|
Joachim Of Zollern
Joachim von Hohenzollern (21 June 1554, in Sigmaringen – 7 July 1587, in Cölln) was a titular Count of Hohenzollern. Life Joachim was the 4th surviving son of Count Karl I of Hohenzollern (1516–1576) from his marriage to Anna (1512–1579), the daughter of Ernst, Margrave of Baden-Durlach. As the younger son, he was destined for a career in the clergy, typically as a canon. In order to avoid this, Joachim converted to the Lutheran faith. He was the only member of the Swabian branch of the House of Hohenzollern to do so. He broke away from the Catholic relatives and moved to the Protestant court of the Elector of Brandenburg in Berlin. Joachim died on 7 July 1587 and was buried in Berlin Cathedral. Marriage and issue On 6 July 1578 in Lohra, he married Anna (d. 1620), the daughter of Count Volkmar Wolf of Hohnstein Volkmar is both a given name and a surname. Notable people with the name include: Given name *Volkmar Andreae (1879–1962), Swiss conductor and com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joachim I Nestor, Elector Of Brandenburg
Joachim I Nestor (21 February 1484 – 11 July 1535) was a Prince-elector of the Margraviate of Brandenburg (1499–1535), the fifth member of the House of Hohenzollern. His nickname was taken from King Nestor of Greek mythology. Biography The eldest son of John Cicero, Elector of Brandenburg, Joachim received an excellent education under the supervision of Dietrich von Bülow, Bishop of Lebus and Chancellor of Frankfurt University. He became Elector of Brandenburg upon his father's death in January 1499, and soon afterwards married Elizabeth of Denmark, daughter of King John of Denmark. They had five children: # Joachim II Hektor (9 January 1505 – 3 January 1571) # Anna (1507 – 19 June 1567) married Albert VII, Duke of Mecklenburg-Güstrow # Elisabeth (24 August 1510 – 25 May 1558) # Margaret (29 September 1511 – 1577), married on 23 January 1530 George I, Duke of Pomerania and after his death in 1534 John V, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst. # John (3 August 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, also , german: Haus Hohenzollern, , ro, Casa de Hohenzollern) is a German royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenburg, Prussia, the German Empire, and Romania. The family came from the area around the town of Hechingen in Swabia during the late 11th century and took their name from Hohenzollern Castle. The first ancestors of the Hohenzollerns were mentioned in 1061. The Hohenzollern family split into two branches, the Catholic Swabian branch and the Protestant Franconian branch,''Genealogisches Handbuch des Adels, Fürstliche Häuser'' XIX. "Haus Hohenzollern". C.A. Starke Verlag, 2011, pp. 30–33. . which ruled the Burgraviate of Nuremberg and later became the Brandenburg-Prussian branch. The Swabian branch ruled the principalities of Hohenzollern-Hechingen and Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen until 1849, and also ruled Romania from 1866 to 1947. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl I, Count Of Hohenzollern
Karl I of Hohenzollern (1516 in Brussels – 18 March 1576 at Sigmaringen Castle) was Count of Hohenzollern from 1525 to 1575. He was Imperial Archchamberlain and chairman of the Aulic Council. Life Karl was the eldest son of the Count Eitel Friedrich III of Hohenzollern (1494–1525) from his marriage to Johanna van Witthem (d. 1544), daughter of Philip, Lord of Beersel and Boutersem. Karl was Imperial Archchamberlain and later chairman of the Aulic Council. In 1534, he received the Counties of Sigmaringen and Veringen as imperial fiefs from Emperor Karl V. Karl married in 1537 with Anna (1512–1579), a daughter of Margrave Ernst of Baden-Durlach, with whom he had several children, among them: * Ferfried (1538–1556), * Marie (1544–1611), * Eitel Friedrich IV (1545–1605), later the first Count of Hohenzollern-Hechingen * Karl II (1547–1606), later the first Count of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen * Johanna (1548–1604), * Jacobea Marie (1549–1578) wife of Leo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmaringen
Sigmaringen ( Swabian: ''Semmerenga'') is a town in southern Germany, in the state of Baden-Württemberg. Situated on the upper Danube, it is the capital of the Sigmaringen district. Sigmaringen is renowned for its castle, Schloss Sigmaringen, which was the seat of the principality of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen until 1850 and is still owned by the Hohenzollern family. Geography Sigmaringen lies in the Danube valley, surrounded by wooded hills south of the Swabian Alb and around 40 km north of Lake Constance. The surrounding towns are Winterlingen (in the district of Zollernalb) and Veringenstadt in the north, Bingen, Sigmaringendorf, and Scheer in the east, Mengen, Krauchenwies, Inzigkofen, and Meßkirch in the south, and Leibertingen, Beuron, and Stetten am kalten Markt in the west. The town is made up of the following districts: Sigmaringen town center, Gutenstein, Jungnau, Laiz, Oberschmeien, and Unterschmeien. History Sigmaringen was first documented in 1077 and wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
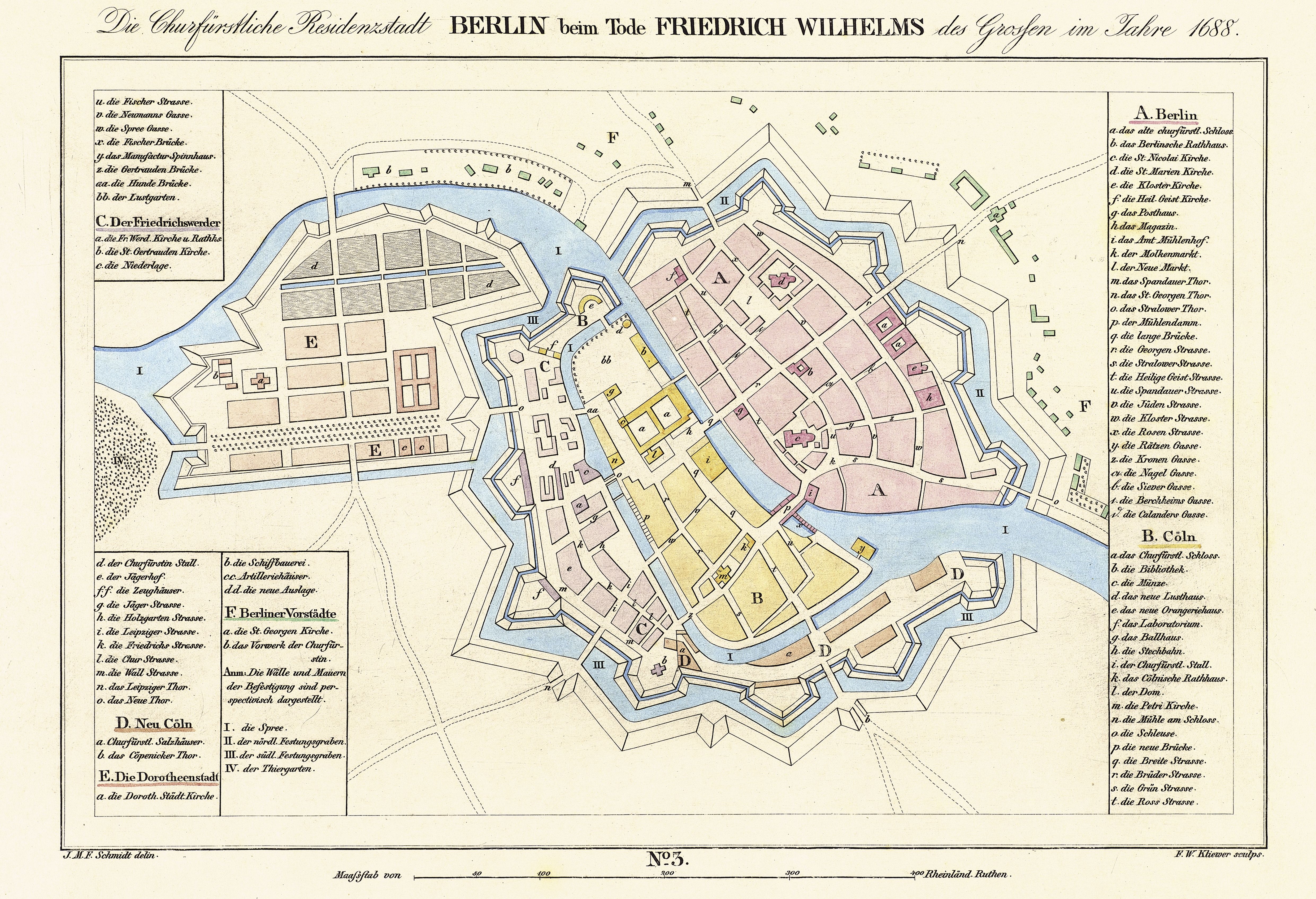
Cölln
Cölln () was the twin city of Old Berlin ( Altberlin) from the 13th century to the 18th century. Cölln was located on the Fisher Island section of Spree Island, opposite Altberlin on the western bank of the River Spree, until the cities were merged by Frederick I of Prussia to form Berlin in 1710. Today, the former site of Cölln is the historic core of the modern Mitte locality of the Berlin-Mitte borough in central Berlin. History Cölln is first mentioned in a 1237 deed, denoting a priest Symeon of Cölln's (Symeon de Colonia) Saint Peter's Church as a witness. This date is commonly regarded as the origin of Berlin, though Altberlin on the eastern bank of the Spree river was not mentioned before 1244 and parts of modern Greater Berlin, such as Spandau and Köpenick, are even older. Cölln and Altberlin were separated only by the river Spree, linked by the ''Mühlendamm'' causeway, hence there was a close connection right from the start. Since the trade route from Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin Cathedral
The Berlin Cathedral (german: link=yes, Berliner Dom), also known as the Evangelical Supreme Parish and Collegiate Church, is a monumental German Evangelical church and dynastic tomb (House of Hohenzollern) on the Museum Island in central Berlin. Having its origins as a castle chapel for the Berlin Palace, several structures have served to house the church since the 15th century. The present collegiate church was built from 1894 to 1905 by order of German Emperor William II according to plans by Julius Raschdorff in Renaissance and Baroque Revival styles. The listed building is the largest Protestant church in Germany and one of the most important dynastic tombs in Europe. In addition to church services, the cathedral is used for state ceremonies, concerts and other events. Since the demolition of the Memorial Church ''(Denkmalskirche)'' section on the north side by the East German authorities in 1975, the Berlin Cathedral has consisted of the large Sermon Church '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst, Margrave Of Baden-Durlach
Margrave Ernest I of Baden-Durlach (7 October 1482, Pforzheim – 6 February 1553, Sulzburg) was the founder of the so-called "Ernestine" line of the House of Baden, the line from which the later Grand Dukes descended. He was the ruling Margrave of Baden-Pforzheim from 1533 and resided in Pforzheim from 1537. In 1565, his son Charles II moved the capital to Durlach and thereby changed the name of his country to Baden-Durlach. He had to deal with the upcoming Reformation and the frequent Ottoman wars in Europe. In this turbulent time, he tried to maintain a neutral position between the Protestants and Catholics. He did not participate in the Schmalkaldic War. Life Ernest was the seventh son of the Margrave Christopher I of Baden and Ottilie of Katzenelnbogen. Ernest was at first – like most of his brothers – destined for the clergy and was ordained in 1496 in Graben-Neudorf by the Vicar General of Diocese of Speyer. But he was not willing to renounce his inherit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon (priest)
A canon (from the Latin , itself derived from the Greek , , "relating to a rule", "regular") is a member of certain bodies in subject to an ecclesiastical rule. Originally, a canon was a cleric living with others in a clergy house or, later, in one of the houses within the precinct of or close to a cathedral or other major church and conducting his life according to the customary discipline or rules of the church. This way of life grew common (and is first documented) in the 8th century AD. In the 11th century, some churches required clergy thus living together to adopt the rule first proposed by Saint Augustine that they renounce private wealth. Those who embraced this change were known as Augustinians or Canons Regular, whilst those who did not were known as secular canons. Secular canons Latin Church In the Latin Church, the members of the chapter of a cathedral (cathedral chapter) or of a collegiate church (so-called after their chapter) are canons. Depending on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched the Reformation, Protestant Reformation. The reaction of the government and church authorities to the international spread of his writings, beginning with the ''Ninety-five Theses'', divided Western Christianity. During the Reformation, Lutheranism became the state religion of numerous states of northern Europe, especially in northern Germany, Scandinavia and the then-Livonian Order. Lutheran clergy became civil servants and the Lutheran churches became part of the state. The split between the Lutherans and the Roman Catholics was made public and clear with the 1521 Edict of Worms: the edicts of the Diet (assembly), Diet condemned Luther and officially banned citizens of the Holy Roman Empire from defending or propagatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies located List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lohra, Germany
Lohra is a municipality in Marburg-Biedenkopf district in the administrative region of Gießen in Hesse, Germany. Geography Lohra's municipal area, measuring 49 km², stretches across the middle Salzböde valley and the ''Versgrund''. Among its neighbouring communities are Weimar an der Lahn in the northeast, Fronhausen in the southeast and in the northwest Gladenbach, all in the Marburg-Biedenkopf district, as well as the town of Lollar, Wettenberg and Biebertal in Gießen district, and Bischoffen in Lahn-Dill district. The community of Lohra is found in the so-called ''Marburger Land''. Together with the communities of Fronhausen, Weimar and Ebsdorfergrund, Lohra forms the southern part of Marburg-Biedenkopf. The community of Lohra is sometimes wrongly said to be part of the ''Hessisches Hinterland'', but not even any of the old villages now belonging to Lohra were part of the old Biedenkopf district, and therefore they were not part of the ''Hinterland''; they had b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volkmar Wolf Of Hohnstein
Volkmar is both a given name and a surname. Notable people with the name include: Given name * Volkmar Andreae (1879–1962), Swiss conductor and composer *Volkmar Leimert (born 1940), German composer and dramaturg *Volkmar Sigusch (born 1940), German physician and sociologist *Volkmar Weiss (born 1944), German scientist and writer *Volkmar Wentzel (1915–2006), German-born American photographer *Volkmar Würtz (born 1938), German fencer Surname * Fred R. Volkmar, American psychiatrist *Theodor Valentin Volkmar (1781–1847), German jurist and politician Fictional characters *Volkmar the Grim, a character in the tabletop game of ''Warhammer'' *Count Volkmar of Gretz, a line of heritage in James A. Michener's ''The Source'' See also *Volkmer *Volckmar Hans Volckmar (October 6, 1900 – ??) was an Austrian bobsledder who competed in the mid-1930s. He finished 19th in the two-man event at the 1936 Winter Olympics in Garmisch-Partenkirchen Garmisch-Partenkirchen (; Bav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
.jpg)