|
Jazz Drummer
Jazz drumming is the art of playing percussion (predominantly the drum kit, which includes a variety of drums and cymbals) in jazz styles ranging from 1910s-style Dixieland jazz to 1970s-era jazz fusion and 1980s-era Latin jazz. The techniques and instrumentation of this type of performance have evolved over several periods, influenced by jazz at large and the individual drummers within it. Stylistically, this aspect of performance was shaped by its starting place, New Orleans,Ted Gioia, Gioia, T. (1997). ''The History of Jazz''. Oxford University Press: New York. as well as numerous other regions of the world, including other parts of the United States, the Caribbean, and Africa.Brown, T, D. (1976). ''A History and Analysis of Jazz Drumming to 1942''. University Microfilms: Ann Arbor, Michigan. Jazz required a method of playing percussion different from traditional European styles, one that was easily adaptable to the different rhythms of the new genre, fostering the creation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Roach
Maxwell Lemuel Roach (January 10, 1924 – August 16, 2007) was an American jazz drummer and composer. A pioneer of bebop, he worked in many other styles of music, and is generally considered one of the most important drummers in history. He worked with many famous jazz musicians, including Clifford Brown, Coleman Hawkins, Dizzy Gillespie, Charlie Parker, Miles Davis, Duke Ellington, Thelonious Monk, Abbey Lincoln, Dinah Washington, Charles Mingus, Billy Eckstine, Stan Getz, Sonny Rollins, Eric Dolphy, and Booker Little. He also played with his daughter Maxine Roach, a Grammy nominated violist. He was inducted into the ''DownBeat'' Hall of Fame in 1980 and the '' Modern Drummer'' Hall of Fame in 1992. In the mid-1950s, Roach co-led a pioneering quintet along with trumpeter Clifford Brown. In 1970, he founded the percussion ensemble M'Boom. Biography Early life and career Max Roach was born to Alphonse and Cressie Roach in the Township of Newland, Pasquotank County ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Spain
In Spain, music has played an important role in the development of Western music, and has greatly influenced Latin American music. Spanish music is often associated with traditional styles such as flamenco and classical guitar. While these forms of music are common, there are many different traditional musical and dance styles across the regions. For example, music from the north-west regions is heavily reliant on bagpipes, the Jota (music), jota is widespread in the centre and north of the country, and flamenco originated in the south. Spanish music played a notable part in the early developments of western classical music, from the 15th through the early 17th century. The breadth of musical innovation can be seen in composers like Tomás Luis de Victoria, styles like the zarzuela of Spanish opera, the ballet of Manuel de Falla, and the classical guitar music of Francisco Tárrega. Nowadays, in Spain as elsewhere, the different styles of commercial popular music are dominant. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melody
A melody (), also tune, voice, or line, is a linear succession of musical tones that the listener perceives as a single entity. In its most literal sense, a melody is a combination of Pitch (music), pitch and rhythm, while more figuratively, the term can include other musical elements such as Timbre, tonal color. It is the foreground to the background accompaniment. A line or Part (music), part need not be a foreground melody. Melodies often consist of one or more musical Phrase (music), phrases or Motif (music), motifs, and are usually repeated throughout a Musical composition, composition in various forms. Melodies may also be described by their melodic motion or the pitches or the interval (music), intervals between pitches (predominantly steps and skips, conjunct or disjunct or with further restrictions), pitch range, tension (music), tension and release, continuity and coherence, cadence (music), cadence, and shape. Function and elements Johann Philipp Kirnberger arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hi-hat (instrument)
A hi-hat (hihat, high-hat, etc.) is a combination of two cymbals and a pedal, all mounted on a metal stand. It is a part of the standard drum kit used by drummers in many styles of music including rock, pop, jazz, and blues. Hi-hats consist of a matching pair of small to medium-sized cymbals mounted on a stand, with the two cymbals facing each other. The bottom cymbal is fixed and the top is mounted on a rod which moves the top cymbal toward the bottom one when the pedal is depressed (a hi-hat that is in this position is said to be "closed" or "closed hi-hats"). The hi-hat evolved from a "sock cymbal", a pair of similar cymbals mounted at ground level on a hinged, spring-loaded foot apparatus. Drummers invented the first sock cymbals to enable one drummer to play multiple percussion instruments at the same time. Over time these became mounted on short stands—also known as "low-boys"—and activated by pedals similar to those used in modern hi-hats. When extended upward rou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snare Drum
The snare drum (or side drum) is a percussion instrument that produces a sharp staccato sound when the head is struck with a drum stick, due to the use of a series of stiff wires held under tension against the lower skin. Snare drums are often used in Orchestra, orchestras, Concert band, concert bands, Marching band, marching bands, Parade, parades, drumlines, drum corps, and more. It is one of the central pieces in a drum set, a collection of percussion instruments designed to be played by a seated drummer and used in many genres of music. Because basic rhythms are very easy to learn to play on a snare drum even for children, the instrument is also suitable for the music education for young children and a rhythm band. Snare drums are usually played with drum sticks, but other beaters such as the Brush (percussion), brush or the Rute (music), rute can be used to achieve different tones. The snare drum is a versatile and expressive percussion instrument due to its sensitivity and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bass Drum
The bass drum is a large drum that produces a note of low definite or indefinite pitch. The instrument is typically cylindrical, with the drum's diameter usually greater than its depth, with a struck head at both ends of the cylinder. The heads may be made of calfskin or plastic and there is normally a means of adjusting the tension, either by threaded taps or by strings. Bass drums are built in a variety of sizes, but size does not dictate the volume produced by the drum. The pitch and the sound can vary much with different sizes,Norman Del Mar, Del Mar, Norman (1981). ''Anatomy of the Orchestra''. . but the size is also chosen based on convenience and aesthetics. Bass drums are percussion instruments that vary in size and are used in several musical genres. Three major types of bass drums can be distinguished. * The type usually seen or heard in orchestral, ensemble or concert band music is the orchestral, or concert bass drum (in Italian: gran cassa, gran tamburo). It is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cymbal
A cymbal is a common percussion instrument. Often used in pairs, cymbals consist of thin, normally round plates of various alloys. The majority of cymbals are of indefinite pitch, although small disc-shaped cymbals based on ancient designs sound a definite note (such as crotales). Cymbals are used in many ensembles ranging from the orchestra, percussion ensembles, jazz bands, heavy metal bands, and marching groups. Drum kits usually incorporate at least a crash, ride, or crash/ride, and a pair of hi-hat cymbals. A player of cymbals is known as a cymbalist. Etymology and names The word cymbal is derived from the Latin , which is the latinisation , which in turn derives . In orchestral scores, cymbals may be indicated by the French ; German , , , or ; Italian or ; and Spanish . Many of these derive from the word for plates. History Cymbals have existed since ancient times. Representations of cymbals may be found in reliefs and paintings from Armenian Highlands (7t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meter (music)
In music, metre (British spelling) or meter (American spelling) refers to regularly recurring patterns and accents such as bar (music), bars and Beat (music), beats. Unlike rhythm (music), rhythm, metric onsets are not necessarily sounded, but are nevertheless implied by the performer (or performers) and expected by the listener. A variety of systems exist throughout the world for organising and playing metrical music, such as the Music of India, Indian system of ''Tala (music), tala'' and similar systems in Rhythm in Arabic music, Arabic and Rhythm in Sub-Saharan Africa, African music. Western culture, Western music inherited the concept of metre from poetry, where it denotes the number of lines in a Verse (poetry), verse, the number of syllables in each line, and the arrangement of those syllables as long or short, accented or unaccented. The first coherent system of Chord chart, rhythmic notation in modern Western music was based on rhythmic modes derived from the Foot (prosod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
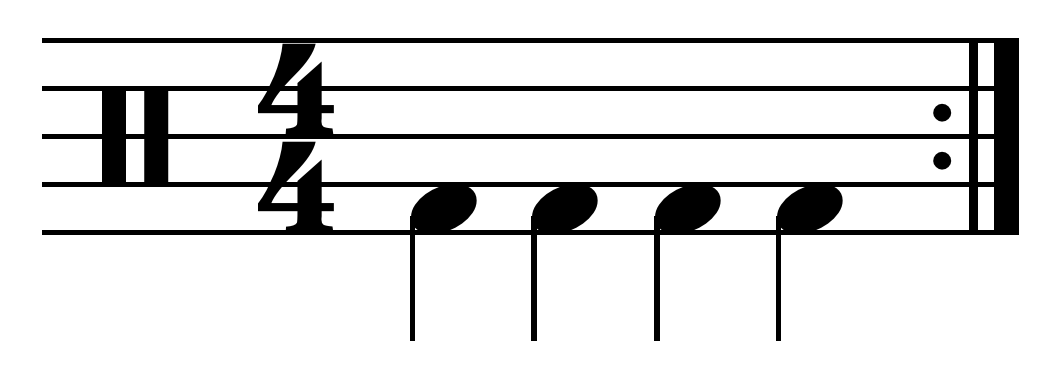
Triple Metre
Triple metre (or Am. triple meter, also known as triple time) is a musical metre characterized by a ''primary'' division of 3 beats to the bar, usually indicated by 3 (simple) or 9 ( compound) in the upper figure of the time signature, with , and being the most common examples. In these signatures, beats form groups of three, establishing a triple meter feel in the music or song. The upper figure being divisible by three does not of itself indicate triple metre; for example, a time signature of usually indicates compound duple metre, and similarly usually indicates compound quadruple metre. Shown below are a simple and a compound triple drum pattern. \new Staff \new Staff Stylistic differences In popular music, the metre is most often quadruple,Schroedl, Scott (2001). ''Play Drums Today!'', p. 42. Hal Leonard. . but this does not mean that triple metre does not appear. In jazz, this and other more adventurous metres have become more common since Dave Brubeck's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudiment
In ''rudimental drumming'', a form of percussion music, a drum rudiment is one of a number of relatively small patterns which form the foundation for more extended and complex drumming patterns. The term "drum rudiment" is most closely associated with various forms of ''field drumming'', where the snare drum plays a prominent role. In this context "rudiment" means not only "basic", but also ''fundamental''. This tradition of drumming originates in military drumming and it is a central component of martial music. Definition Rudimental drumming has something of a flexible definition, even within drumming societies devoted to that form of drumming. RudimentalDrumming.com defines it as "the study of coordination." The Percussive Arts Society defines it as a particular method for learning the drums—beginning with rudiments, and gradually building up speed and complexity through practicing those rudiments. ''Camp Duty Update'' defines a drum rudiment as an excerpt from a mili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Grip
In percussion, grip refers to the manner in which the player holds the sticks or mallets, whether drum sticks or other mallets. For some instruments, such as triangles and gongs, only a single mallet or beater is normally used, held either in one hand or both for larger beaters. For others, such as snare drums, two beaters are often used, one in each hand. More rarely, more than one beater may be held in one hand. For example, when four mallets are used on a vibraphone, or when a kit drummer performs a cymbal roll by holding two soft sticks in one hand while keeping a rhythm with the other. Matched or unmatched When two identical beaters are used, one in each hand, there are two main varieties of grip: * Unmatched grips, known as traditional grips because of their association with traditional snare drum and drum kit playing, in which the right and left hands grip the sticks in different ways, often one underhand and one overhand. * Matched grips in which the hands hol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zutty Singleton
Arthur James "Zutty" Singleton (May 14, 1898 – July 14, 1975) was an American jazz drummer. Career Singleton was born in Bunkie, Louisiana, United States, and raised in New Orleans. According to his ''Jazz Profiles'' biography, his unusual nickname, acquired in infancy, is the Creole word for "cute". by Steven A. Cerra, a Jazz Profiles Retrieved April 28, 2017. He was working professionally with Steve Lewis by 1915. He served with the |