|
Jewish History Of Sopron
Sopron (, ) was historically the capital of a district with the same name. It was home to a Jewish community, according to a document of 1526, which dated back from the 10th century and is one of the oldest in Hungary. The town was destroyed by fire in 1317. Charles Robert invited Jewish colonists into the town in 1324; they lived there in peace until 1354, when they were expelled by Louis the Great. Most of them went to Austria and settled in Wiener-Neustadt. A few years afterward they were allowed to return, and in 1379 the Jewish population in Oedenburg amounted to 80, reaching 400 toward the end of the 15th century. Recognizing that the Jews constituted a valuable fiscal asset, Frederick III, to whom Elizabeth had mortgaged Oedenburg, took energetic measures to protect the Jews there against the aggression of their Christian fellow citizens and prevent their expulsion (1441). In 1490 the citizens of Oedenburg seized upon the Jews and cast them into prison with the declared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
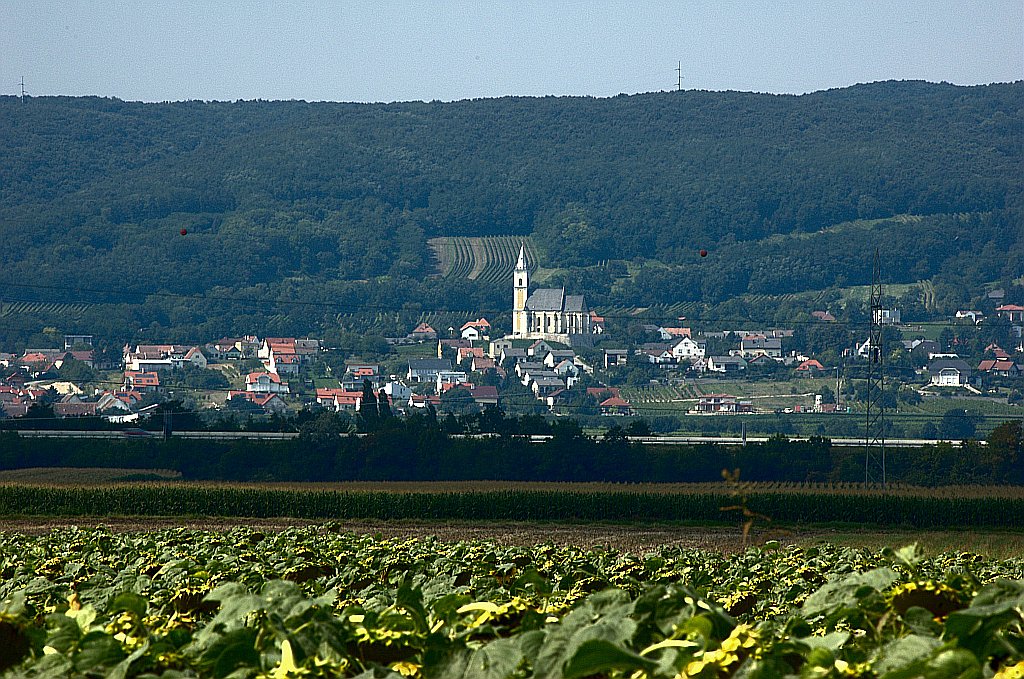
Sopron
Sopron (; , ) is a city in Hungary on the Austrian border, near Lake Neusiedl/Lake Fertő. History Ancient times-13th century In the Iron Age a hilltop settlement with a burial ground existed in the neighbourhood of Sopron-Várhely. When the area that is today Western Hungary was a province of the Roman Empire, a city called ''Scarbantia'' stood here. The site of its forum is now the main square of Sopron. During the Migration Period, Scarbantia was believed to be deserted. When Hungarians arrived in the area, the city was in ruins. From the 9th to the 11th centuries, Hungarians strengthened the old Roman city walls and built a castle. The city was named in Hungarian after a castle steward named ''Suprun''. In 1153, it was mentioned as an important city. In 1273, King Otakar II of Bohemia occupied the castle. Even though he took the children of Sopron's nobility with him as hostages, the city opened its gates when the armies of King Ladislaus IV of Hungary arrived. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eisenstadt
Eisenstadt (; ; ; or ; ) is the capital city of the Provinces of Austria, Austrian state of Burgenland. With a population of 15,074 (as of 2023), it is the smallest state capital and the 38th-largest city in Austria overall. It lies at the foot of the Leitha Mountains hill range. From 1648 to 1921, Kismarton/Eisenstadt was part of the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg Empire's Kingdom of Hungary and the seat of the Hungarian nobility, Hungarian noble family House of Esterházy, Eszterházy. During this time, the composer Joseph Haydn lived and worked in Eisenstadt as a court musician under the patronage of the Esterházy family. After the cession of Burgenland to Austria in 1921, the city became the province's capital in 1925. As the state capital of Burgenland, it functions as a center of public administration and services and is the seat of three institutes of higher education. Geography Eisenstadt lies on a plain leading down to the river Wulka, at the southern foot of the Leitha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heiligen-Kreuz
Heiligenkreuz im Lafnitztal (, ) is a town in the district of Jennersdorf in the Austrian state of Burgenland Burgenland (; ; ; Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian: ''Burgnland''; Slovene language, Slovene: ''Gradiščanska''; ) is the easternmost and least populous Bundesland (Austria), state of Austria. It consists of two statutory city (Austria), statut ... close to the Austria/Hungary border. Geography Cadastral communities are Heiligenkreuz im Lafnitztal and Poppendorf im Burgenland. www.bev.gv.at Population References External links * * http://www.lafnitztal.info/ Cities and towns in Jennersdo ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lackenbach
Lackenbach (, ) is an Austrian municipality in the District of Oberpullendorf (district), Oberpullendorf, Burgenland. Geography Lackenbach lies in the Oberpullendorf District, the Middle Burgenland and is not divided into any districts. History Between 1548 and 1552, Lackenbach was developed as a fort. After 1670-71 many Jews from Vienna settled there. From the 18th century, Lackenbach belonged to Prince House of Esterházy, Esterházy's Siebengemeinden where the Jews had their own autonomous administration. The town, like the rest of Burgenland, belonged to the Kingdom of Hungary until 1920–21. After the end of the First World War, the western border area of Hungary was awarded to Austria by the Treaties of Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1919), St. Germain and Treaty of Trianon, Trianon. Since 1921, the town has belonged to the newly founded State of Burgenland. In 1940, a "Gypsy-''Anhaltelager''" was established on municipal territory at a former estate of the Esterh� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Population
the world's core Jewish population (those identifying as Jews above all else) was estimated at 15.8 million, which is approximately 0.2% of the 8 billion worldwide population. Israel hosts the largest core Jewish population in the world with 7.2 million, followed by the United States with 6.3 million. Other countries with core Jewries above 100,000 include France (440,000), Canada (398,000), the United Kingdom (312,000), Argentina (171,000), Russia (132,000), Germany (125,000), and Australia (117,200). The number of Jews worldwide rises to 18 million with the addition of the "connected" Jewish population, including those who say they are partly Jewish or that have Jewish backgrounds from at least one Jewish parent, and rises again to 21 million with the addition of the "enlarged" Jewish population, including those who say they have Jewish backgrounds but no Jewish parents and all non-Jewish household members who live with Jews. Counting all those who are eligible for Israeli c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Free City
A royal free city, or free royal city (Latin: ''libera regia civitas''), was the official term for the most important cities in the Kingdom of Hungary from the late 12th centuryBácskai Vera – Nagy Lajos: Piackörzetek, piacközpontok és városok Magyarországon 1828-ban. Budapest, 1984. to the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. The cities were granted certain privileges by the King of Hungary to prevent their control by the Hungarian nobility, hence "royal", and exercised some self-government in relation to their internal affairs and so were "free". From the late 14th century, the elected envoys of the royal free cities participated in the sessions of the Diet of Hungary, Hungarian Diet and so they became part of the legislature. This list also includes cities in the Kingdom of Croatia (other), Kingdom of Croatia and the Banate of Bosnia, which were part of the Lands of the Hungarian Crown. The term "royal free city" in the kingdom's languages is as follows: * * * * * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toleration
Toleration is when one allows or permits an action, idea, object, or person that they dislike or disagree with. Political scientist Andrew R. Murphy explains that "We can improve our understanding by defining 'toleration' as a set of social or political practices and 'tolerance' as a set of attitudes." ''Random House Dictionary'' defines tolerance as "a fair, objective, and permissive attitude toward those whose opinions, beliefs, practices, racial or ethnic origins, etc., differ from one's own". The Merriam-Webster Dictionary associates toleration both with "putting up with" something undesirable, and with neglect or failure to prevent or alleviate it. Both these concepts contain the idea of alterity: the state of ''otherness''. Additional choices of how to respond to the "other", beyond toleration, exist. Therefore, in some instances, toleration has been seen as "a flawed virtue" because it concerns acceptance of things that were better overcome. Toleration cannot, therefore, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batthyány
The House of Batthyány () is an ancient and distinguished Hungarian noble magnate family. The Head of the family bears the title Prince (Fürst) of Batthyány-Strattmann, while other members of this family bear the title Count/Countess ( Graf/Gräfin) Batthyány von Német-Ujvar respectively. A branch of the family () was notable in Bosnia and Croatia as well, producing several Bans (viceroys) of Jajce in the 15th and 16th century and later Bans of Croatia in the 16th, 17th and 18th century. History The Batthyány family can trace its roots to the founding of Hungary in 896 CE by Árpád. The family derives from a chieftain called Örs. Árpád had seven chieftains, one by the name of Örs, which later became Kővágó-Örs. In 1398, Miklós Kővágó-Örs married Katalin Battyány. King Zsigmond (Sigismund) gave Miklós the region around the town of Battyán (now called Szabadbattyán) and he took the name Batthyány (lit. "from Battyán"). The family were first mentione ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Esterházy
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.Schoenauer, Norbert (2000). ''6,000 Years of Housing'' (rev. ed.) (New York: W.W. Norton & Company). Houses use a range of different roofing systems to keep precipitation such as rain from getting into the dwelling space. Houses generally have doors or locks to secure the dwelling space and protect its inhabitants and contents from burglars or other trespassers. Most conventional modern houses in Western cultures will contain one or more bedrooms and bathrooms, a kitchen or cooking area, and a living room. A house may have a separate dining room, or the eating area may be integrated into the kitchen or another room. Some large houses in North America have a recreation room. In traditional agriculture-oriented soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pfennig
The pfennig (; . 'pfennigs' or 'pfennige' ; currency symbol, symbol pf or ₰) or penny is a former Germany, German coin or note, which was an official currency from the 9th century until the introduction of the euro in 2002. While a valuable coin during the Middle Ages, it lost its value through the years and was the minor coin of the Mark (money), Mark currencies in the German Reich, West Germany and East Germany, and the German reunification, reunified Germany until the introduction of the euro. Pfennig was also the name of the subunit of the Danzig mark (1922–1923) and the Danzig gulden (1923–1939) in the Free City of Danzig (modern Gdańsk, Poland). Overview Name The word ''Pfennig'' (replacing the ''denarius'' or ''denarius'' as a low-denomination silver coin) can be traced back to the 8th century and also became known as the ''Penning'', ''Panni(n)g '', ''Pfenni(n)c'', ''Pfending'' and by other names, e.g. in Prussia until 1873, ''Pfenning''. The ''-ing''- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul I, 1st Prince Esterházy Of Galántha
Paul may refer to: People * Paul (given name), a given name, including a list of people * Paul (surname), a list of people * Paul the Apostle, an apostle who wrote many of the books of the New Testament * Ray Hildebrand, half of the singing duo Paul & Paula * Paul Stookey, one-third of the folk music trio Peter, Paul and Mary * Billy Paul, stage name of American soul singer Paul Williams (1934–2016) * Vinnie Paul, drummer for American Metal band Pantera * Paul Avril, pseudonym of Édouard-Henri Avril (1849–1928), French painter and commercial artist * Paul, pen name under which Walter Scott wrote ''Paul's letters to his Kinsfolk'' in 1816 * Jean Paul, pen name of Johann Paul Friedrich Richter (1763–1825), German Romantic writer Places *Paul, Cornwall, a village in the civil parish of Penzance, United Kingdom *Paul (civil parish), Cornwall, United Kingdom *Paul, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community *Paul, Idaho, United States, a city *Paul, Nebraska, United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |