|
John William Friso
John William Friso (; 14 August 1687 – 14 July 1711) became the (titular) Prince of Orange in 1702. He was the Stadtholder of Friesland and Groningen in the Dutch Republic. He also served in the Dutch States Army during the War of the Spanish Succession until his death by accidental drowning in the Hollands Diep in 1711. Background Born on 14 August 1687 in Dessau, Anhalt, Friso was the son of Henry Casimir II, Prince of Nassau-Dietz, and Princess Henriëtte Amalia of Anhalt-Dessau who were both first cousins of William III. He was also a member of the House of Nassau (the branch of Nassau-Dietz), and through the testamentary dispositions of William III became the progenitor of the new line of the House of Orange-Nassau. He was educated under Jean Lemonon, professor at the University of Franeker. Succession With the death of William III of Orange, the legitimate male line of William the Silent (the second House of Orange) became extinct. John William Friso, the senior ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
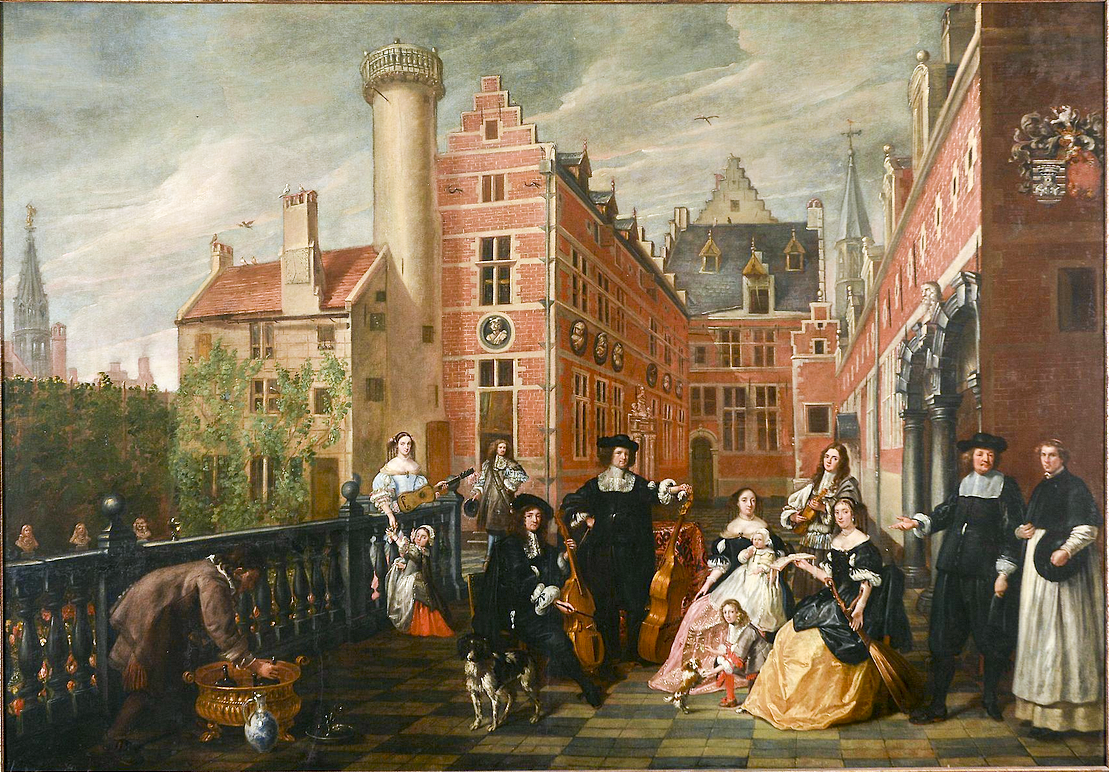
Lancelot Volders
Lancelot Volders also erroneously known as Louis Volders, Lois Volders and Jan Volders (10 March 1636 (baptized) – 23 March 1723 (buried)) was a Flemish painter who specialised mainly in individual and group portraits but also produced a few history paintings and genre art, genre scenes.Lancelot Volders at the Netherlands Institute for Art History After training and working in Brussels, he may have worked after about 1700 from time to time at the Stadhouderlijk Hof in Leeuwarden. Life For a long time it was believed that the painters Lancelot Volders and Louis Volders were different persons and that the works signed 'L. Volders' and in a single case 'Louis Volders' had to be ascribed to the painter Louis Volders. Research by art historian Leen Kelchtermans published in 2013 has demonstrated that th ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Princess Amalia Of Nassau-Dietz
Princess Amalia of Nassau-Dietz (Anna Charlotte Amalie; – 18 September 1777) was a Dutch princess and the wife of Frederick, Hereditary Prince of Baden-Durlach, and mother of Charles Frederick, Grand Duke of Baden, Charles Frederick, the first Grand Duke of Baden. Life Anna Charlotte Amalia was the only daughter of John William Friso, Prince of Orange, Johan Willem Friso of Nassau-Dietz (after 1702 Prince of Orange) and his wife, Landgravine Marie Louise of Hesse-Kassel. She had a brother, William IV, Prince of Orange (1711-1751). She grew up in Friesland and spoke West Frisian language, West Frisian herself. Amalia was often described as quite introvert and often Melancholia, melancholic. After her marriage to Frederick, Hereditary Prince of Baden-Durlach, Friedrich of Baden-Durlach in 1727 she moved to Durlach. During her pregnancies, Amalia tyrannized her servants, and because of the princess's many tantrums, rumors circulated at the court of Durlach that she was mentall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands and the first independent Dutch people, Dutch nation state. The republic was established after seven Dutch provinces in the Spanish Netherlands Dutch Revolt, revolted against Spanish Empire, Spanish rule, forming a mutual alliance against Spain in 1579 (the Union of Utrecht) and declaring their independence in 1581 (the Act of Abjuration). The seven provinces it comprised were Lordship of Groningen, Groningen (present-day Groningen (province), Groningen), Lordship of Frisia, Frisia (present-day Friesland), Lordship of Overijssel, Overijssel (present-day Overijssel), Duchy of Guelders, Guelders (present-day Gelderland), lordship of Utrecht, Utrecht (present-day Utrecht (province), Utrecht), county of Holland, Holland (present-day North Holla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lordship Of Groningen
The Lordship of Groningen (; ) was a heerlijkheid, lordship under the rule of the House of Habsburg between 1536 and 1594, which is the present-day province of Groningen (province), Groningen. Before 1536 A distinction must be made between the Groningen, City of Groningen and the surrounding countryside, known as the Ommelanden. The city of Groningen had already gained its independence from its formal landlord, the Prince-Bishopric of Utrecht, Bishop of Utrecht in the 12th century. The Ommelanden, together with their Frisian neighbours, enjoyed the Frisian freedom and had never had a Lord. Therefore, before 1536, the concept of a ''Lord of Groningen'' had never existed. Charles V After the Habsburg victory in the Battle of Heiligerlee (1536), Battle of Heiligerlee during the Guelders Wars, the city of Groningen and the Ommelanden came under the rule of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. They were joined in the ''Lordship of Groningen'' and ruled by a Stadtholder, but with preser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lordship Of Frisia
The Lordship of Frisia () or Lordship of Friesland (; ; ) was a feudal dominion in the Netherlands. It was formed in 1498 by King Maximilian I and reformed in 1524 when Emperor Charles V conquered Frisia. History The former Frisian kingdom (''Magna Frisia'') had been incorporated into Francia after the Frisian–Frankish wars, that ended with the victory of the Frankish troops led by ''majordomo'' Charles Martel at the Battle of the Boarn in 734. The remaining territory east of the Lauwers River was conquered by Charlemagne in the course of the Saxon Wars until 785. During the decline of the Carolingian Empire in the 9th century, the Frisian coast with the important trading place of Dorestad was strongly affected by Viking raids. In turn the Frankish emperor Louis the Pious and his successor Lothair I, ruler of Middle Francia since 843, tried to pacify the Viking leaders such as Harald Klak or Rorik of Dorestad by vesting them with large estates in the Frisian lands. By the 870 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
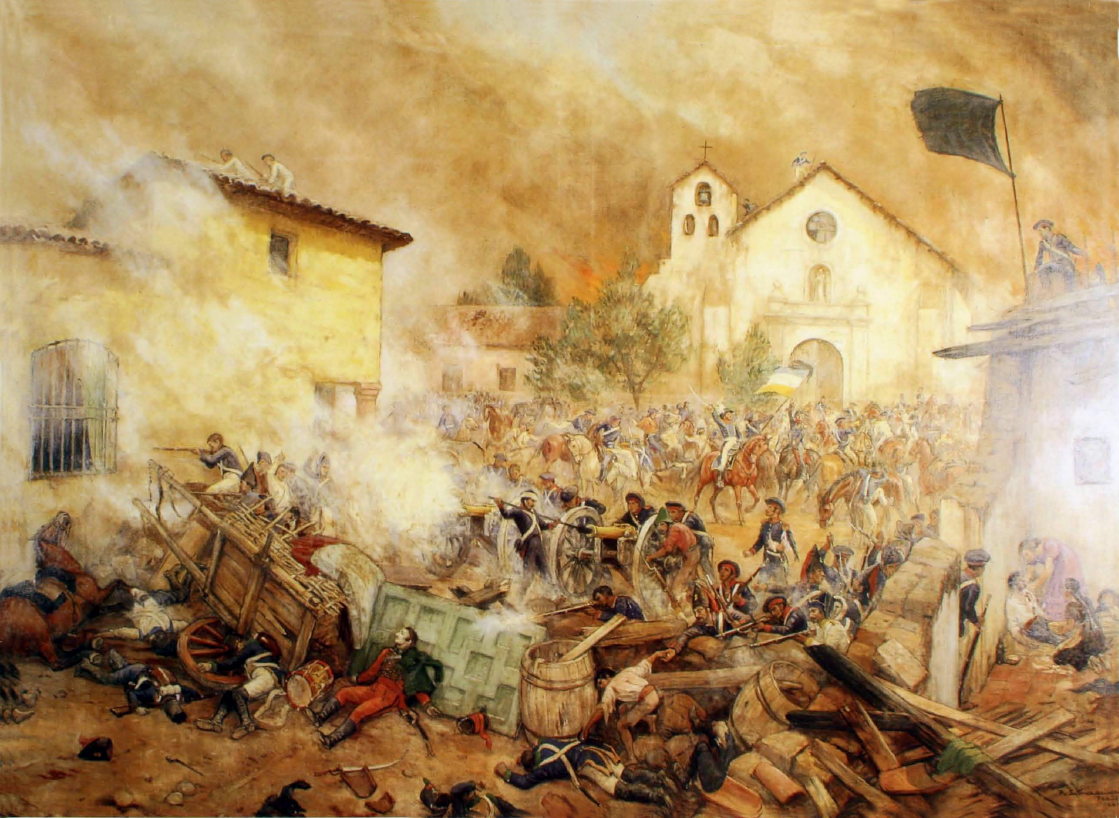
Siege Of Saint-Vernant
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to surrender (military), surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block provision of supplies and reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as "investment (military), investment"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engines, artillery bombardment, mining (military), mining (also known as sapping), or the use of deception or treachery to bypass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siege Of Douai (1710)
The siege of Douai, which lasted from 22 April 1710 until the capitulation of the garrison under lieutenant-general François Zénobe Philippe Albergotti on 25 June 1710 was part of the Allied Campaign of 1710 in the War of the Spanish Succession. The siege was conducted under the joint command of the John William Friso, Princ of Orange and Leopold I, Prince of Anhalt-Dessau and successfully concluded despite the fact that halfway through the French army under marshal Claude Louis Hector de Villars, 1st Duke of Villars made an attempt to relieve the fortress city, which led to an indecisive stand-off for four days with the Allied Army under John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough and Prince Eugene of Savoy. After Douai the Allies went on to besiege Béthune. Background At the start of the new campaign season of 1710 of the War of the Spanish Succession the Allies hoped to be able to break through the double line of fortresses (the ''frontière de fer'' or iron border) that had p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siege Of Mons (1709)
The siege of Mons took place between 19 September and 23 October 1709 during the War of the Spanish Succession. It saw a Franco-Spanish garrison in the fortified town of Mons, Belgium, Mons, then in the Spanish Netherlands, siege, besieged by a force of the John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, Duke of Marlborough's Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance army under the command of the John William Friso, Prince of Orange, Prince of Orange. The attempt of the French Claude Louis Hector de Villars, 1st Duke of Villars, Duke of Villars to relieve the siege resulted in the costly Allied victory at the Battle of Malplaquet on 11 September 1709. Following the battle, greater numbers of Allied soldiers under Prince Eugene of Savoy, Eugene of Savoy joined the besieging army from late September. The Franco-Spanish garrison capitulated the following month. Owing to high Allied and French losses at Malplaquet, the capture of Mons was the final significant engagement of the camp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Malplaquet
The Battle of Malplaquet took place on 11 September 1709 during the War of the Spanish Succession, near Taisnières-sur-Hon in modern France, then part of the Spanish Netherlands. A French army of around 75,000 men, commanded by the Duke of Villars, engaged a Grand Alliance force of 86,000 under the Duke of Marlborough. In one of the bloodiest battles of the 18th century, the allies won a narrow victory, but suffered heavy casualties. Allied advances in 1708 led to the renewal of peace talks, which collapsed in April 1709. After taking Tournai in early September, the allies besieged Mons, whose capture would allow them to enter France itself, and Louis XIV ordered Villars to prevent its loss. Although the two armies made contact on 10 September, the attack was delayed until the next day, giving Villars time to construct strong defensive positions. After an opening artillery barrage, the allied infantry made simultaneous assaults on the French flanks. These were intended to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siege Of Tournai (1709)
The siege of Tournai was a siege of the city of Tournai, then part of the Kingdom of France, between 28 June and 3 September 1709. A Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance army under the British John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, Duke of Marlborough successfully forced the surrender of the French garrison during the War of the Spanish Succession. The siege was the first significant engagement of the 1709 campaign. Marlborough intended to take the city quickly, thereby enabling an Allied advance into northern France. The garrison however, under the Louis-Charles de Hautefort de Surville, Marquis de Surville, held out for considerably longer than had been expected and the siege consumed much of the fighting season. It saw extensive use of Tunnel warfare, mining and countermining as the Allies sought to break through strong French fortifications, particularly Tournai's citadel. The British historian, David G. Chandler, described the siege as "one of the hardest foug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Siege Of Ghent (1708)
The siege of Ghent (18–30 December 1708) was the last operation of the 1708 campaign season during the War of the Spanish Succession. After successfully taking Lille shortly before, the Duke of Marlborough moved his forces onto the town of Ghent where after a 12-day siege the town's governor, Count Charles de La Mothe-Houdancourt, surrendered. Background The War of the Spanish Succession was triggered by the death of Charles II of Spain, who had no children. He left the Spanish throne to Philip of Anjou, a member of the French House of Bourbon, but the Archduke Charles of Austria also felt he had a claim to the throne. The Grand Alliance of Great Britain, the Dutch Republic, the Holy Roman Empire and Habsburg Spain, declared war on France and Bourbon Spain in May 1702. Prelude During the 1708 campaign of the War, the Duke of Marlborough, commanding the Alliance's army in the Low Countries, planned with the Dutch commanders to move all of their forces to attack the French. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Assault On Brussels (1708)
The assault on Brussels or siege of Brussels occurred during the War of the Spanish Succession, from 22 to 27 November 1708 involving French and pro-Bourbon Spanish troops under Maximilian II Emanuel, Elector of Bavaria, Maximilian of Bavaria against the garrison and citizens of the city of Brussels. While the army of the Grand Alliance was occupied with the Siege of Lille (1708), Siege of Lille, the Elector of Bavaria, Maximilian, made an attempt to capture Brussels. He believed the city, with its weak defenses and small garrison, would be an easy target. Despite his confidence the Allies were forewarned of the plan and had already reinforced Brussels' garrison. Maximilian, expecting a swift victory, faced strong resistance from Colonel Pascale, the governor of Brussels, and his well-prepared garrison. Despite his demands for surrender, Pascale defiantly refused. Maximilian's plan quickly unraveled, and what he thought would be a quick assault turned into a protracted and bloody ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |