Public Works (1865). He was elected a Deputy (legislator), Deputy for Cádiz in 1822 and served sporadically through ten successive legislatures, until his death. Biography He was born to an influential military family. His father, the explorer Dionisio Alcalá Galiano, was killed at the Battle of Trafalgar and his uncle, Don , was Captain general of the Armada and a Regent of the Kingdom during the interregnum in the reign of Ferdinand VII of Spain, Ferdinand VII. After his secondary studies at the "" (now known as "IES Aguilar y Eslava"), he travelled through the Mediterranean with his father and spent some time in Naples. In 1806, he enrolled as a cadet in the "Guardias Marinas Españolas" and the following year was named Master ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Santiago
The Order of Santiago (; ) is a religious and military order founded in the 12th century. It owes its name to the patron saint of Spain, ''Santiago'' ( St. James the Greater). Its initial objective was to protect the pilgrims on the Way of St. James, to defend Christendom and to remove the Muslim Moors from the Iberian Peninsula with the Reconquista. Entrance was not restricted to nobility of Spain exclusively, and some members have been Catholic Europeans from other parts of Europe. The Order's insignia is particularly recognisable and abundant in Western art. With the culmination of the Reconquista and the death of the Grand Master Alonso de Cárdenas, the Catholic Monarchs incorporated the Order into the Spanish Crown, and the Pope Adrian VI forever united the office of Grand Master of Santiago to the Crown in 1523. The First Republic suppressed the Order in 1873, but it was re-established in the Restoration as a nobiliary institute of honorable character. The Orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |