|
John Macdonald Kinneir
Sir John Macdonald Kinneir (3 February 1782 – 11 June 1830) was a Scottish army officer of the East India Company, diplomat and traveller. Life Born at Carnden, Linlithgow, on 3 February 1782, Kinneir was the son of John Macdonald, comptroller of customs at Borrowstounness, and Cecilia Maria Kinneir. In 1802, he was nominated to a cadetship by Sir William Bensley, under the surname Macdonald, which was used in Indian army lists for the rest of his life. He published his books under the name Macdonald Kinneir. On 21 September 1804 Kinneir was appointed ensign in the Madras infantry, but was not posted until the formation of the 24th Madras Native Infantry on 1 January 1807, when he joined the new corps as lieutenant. He became captain in his regiment on 14 April 1818, and was later brevet lieutenant-colonel. For some time he was secretary to the officer commanding in Malabar and Kanara. Kinneir was attached to Sir John Malcolm's mission in Persia in 1808–9, during part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South Asia and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company gained Company rule in India, control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent and British Hong Kong, Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world by various measures and had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British Army at certain times. Originally Chartered company, chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies," the company rose to account for half of the world's trade during the mid-1700s and early 1800s, particularly in basic commodities including cotton, silk, indigo dye, sugar, salt, spices, Potass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neil Campbell (British Army Officer)
Major-General Sir Neil Campbell (1 May 1776 – 14 August 1827) was a British Army officer who fought during the Napoleonic Wars, administered several British colonies, and escorted Napoleon Bonaparte into exile. Biography Born on 1 May 1776, Campbell was the son of a British Army officer. Early career In 1797, Campbell purchased his first commission in the Army as an ensign with a regiment stationed in the Turks and Caicos Islands. In 1799, Campbell purchased a lieutenancy. In 1800, Campbell returned to England and joined a regiment of light troops there. From February 1802 to September 1803, he attended the Royal Military College, then located at Great Marlow. After his time at the college, Campbell became an assistant quartermaster-general. In 1805, Campbell purchased a promotion to major in a regiment that spent two years in Jamaica. After returning to England, Campbell purchased a promotion to lieutenant colonel. Over the next three years, Campbell participated in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
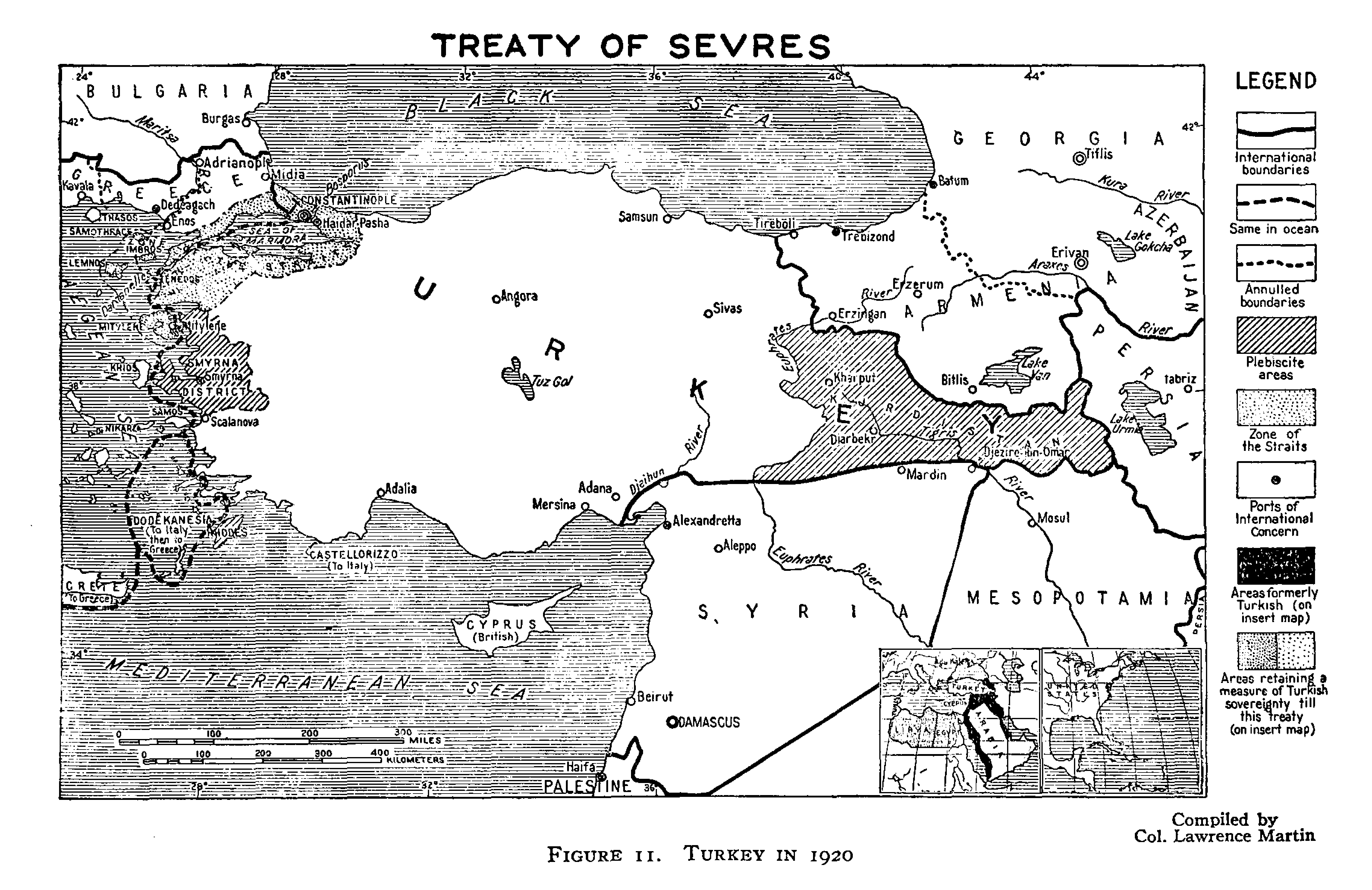
Tabriz
Tabriz (; ) is a city in the Central District (Tabriz County), Central District of Tabriz County, in the East Azerbaijan province, East Azerbaijan province of northwestern Iran. It serves as capital of the province, the county, and the district. It is the List of largest cities of Iran, sixth-most-populous city in Iran. Tabriz is in the Quri Chay, Quru River valley in Iran's historic Azerbaijan (Iran), Azerbaijan region between long ridges of volcanic cones in the Sahand and Eynali mountains. Tabriz's elevation ranges between above sea level. The valley opens up into a plain that gently slopes down to the eastern shores of Lake Urmia, to the west. The city was named World Carpet Weaving City by the World Crafts Council in October 2015 and Exemplary Tourist City of 2018 by the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation. With a population of over 1.7 million (2016), Tabriz is the largest economic hub and metropolitan area in northwest Iran. The population is bilingual with most peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Paskievich
Count Ivan Fyodorovich Paskevich-Erevansky, Serene Prince of Warsaw ( – ) was a Russian military leader who was the ''namiestnik'' of Poland. Paskevich is known for leading Russian forces in Poland during the November Uprising and for a series of leadership roles throughout the early and mid-19th century, such as the Russo-Persian War of 1826–1828, and the beginning phase of the Crimean War. In Russian history, he is remembered as a prominent military commander, rated on a par with Ivan Dibich-Zabalkansky, commander of the Russian armies during the same time. Paskevich started as an officer during the Napoleonic Wars serving in the battles of Austerlitz and Borodino. After the war, he was a leader in the Russo-Persian War. He was made count of Yerevan in 1828. Afterwards, he became the ''namiestnik'' of Poland in 1831 after he crushed the Polish rebels in the November Uprising. He then helped crush the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. His last engagement was the Crimean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erivan Fortress
Erivan Fortress or Yerevan Fortress (; ''Yerevani berdë''; , ''Ghaleh-ye Iravân''; ''E'rivanskaya krepost' '') was a 16th-century fortress in Yerevan. History The fortress was built during the Yerevan#Arab, Persian and Ottoman rule, Ottoman rule in 1582–83 by Serdar Ferhat Pasha. The fortress was destroyed by an 1679 Armenia earthquake, earthquake in 1679. After the earthquake, the Safavid Yerevan Province (Safavid Empire), governor of Erivan, Zal Khan, asked the Shah for help to rebuild Erivan, including the fortress and the Palace of the Sardars. In 1853, the fortress was ruined by another earthquake. In 1865 the territory of the fortress was purchased by Nerses Tairyants, a merchant of the first guild. Later in 1880s, Tairyants built a brandy factory in the northern part of the fortress. The fortress was completely demolished in 1930s during the Soviet rule, although some parts of the defensive walls still remain. Description The Erivan Fortress was considered to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Persian War (1826–28)
The Russo-Persian Wars ( ), or the Russo-Iranian Wars ( ), began in 1651 and continued intermittently until 1828. They consisted of five conflicts in total, each rooted in both sides' disputed governance of territories and countries in the Caucasus, particularly Arran (modern-day Azerbaijan), Georgia, and Armenia, as well as much of Dagestan. Generally referred to as Transcaucasia, this region was considered to be part of Persia prior to the 17th century. Between the War of 1722–1723 and the War of 1796, there was an interbellum period in which a number of treaties were drawn up between the two nations themselves and between them and the neighbouring Ottoman Empire; Turkish interest in the Caucasian territories further complicated the Russo-Persian Wars, as the two belligerents started forming alliances with the Ottoman Empire at different points of the conflict. Finally, as a consequence of the Treaty of Turkmenchay, the Persians ceded much of their Transcaucasian holdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahar
Ahar () is a city in the Central District of Ahar County, East Azerbaijan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. Ahar was the capital of Karadag Khanate in 18th and 19th centuries. History Ahar is one of the ancient cities of the Azerbaijan region, its name before Islam was "meimad". In the 12th-13th centuries, Ahar was a minor and short-lived, but prosperous emirate ruled by the Pishteginid dynasty of Georgian origin (1155—1231). Yaqut al-Hamawi, writing in early thirteenth century, describes Ahar as ''very flourishing despite its small extent''.Yaqut ibn 'Abd Allah al-Rumi al-Hamawi, Charles Adrien Casimir Barbier de Meynard, Dictionnaire géographique, historique et littéraire de la Perse et des contrees adjacentes, 1851, Paris, p. 57 The city lost most of its importance during the rule of Ilkhanate. Hamdallah Mustawfi, writing in mid fourteenth century, describes Ahar as a little town. He estimates the tax revenue of the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fath-Ali Shah Qajar
Fath-Ali Shah Qajar (; 5 August 1772 – 24 October 1834) was the second Shah of Qajar Iran. He reigned from 17 June 1797 until his death on 24 October 1834. His reign saw the irrevocable ceding of Iran's northern territories in the Caucasus, comprising what is nowadays Georgia (country), Georgia, Dagestan, Azerbaijan, and Armenia, to the Russian Empire following the Russo-Persian Wars of Russo-Persian War (1804–1813), 1804–1813 and Russo-Persian War (1826–1828), 1826–1828 and the resulting treaties of Treaty of Gulistan, Gulistan and Treaty of Turkmenchay, Turkmenchay., page 728 These two treaties are closely tied to Fath-Ali Shah's legacy amongst Iranians, who often view him as a weak ruler. Fath-Ali Shah successfully reconstituted his realm from a mostly Turkic tribal khanship into a centralized and stable monarchy based on the old imperial design. At the end of his reign, his difficult economic problems and military and technological liabilities took Iran to the verge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nawab Of The Carnatic
The Carnatic Sultanate ( Persian: ; Tamil: ; Urdu: ) also known as Carnatic State or Arcot State was a kingdom in southern India between about 1690 and 1855, ruled by a Muslim nawab under the legal purview of the Nizam of Hyderabad, until their demise. They initially had their capital at Arcot in the present-day Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Their rule is an important period in the history of the Carnatic and Coromandel Coast regions, in which the Mughal Empire gave way to the rising influence of the Maratha India, and later the emergence of the British India. Borders The old province, known as the Carnatic, in which Madras (Chennai) was situated, extended from the Krishna River to the Kaveri River, and was bounded on the West by Mysore kingdom and Dindigul, (which formed part of the Sultanate of Mysore). The Northern portion was known as the ' Mughal Carnatic', the Southern the 'Maratha Carnatic' with the Maratha fortresses of Gingee and Ranjankudi. Carnatic thus was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort St George, Madras
Fort St. George (or historically, White Town) is a fortress at the coastal city of Chennai, India. Founded in 1639, it was the first English overseas possessions, English (later British Empire, British) fortress in India. The construction of the fort provided the impetus for further settlements and trading activity, in what was originally an uninhabited land. Thus, it is a feasible contention to say that the city (named Madras since before the arrival of the Europeans until July 1996) evolved around the fortress. The fort currently houses the Tamil Nadu legislative assembly and other official buildings. History The East India Company (EIC), which had entered India around 1600 for trading activities, had begun licensed trading at Surat, which was its initial bastion. However, to secure its trade lines and commercial interests in the spice trade, it felt the necessity of a port closer to the Straits of Malacca, Malaccan Straits. Thanks to negotiations led by Francis Day (Madr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombay
Mumbai ( ; ), also known as Bombay ( ; its official name until 1995), is the capital city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Maharashtra. Mumbai is the financial centre, financial capital and the list of cities in India by population, most populous city proper of India with an estimated population of 12.5 million (1.25 crore). Mumbai is the centre of the Mumbai Metropolitan Region, the List of largest cities, seventh-most populous metropolitan area in the world with a population of over 23 million (2.3 crore). Mumbai lies on the Konkan coast on the west coast of India and has a deep natural harbour. In 2008, Mumbai was named an Globalization and World Cities Research Network#Alpha, alpha world city. Mumbai has the List of cities by number of billionaires, highest number of billionaires out of any city in Asia. The seven islands that constitute Mumbai were earlier home to communities of Marathi language-speaking Koli people. For cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdistan
Kurdistan (, ; ), or Greater Kurdistan, is a roughly defined geo- cultural region in West Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, languages, and national identity have historically been based. Geographically, Kurdistan roughly encompasses the northwestern Zagros and the eastern Taurus mountain ranges. Kurdistan generally comprises the following four regions: southeastern Turkey ( Northern Kurdistan), northern Iraq ( Southern Kurdistan), northwestern Iran ( Eastern Kurdistan), and northern Syria ( Western Kurdistan). Some definitions also include parts of southern Transcaucasia. Certain Kurdish nationalist organizations seek to create an independent nation state consisting of some or all of these areas with a Kurdish majority, while others campaign for greater autonomy within the existing national boundaries. The delineation of the region remains disputed and varied, with some maps greatly exaggerating its boundaries. Histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |