|
Joshua Ben Gamla
Joshua ben Gamla (), also called Jesus the son of Gamala (), was a Jewish high priest in about 64-65 CE. He was killed during the First Jewish–Roman War. While the Talmud refers to Joshua ben Gamla, the earlier Greek works of Josephus Flavius call him ''Γαμάλα μὲν υἱὸς Ἰησοῦς'' (''Gamala men huios Iesous'') a semitism for: ''The son of Gamala, Jesus''. Joshua married the rich widow Martha of the high-priestly family Boethus and was appointed High Priest by Herod Agrippa II. According to Talmudic sources, Martha bribed a "King Jannai" into appointing Joshua High Priest with a tarkab of denarii. This cannot refer to Alexander Jannaeus, who reigned 150 years earlier and was himself the High Priest, but may refer to King Agrippa II as is mentioned in the Talmudic notes. The two lots used on Yom Kippur, previously of boxwood, he made of gold. Joshua did not remain long in office, being forced, after a year, to give way to Mattathias ben Theophilus. Althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
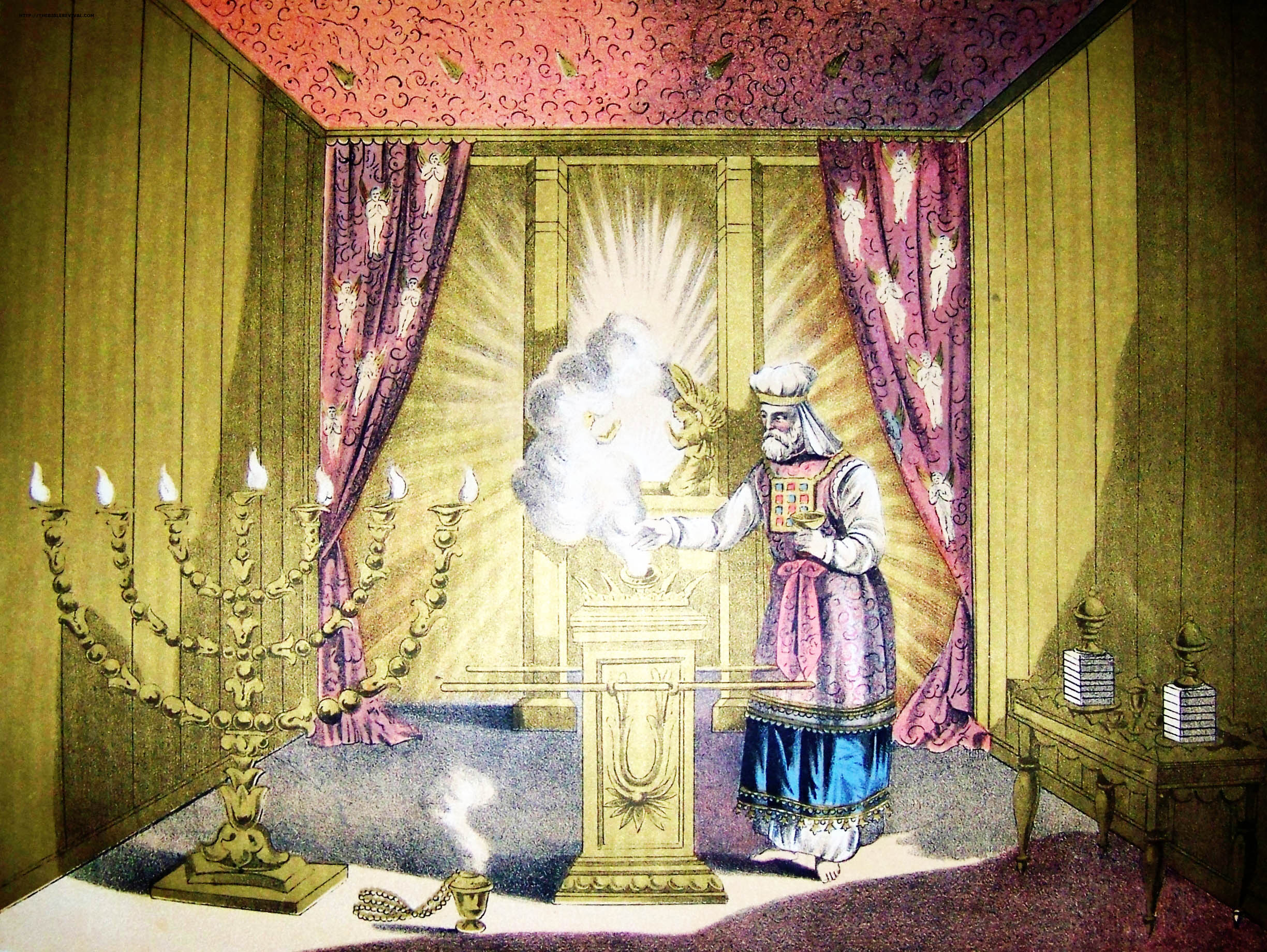
Kohen Gadol
In Judaism, the High Priest of Israel (, lit. ‘great priest’; Aramaic: ''Kahana Rabba'') was the head of the Israelite priesthood. He played a unique role in the worship conducted in the Tabernacle and later in the Temple in Jerusalem, as well as in some non-ritual matters. Like all priests, he was required to be descended from Aaron (the first biblical priest). But unlike other priests, the high priest followed more restrictive laws, wore unique priestly garments, and was the only priest allowed to perform certain ceremonies. Titles The high priest is referred to by a number of titles in the Hebrew Bible; the title ''kohen gadol'' did not become dominant until well into the Second Temple period. In addition to the title of "great priest" (''kohen gadol'') which later became the standard Hebrew title, the term "head priest" (''kohen harosh''; ) was used, as was "anointed priest" (''kohen mashiach''; )., , The Torah sometimes uses longer descriptions: "the great priest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phinehas B
According to the Hebrew Bible, Phinehas (also spelled Phineas, ; , ''Phinees'', ) was a priest during the Exodus. The grandson of Aaron and son of Eleazar, the High Priests (), he distinguished himself as a youth at Shittim with his zeal against the heresy of Peor. Displeased with the immorality with which the Moabites and Midianites had successfully tempted the Israelites () to inter-marry and to worship Baal-peor, Phinehas personally executed an Israelite man and a Midianite woman while they were together in the man's tent, running a javelin or spear through the man and the belly of the woman, bringing to an end the plague sent by Yahweh to punish the Israelites for sexually intermingling with the Midianites. Phinehas is commended by Yahweh in Numbers 25:10–13, as well as King David in Psalm 106 () for having stopped Israel's fall into idolatrous practices brought in by Midianite women, as well as for stopping the desecration of Yahweh's sanctuary. After the entry to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Of The First Jewish–Roman War
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st-century Rabbis
File:1st century collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Jesus is crucified by Roman authorities in Judaea (17th century painting). Four different men (Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian) claim the title of Emperor within the span of a year; The Great Fire of Rome (18th-century painting) sees the destruction of two-thirds of the city, precipitating the empire's first persecution against Christians, who are blamed for the disaster; The Roman Colosseum is built and holds its inaugural games; Roman forces besiege Jerusalem during the First Jewish–Roman War (19th-century painting); The Trưng sisters lead a rebellion against the Chinese Han dynasty (anachronistic depiction); Boudica, queen of the British Iceni leads a rebellion against Rome (19th-century statue); Knife-shaped coin of the Xin dynasty., 335px rect 30 30 737 1077 Crucifixion of Jesus rect 767 30 1815 1077 Year of the Four Emperors rect 1846 30 3223 1077 Great Fire of Rome rect 30 1108 1106 2155 Boudican revolt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mishnah Rabbis
''Tannaim'' ( Amoraic Hebrew: תנאים "repeaters", "teachers", singular ''tanna'' , borrowed from Aramaic) were the rabbinic sages whose views are recorded in the Mishnah, from approximately 10–220 CE. The period of the Tannaim, also referred to as the Mishnaic period, lasted about 210 years. It came after the period of the Zugot "Pairs" and was immediately followed by the period of the Amoraim "Interpreters". The root ''tanna'' () is the Aramaic equivalent of the Hebrew root ''shanah'' (), which also is the root word of ''Mishnah''. The verb ''shanah'' means "to repeat hat one was taught and is used to mean "to learn". The Mishnaic period is commonly divided into five periods according to generations. There are approximately 120 known Tannaim. The Tannaim lived in several areas of the Land of Israel. The spiritual center of Judaism at that time was Jerusalem, but after the destruction of the city and the Second Temple, Yohanan ben Zakkai and his students founded a new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st-century High Priests Of Israel
File:1st century collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Jesus is crucified by Roman authorities in Judaea (17th century painting). Four different men (Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian) claim the title of Emperor within the span of a year; The Great Fire of Rome (18th-century painting) sees the destruction of two-thirds of the city, precipitating the empire's first persecution against Christians, who are blamed for the disaster; The Roman Colosseum is built and holds its inaugural games; Roman forces besiege Jerusalem during the First Jewish–Roman War (19th-century painting); The Trưng sisters lead a rebellion against the Chinese Han dynasty (anachronistic depiction); Boudica, queen of the British Iceni leads a rebellion against Rome (19th-century statue); Knife-shaped coin of the Xin dynasty., 335px rect 30 30 737 1077 Crucifixion of Jesus rect 767 30 1815 1077 Year of the Four Emperors rect 1846 30 3223 1077 Great Fire of Rome rect 30 1108 1106 2155 Boudican revolt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesus Son Of Damneus
Jesus son of Damneus (Greek: Ἰησοῦς του Δαμναίου, Hebrew: ישוע בן דמנאי, ''Yeshua` ben Damnai'') was a Herodian-era High Priest of Judaea in Jerusalem, Iudaea Province. In the ''Antiquities of the Jews'' ( Book 20, Chapter 9) first-century historian Josephus states that Jesus ben Damneus was made high priest after the previous high priest, Ananus son of Ananus, was removed from his position for executing James the brother of Jesus of Nazareth (James the Just). This occurred after a large number of Jews complained and petitioned the king. Jesus ben Damneus himself was deposed less than a year later. While the authenticity of some passages in Book 18 of ''Antiquities of the Jews'' has been subject to debate, the overwhelming majority of scholars consider the discussion of the death of James in Section 9 of Book 20 to be authentic. The works of Josephus refer to at least twenty different people with the name Jesus. There is a scholarly consen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zealot Coup In Jerusalem
The Zealot coup in Jerusalem was a violent seizure of power in 66–68 CE, in which the Zealots, a radical Jewish faction, overthrew the moderate government established at the outset of the First Jewish–Roman War (66–73 CE). The coup marked a turning point in the growing internal conflict among Jewish factions resisting Roman rule. The zealot coup took place as Vespasian's forces were concluding their Galilee campaign, while Jerusalem faced mounting instability due to an influx of refugees and rebel fighters. Led by Eleazar ben Simon, the Zealots executed prominent figures accused of collaboration with the Romans, seized the Temple precinct, and replaced the traditional high priesthood with Phannias ben Samuel, chosen by lot. Moderate leader Ananus ben Ananus gained popular support and began raising an army to challenge the Zealots. In response, the Zealots launched a counteroffensive, but were outnumbered and forced to retreat and fortify themselves in the Temple. Urg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and is considered Holy city, holy to the three major Abrahamic religions—Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israel and Palestine claim Jerusalem as their capital city; Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there, while Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power. Neither claim is widely Status of Jerusalem, recognized internationally. Throughout History of Jerusalem, its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, Siege of Jerusalem (other), besieged 23 times, captured and recaptured 44 times, and attacked 52 times. According to Eric H. Cline's tally in Jerusalem Besieged. The part of Jerusalem called the City of David (historic), City of David shows first signs of settlement in the 4th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idumean
Edom (; Edomite: ; , lit.: "red"; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Egyptian: ) was an ancient kingdom that stretched across areas in the south of present-day Jordan and Israel. Edom and the Edomites appear in several written sources relating to the late Bronze Age and to the Iron Age in the Levant, including the list of the Egyptian pharaoh Seti I from c. 1215 BC as well as in the chronicle of a campaign by Ramesses III (r. 1186–1155 BC), and the Tanakh. Archaeological investigation has shown that the nation flourished between the 13th and the 8th centuries BC and was destroyed after a period of decline in the 6th century BC by the Babylonians. After the fall of the kingdom of Edom, the Edomites were pushed westward towards southern Judah by nomadic tribes coming from the east; among them were the Nabataeans, who first appeared in the historical annals of the 4th century BC and had already established their own kingdom in what used to be Edom by the first half of the 2nd century B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ananus Ben Ananus
Ananus ben Ananus (Hebrew: ''Hanan ben Hanan''; Greek: ''Ananos son of Ananos''; or ; d. 68 CE) was a Herodian-era High Priest of Israel in Jerusalem, Judea Province. He was the High Priest who ordered the execution by stoning of James, the brother of Jesus (James the Just), according to the ''Antiquities of the Jews'' of Josephus. A delegation sent by citizens upset over the perceived breach of justice met Lucceius Albinus before he reached Judea, and Albinus responded with a letter informing Ananus that it was illegal to convene the Sanhedrin without Albinus' permission and threatening to punish the priest. Ananus was therefore deposed by King Herod Agrippa II before Albinus's arrival and replaced with Jesus ben Damneus.Josephus, ''Antiquities of the Jews'', Book 20, Chapter 9, Section 1 Ananus was one of the main leaders of the Great Revolt of Judea, which erupted in 66 CE. He was appointed as one of the heads of the Judean provisional government together with Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |