|
JetOS
The JetOS RTOS () is a Unix-like real-time operating system under development by the Russian State Scientific Research Institute of Aviation Systems and the Institute for System Programming. JetOS is primarily designed for use in embedded systems for civil aviation, as part of the Russian strategy of import substitution. JetOS is designed to power avionics systems on commercial aircraft such as the Yakovlev SJ-100 and Yakovlev MC-21, enabling real-time data acquisition, processing and display for control systems, navigation and other flight parameters. The operating systems supports running up to 30 applications to be run during flight, meeting the requirements for DO-178C and ARINC 653. History Development of JetOS began in 2016 on order of the Ministry of Industry and Trade as part of import-substitution measures to create an alternative to foreign operating systems such as LynxOS, VxWorks and PikeOS. The first version of the operating system was operational in 2019, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhoi Superjet 100
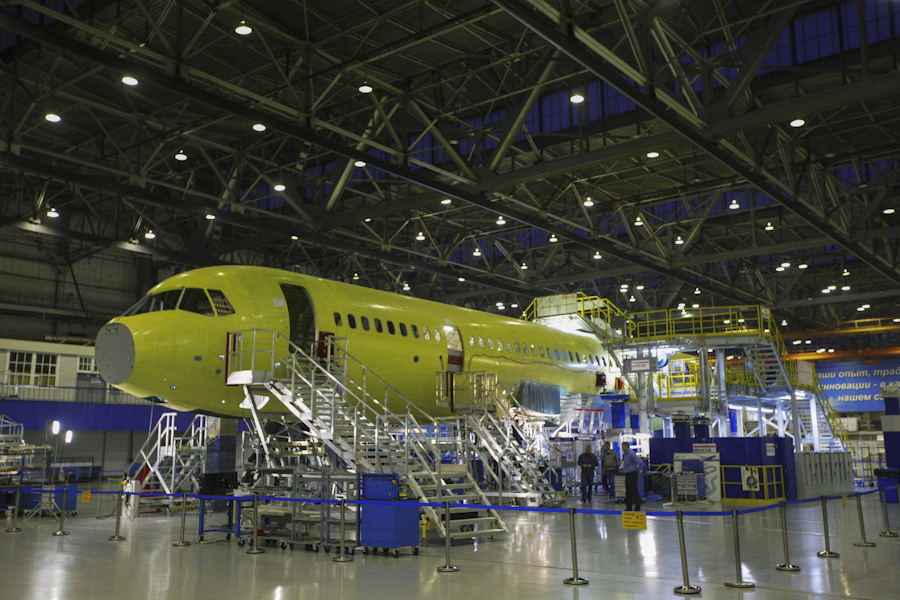
The Yakovlev SJ-100 (until August 2023: Sukhoi Superjet 100 SJ100 ) is a regional jet originally designed by the now-merged Russian aircraft company Sukhoi Civil Aircraft, a division of the United Aircraft Corporation (now: "Regional Aircraft" company branch). With development starting in 2000, it made its maiden flight on 19 May 2008 and its first commercial flight on 21 April 2011 with Armavia. The MTOW plane typically seats 87 to 98 passengers. Aircraft built before 2025 are powered by two PowerJet SaM146 turbofans developed by a joint venture between French Safran and Russian NPO Saturn. By May 2018, 127 aircraft were in service, and by September the fleet had logged 300,000 revenue flights and 460,000 hours. By November 2021 the fleet had logged at least 2 million hours. The type has recorded four hull loss accidents and 89 deaths . In 2022, Sukhoi announced a Russified version of the body and electronics, without most of the Western components. The engines were al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakovlev MC-21
The Yakovlev MC-21 () is a Narrow-body airliner, single-aisle airliner, under development in Russia by the Yakovlev Corporation (formerly known as Irkut Corporation), a branch of the United Aircraft Corporation (UAC), itself a 92%-owned subsidiary of Russia's state-owned aviation giant Rostec. The variant MC-21-310 of the airliner powered by the Russian-made Aviadvigatel PD-14 engine made its maiden flight on 15 December 2020 from Irkutsk. Project history The program to build the MC-21 was launched in 2007. Irkut rolled out the first MC-21-300 with Pratt & Whitney engines on 8 June 2016 and first flew the aircraft on 28 May 2017. The twinjet has a carbon fibre reinforced polymer wing and was to be powered by Aviadvigatel PD-14 turbofans or Pratt & Whitney PW1000G engines. By July 2018, the company had received 175 firm orders. In early 2022, international sanctions against Russia were imposed due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Irkut Corporation was placed on the I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X86 Operating Systems
x86 (also known as 80x86 or the 8086 family) is a family of complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set architectures initially developed by Intel, based on the 8086 microprocessor and its 8-bit-external-bus variant, the 8088. The 8086 was introduced in 1978 as a fully 16-bit extension of 8-bit Intel's 8080 microprocessor, with memory segmentation as a solution for addressing more memory than can be covered by a plain 16-bit address. The term "x86" came into being because the names of several successors to Intel's 8086 processor end in "86", including the 80186, 80286, 80386 and 80486. Colloquially, their names were "186", "286", "386" and "486". The term is not synonymous with IBM PC compatibility, as this implies a multitude of other computer hardware. Embedded systems and general-purpose computers used x86 chips before the PC-compatible market started, some of them before the IBM PC (1981) debut. , most desktop and laptop computers sold are based on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embedded Operating Systems
An embedded operating system (EOS) is an operating system designed specifically for embedded computer systems. These systems aim to enhance functionality and reliability to perform dedicated tasks. When the multitasking method employed allows for timely task execution, such an OS may qualify as a real-time operating system (RTOS). Overview Embedded operating systems are integral to consumer electronics such as cameras and mobile phones. Additionally, they power automotive electronics, aiding in functions like cruise control and navigation. Moreover, they are essential for factory automation infrastructure. Everyday applications of EOS include office automation devices such as image scanners, photocopiers, and wireless access points. Home automation systems, including security systems, also depend on EOS. Design Embedded systems comprise a processor and corresponding software. Embedded software requires storage for executables and temporary data processing during runtim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real-time Operating Systems
A real-time operating system (RTOS) is an operating system (OS) for real-time computing applications that processes data and events that have critically defined time constraints. A RTOS is distinct from a time-sharing operating system, such as Unix, which manages the sharing of system resources with a scheduler, data buffers, or fixed task prioritization in multitasking or multiprogramming environments. All operations must verifiably complete within given time and resource constraints or else fail safe. Real-time operating systems are event-driven and preemptive, meaning the OS can monitor the relevant priority of competing tasks, and make changes to the task priority. Characteristics A key characteristic of an RTOS is the level of its consistency concerning the amount of time it takes to accept and complete an application's task; the variability is "jitter". A "hard" real-time operating system (hard RTOS) has less jitter than a "soft" real-time operating system (soft RTOS); a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tupolev Tu-204
The Tupolev Tu-204 () is a twin-engined medium- range narrow-body jet airliner capable of carrying 210 passengers, designed by Tupolev and produced by Aviastar-SP and Kazan Aircraft Production Association. First introduced in 1995, it was intended to be broadly equivalent to the Boeing 757, with slightly lower range and payload, and had competitive performance and fuel efficiency in its class. It was developed for Aeroflot as a replacement for the medium-range Tupolev Tu-154 trijet in the 1990s. The latest version, with significant upgrades and improvements, is the narrow-body Tu-204SM, which made its maiden flight on 29 December 2010. In April 2022, United Aircraft Corporation (UAC) announced plans to assemble 70 Tu-214s by 2030. However, in early 2024, Aeroflot expressed intention to transfer its order for fleets exclusively to next-generation MC-21 jets. The rejection of the Tupolev has various reasons, including no two-member cockpit, and also the evacuation ramps and ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PikeOS
PikeOS is a commercial hard real-time operating system (RTOS) which has a separation kernel-based hypervisor that supports multiple logical partition types for various operating systems (OS) and applications, each referred to as a GuestOS. PikeOS is engineered to support the creation of certifiable smart devices for the Internet of Things (IoT). In instances where memory management units (MMU) are not present but memory protection units (MPU) are available on controller-based systems, PikeOS for MPU is designed for critical real-time applications and provides up-to-standard safety and security. Overview PikeOS was introduced in 2005 and combines a real-time operating system (RTOS) with a virtualization platform and Eclipse-based integrated development environment (IDE) for embedded system (embedded systems). It is a commercial clone of the L4 microkernel family. PikeOS has been developed for safety and security-critical applications with certification needs in the fields o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VxWorks
VxWorks is a real-time operating system (or RTOS) developed as proprietary software by Wind River Systems, a subsidiary of Aptiv. First released in 1987, VxWorks is designed for use in embedded systems requiring real-time, Deterministic system, deterministic performance and in many cases, safety and security certification for industries such as Aerospace engineering, aerospace, Arms industry, defense, medical devices, industrial equipment, robotics, energy, transportation, network infrastructure, automotive, and consumer electronics.VxWorks Goes 64-bit", Electronic Design, March 25, 2011 VxWorks supports AMD/Intel architecture, POWER architecture, ARM architectures, and RISC-V. The RTOS can be used in multicore asymmetric multiprocessing (AMP), symmetric multiprocessing (SMP), and mixed modes [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LynxOS
The LynxOS RTOS is a Unix-like real-time operating system from Lynx Software Technologies (formerly "LynuxWorks"). Sometimes known as the Lynx Operating System, LynxOS features full POSIX conformance and, more recently, Linux compatibility. LynxOS is mostly used in real-time embedded systems, in applications for avionics, aerospace, the military, industrial process control and telecommunications. History The first versions of LynxOS were written in 1986 in Dallas, Texas, by Mitchell Bunnell and targeted at a custom-built Motorola 68010-based computer. The first platform LynxOS ran on was an Atari 1040ST with cross development done on an Integrated Solutions UNIX machine. In 1988-1989, LynxOS was ported to the Intel 80386 architecture. Around 1989, application binary interface (ABI) compatibility with UNIX System V.3 was added. Compatibility with other operating systems, including Linux, followed. Full Memory Management Unit support has been included in the kernel since 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARINC 653
ARINC 653 (Avionics Application Software Standard Interface) is a software specification for space and time partitioning in safety-critical avionics real-time operating systems (RTOS). It allows the hosting of multiple applications of different software levels on the same hardware in the context of an Integrated Modular Avionics architecture. It is part of ARINC 600-Series Standards for Digital Aircraft & Flight Simulators. Overview In order to decouple the real-time operating system platform from the application software, ARINC 653 defines an API called APplication EXecutive (APEX). Each application software is called a partition and has its own memory space. It also has a dedicated time slot allocated by the APEX API. Within each partition, multitasking is allowed. The APEX API provides services to manage partitions, processes and timing, as well as partition/process communication and error handling. The partitioning environment can be implemented by using a hypervisor to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DO-178C
DO-178C, Software Considerations in Airborne Systems and Equipment Certification is the primary document by which the certification authorities such as Federal Aviation Administration, FAA, European Aviation Safety Agency, EASA and Transport Canada approve all commercial software-based aerospace systems. The document is published by RTCA, Incorporated, in a joint effort with EUROCAE, EUROC and replaces DO-178B. The new document is called DO-178C/ED-12C and was completed in November 2011 and approved by the RTCA in December 2011. It became available for sale and use in January 2012. Except for Federal_Aviation_Regulations#Organization, FAR 33/Joint Aviation Requirements, JAR E, the Federal Aviation Regulations do not directly reference software airworthiness. On 19 Jul 2013, the FAA approved AC 20-115, AC 20-115C, designating DO-178C a recognized "acceptable means, but not the only means, for showing compliance with the applicable FAR airworthiness regulations for the software asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Scientific Research Institute Of Aviation Systems
State Scientific Research Institute of Aviation Systems or GosNIIAS for short () is a Russian aerospace research centre. Founded by the decree of the Council of Ministers of the USSR on 26 February 1946 from a number of laboratories of the Flight Research Institute for operations research and aviation weapons system A weapon, arm, or armament is any implement or device that is used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime (e.g., murder), law e ...s development. The new institute was named NII-2. In March 1994 the institute was re-named with its current name (GosNIIAS). Initially, the institute was located in the buildings of the former Sergievo-Elizabethan Asylum. In GosNIIAS, there are six basic departments leading students and graduate students from three universities: * Department FUPM MIPT “Avionics. Control and Information Systems. Organized in 1969, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |