|
Jethwa
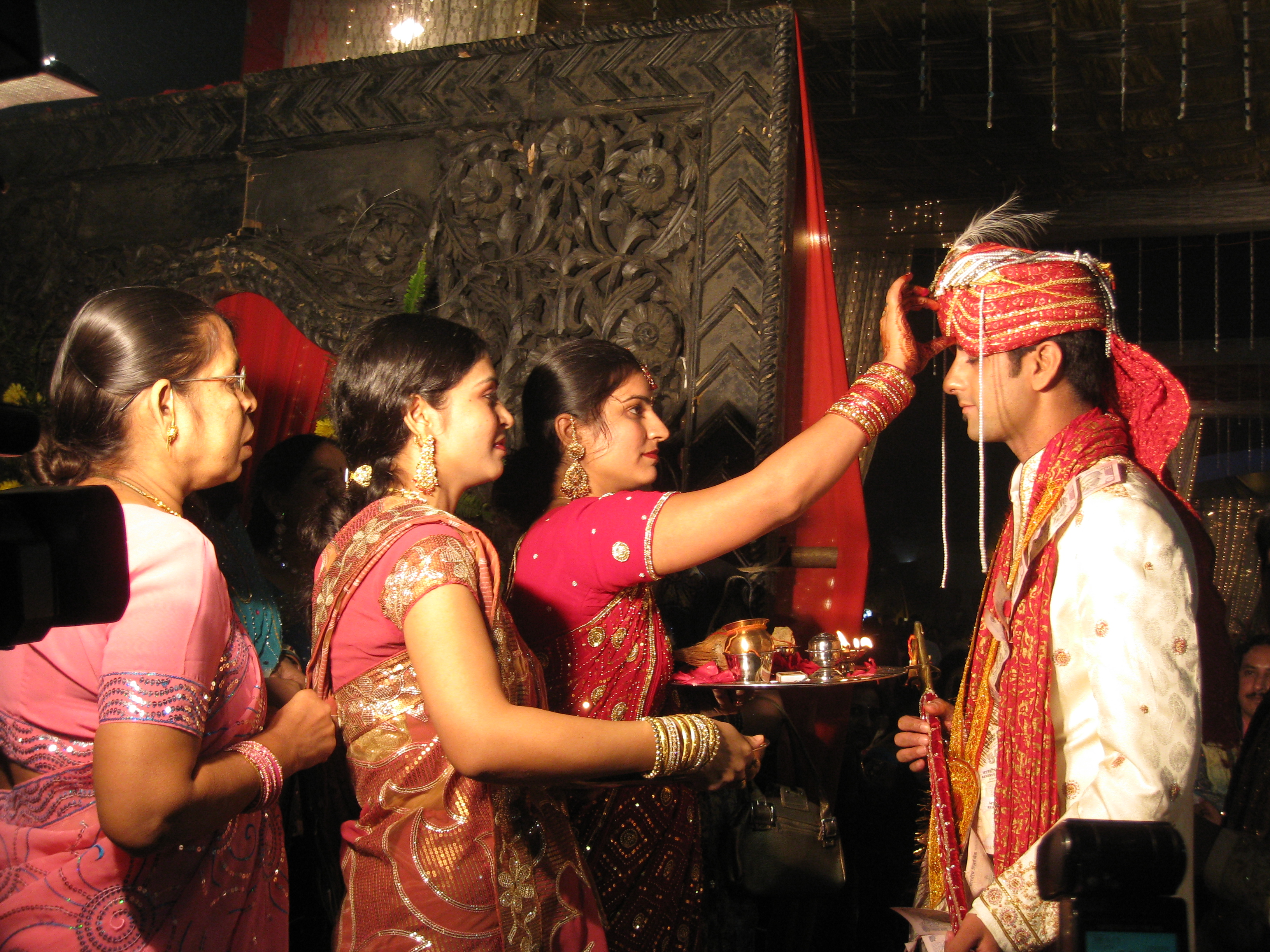
Jethwa (Jethva, Jaitwa or Jethi) is a clan of Rajputs and caste of Gujarat. Jethwa surname is also found amongst the Koli Darji, Mistris of Kutch, and Gurjar Kshatriya Kadias castes of Gujarat. Origin It has been suggested that the Saindhava dynasty ruling eastern part of Saurashtra peninsula is now represented by the present day Jethwa dynasty. It is also suggested that the term Jethwa probably originating from Jayadratha (another name of Saindhawa dynasty), Jyeshtha (the elder branch) or Jyeshthuka from which the region derived its name Jyeshthukadesha. Other details and Kuldevis The ''Jethwa'' Rajputs belong to the Gautam/Vajas Gotra and their Kuldevi is Vindhyavasini Devi ''Devī'' (; ) is the Sanskrit word for 'goddess'; the masculine form is Deva (Hinduism), ''deva''. ''Devi'' and ''deva'' mean 'heavenly, divine, anything of excellence', and are also gender-specific terms for a deity in Hinduism. The concept .... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jethwa Dynasty
Jethwa dynasty was a dynasty that ruled over present day Gujarat region of India from 7th century AD till middle of 20th century, when India became independent. It was a Rajput dynasty ruled by Jethwa clan of Rajputs. Origin Jethwa (or Jethva, Jatava, Jaitwa or Camari,Jaitwa or Camari.—; one of the thirty-six royal races mentioned by Colonel Tod. The Tribes and Castes of the Central Provinces of India—Volume I (of IV), by R.V. Russell. The Jethwa claim their descent from , son of . [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mestri (community)
Kutch Gurjar Kshatriya (also known as Mistri or Mestri) are a minority Hindu community of Gujarat in India, who claim to be Kshatriya. They are an artisan community related with masonry, artistic carvings, sculpting and building and construction works. They are also known as the Mistris of Kutch adopting word Mistri, a term used in British India for master-craftsman, thekedar, foreman or supervisor or for those who were expert in building and construction.Mistri Encyclopaedia of Backward Castes By Neelam Yadav Page 316. History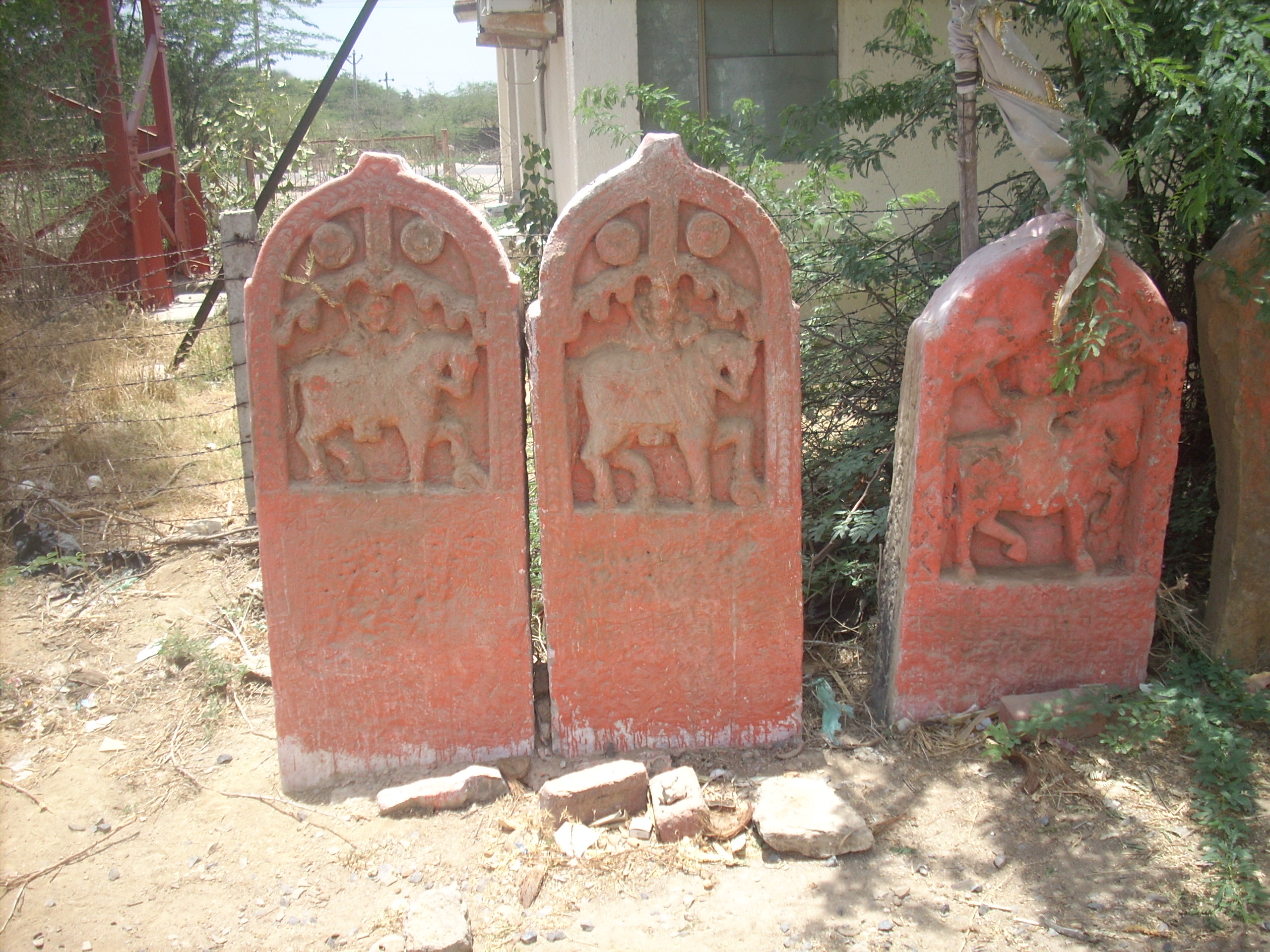  The community is believe ...
The community is believe ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saindhava
The Saindhavas, also known as Jayadrathas, was a medieval Indian dynasty that ruled western Saurashtra (now in Gujarat, India) from c. 735 CE to c. 920 CE, probably in alliance with Maitrakas in its early years. Their capital was at Bhutamabilika (now Ghumli). The known historical events during their rule are the attacks of Arabs repulsed by Agguka I. Sources of information The earliest reference of Saindhava was found in Navsari copperplate of Chalukya governor of Lata region (modern-day South Gujarat) Avanijanashraya Pulakeshin dated 738-39 CE which enlisted the dynasties defeated by Arabs and finally repelled by him. The eighth verse in Gwalior ''prashasti'' of Bhojadeva describes the Saindhava ruler defeated by Pratihara king Nagabhatta. The nine copper plate grants issued by Saindhavas help to establish their genealogy as well as provides useful information about the dynasty. Six grants inscribed in 12 copper plates were discovered while digging on roadside in Ghuml ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, a clan may claim descent from a founding member or apical ancestor who serves as a symbol of the clan's unity. Many societies' exogamy rules are on a clan basis, where all members of one's own clan, or the clans of both parents or even grandparents, are excluded from marriage as incest. Clans preceded more centralized forms of community organization and government, and have existed in every country. Members may identify with a coat of arms or other symbol. Etymology The word "clan" is derived from the Gaelic word meaning "children", "offspring", "progeny" or "descendants". According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', the word "clan" was introduced into English in around 1406, as a descriptive label for the organization of society in Ireland and the Scottish Highlands. None of the Irish and Scottish Gaelic terms for kinship groups is cognate to English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Dynasties
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. It is assumed that the term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Avestan scripture Vendidad which refers to land of seven rivers as Hapta Hendu which itself is a cognate to Sanskrit term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ''. (The term ''Sapta Sindhuḥ'' is mentioned in Rig Veda and refers to a North western Indian region of seven rivers and to India as a whole.) The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). Likewise the Hebrew cognate ''hōd-dū'' refers to India mentioned in Hebrew BibleEsther 1:1. The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suryavansha
The Solar dynasty or (; ), also called the Ikshvaku dynasty, is a legendary Indian dynasty said to have been founded by Ikshvaku. In Hindu literature, it ruled the Kosala Kingdom, with its capital at Ayodhya, and later at Shravasti. They worshipped their clan deity, Surya (a Hindu solar deity), after whom the dynasty is named. Along with the Lunar dynasty, the Solar dynasty comprises one of the main lineages of the Kshatriya varna in Hinduism. According to Jain literature, the first ''Tirthankara'' of Jainism, Rishabhanatha himself, was King Ikshvaku. Twenty-one further ''Tirthankaras'' were born in this dynasty. According to Buddhist literature, Gautama Buddha descended from the this dynasty. The important personalities belonging to this royal house are Mandhatri, Muchukunda, Ambarisha, Bharata, Bahubali, Harishchandra, Dilīpa, Sagara, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devi
''Devī'' (; ) is the Sanskrit word for 'goddess'; the masculine form is Deva (Hinduism), ''deva''. ''Devi'' and ''deva'' mean 'heavenly, divine, anything of excellence', and are also gender-specific terms for a deity in Hinduism. The concept and reverence for goddesses appears in the Vedas, which were composed around the 2nd millennium BCE. However, they did not play a vital role in that era. Goddesses such as Durga, Kali, Lakshmi, Parvati, Radha, Saraswati and Sita have continued to be revered in the modern era. The medieval era Puranas witness a major expansion in mythology and literature associated with Devi, with texts such as the ''Devi Mahatmya'', wherein she manifests as the ultimate truth and supreme power. She has inspired the Shaktism tradition of Hinduism. Further, Devi is viewed as central in the Hindu traditions of Shaktism and Shaivism. Etymology ''Devi'' and ''deva'' are Sanskrit terms found in Vedic literature around the 3rd millennium BCE. ''Deva'' is masculi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yogamaya
Yogamaya (, ) is a Hinduism, Hindu goddess who serves as the personification of Vishnu's powers of illusion. In Vaishnavism, Vaishnava tradition, she is accorded the epithet Narayani—"the sister of Narayana (Vishnu)"—and is regarded as the benevolent aspect of the goddess Durga. According to Hindu texts, Yogamaya plays the role of the facilitator of the earthly birth of Krishna, an incarnation of Vishnu. She took the avatar of the daughter of Yadava cowherd Nanda (Hinduism), Nanda and Yashoda, after which her place is swapped with Krishna to protect the latter from the tyrant ruler Kamsa. After warning Kamsa about his impending death, Yogamaya vanished and resided in the Vindhya Range, Vindhya hills, due to which she is accorded the epithet Vindhyavasini. Yogamaya is also an important goddess in Shaktism sect, and is worshipped as a form of Mahadevi. Etymology Yogamaya refers to “the internal potency of Vishnu, Bhagavan, that arranges and enhances all his pastimes� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuldevi
A ''kuladevata'' (), also known as a ''kuladaivaṃ'' (), is an ancestral tutelary deity in Hinduism and Jainism. Such a deity is often the object of one's devotion (''bhakti''), and is coaxed to watch over one's clan (''kula''), gotra, family, and children from misfortune. This is distinct from an '' ishta-devata'' (personal tutelar) and a grāmadevatā (village deities). A male deity is called a ''kuladeva'' and female deity ''kuladevi'' (sometimes spelled ''kuldev'' and ''kuldevi'' respectively). Etymology The word ''kuladevata'' is derived from two words: ''kula'', meaning clan, and ''devata'', meaning deity, referring to the ancestral deities that are worshipped by particular clans. Veneration Kuladaivams of the Shaiva tradition are often considered to be forms of Shiva and Parvati, while those of the Vaishnava tradition are often regarded to be forms of Vishnu and Lakshmi. Due to the veneration of holy men (''babas'') in several regions of the subcontinent, several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotra
In Hindu culture, the term gotra (Sanskrit: गोत्र) is considered to be equivalent to lineage. It broadly refers to people who are descendants in an unbroken male line from a common male ancestor or patriline. Generally, the gotra forms an exogamous unit, with marriage within the same gotra being regarded as incest and prohibited by custom. The name of the gotra can be used as a surname, but it is different from a surname and is strictly maintained because of its importance in marriages among Hindus, especially among castes. Pāṇini defines ''gotra'' as ''apatyam pautraprabhrti gotram'' (IV. 1. 162), which means "the word ''gotra'' denotes the descendance (or descendants), ''apatya'', of a couple consisting of a ''pautra'', a son and a ''bharti'', a mother, i.e. a daughter-in-law." (Based on Monier Williams Dictionary definitions.) Foundational structure According to the Brihadaranyaka Upanishad 2.2.4,'' Kashyapa, Atri, Vasistha, Vishvamitra, Gautama Maharish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gautama Maharishi
Gautama (, ), was a sage in Hinduism and son of Brahmin sage Dirghatamas who is also mentioned in Jainism and Buddhism. Gautama is mentioned in the Yajurveda, Ramayana, and Ganesha Purana, Gaṇeśa Pūrana and is known for cursing his wife Ahalya, Ahalyā. Another important story related to Gautama is about the creation of river Godavari River, Godavari, which is also known as Gautami. Children According to the Ramayana, Gautama's eldest son with Ahalya is Shatananda. But according to the Adi Parva of Mahabharata, he had two sons named Sharadvana and Cirakari. Sharadvana was also known as Gautama, hence his children Kripa and Kripi were called Gautama and Gautami respectively. A daughter of Gautama is referred too, but her name is never disclosed in the epic. In the Sabha Parva, he is described to beget many children through Aushinara (daughter of Ushinara), amongst whom the eldest in Kakshivata. Gautama and Aushinara's wedding takes place at Magadha, the kingdom of Jarasandha. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharaja Sayajirao University Of Baroda
Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, formerly Baroda College, is a public university in the city of Vadodara, Gujarat, India. Originally established as a college in 1881, it became a public university on April 30, 1949 and was renamed after its benefactor Maharaja Sayajirao Gaekwad III, the former ruler of Baroda State. The university offers undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral programs. It houses 89 departments spread over 6 campuses (2 rural and 4 urban) covering 275 acres of land. History The university has its origins in the Baroda College, established in 1881 by Baroda State. The main building, which houses the Faculty of Arts, was designed by Robert Chisholm (architect), Robert Fellowes Chisholm in Indo-Saracenic architecture style, in a fusion of Indian and Byzantine arches and domes in brick and polychrome stone. The main dome on the convocation hall was modelled after the great dome of the Gol Gumbaz in Bijapur, Karnataka, Bijapur. Pratap Singh Gaekwad of Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |