|
Japanese People In Russia
Japanese people in Russia form a small part of the worldwide community of ''Nikkeijin'', consisting mainly of Japanese people, Japanese expatriates and their descendants born in Russia. They count various notable political figures among their number. Early settlement The first Japanese people, Japanese person to settle in Russia is believed to have been Dembei, a fisherman stranded on the Kamchatka Peninsula in 1701 or 1702. Unable to return to his native Ōsaka due to the Tokugawa Shogunate's ''sakoku'' policy, he was instead taken to Moscow and ordered by Peter I of Russia, Peter the Great to begin teaching the language as soon as possible; he thus became the father of Japanese language education in Russia. Japanese settlement in Russia remained sporadic, confined to the Russian Far East, and also of a largely unofficial character, consisting of fishermen who, like Dembei, landed there by accident and were unable to return to Japan. However, a Japanese trading post is known to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ōsaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third-most populous city in Japan, following the special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of 2.7 million in the 2020 census, it is also the largest component of the Keihanshin Metropolitan Area, which is the second-largest metropolitan area in Japan and the 10th- largest urban area in the world with more than 19 million inhabitants. Ōsaka was traditionally considered Japan's economic hub. By the Kofun period (300–538) it had developed into an important regional port, and in the 7th and 8th centuries, it served briefly as the imperial capital. Osaka continued to flourish during the Edo period (1603–1867) and became known as a center of Japanese culture. Following the Meiji Restoration, Osaka greatly expanded in size and underwent rapid industrialization. In 1889, Osaka was officially established as a municipality. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War (8 February 1904 – 5 September 1905) was fought between the Russian Empire and the Empire of Japan over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major land battles of the war were fought on the Liaodong Peninsula and near Shenyang, Mukden in Southern Manchuria, with naval battles taking place in the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. Russia had pursued an expansionist policy in Siberia and the Russian Far East, Far East since the reign of Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century. At the end of the First Sino-Japanese War, the Treaty of Shimonoseki of 1895 had ceded the Liaodong Peninsula and Lüshun Port, Port Arthur to Japan before the Triple Intervention, in which Russia, Germany, and France forced Japan to relinquish its claim. Japan feared that Russia would impede its plans to establish a sphere of influence in mainland Asia, especially as Russia built the Trans-Siberian Railway, Trans-Siberian Railroad, began making inroads in K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese-Russian Relations
Japanese Russian or Russian Japanese may refer to: * Japanese-Russian relations (cf. "a Japanese-Russian treaty") * Japanese language education in Russia (cf. "Russian Japanese education") ** Cyrillization of Japanese See also *Japanese people in Russia Japanese people in Russia form a small part of the worldwide community of ''Nikkeijin'', consisting mainly of Japanese people, Japanese expatriates and their descendants born in Russia. They count various notable political figures among their num ... * Russians in Japan {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyūshū
is the third-largest island of Japan's four main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands (i.e. excluding Okinawa and the other Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Islands). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surrounding islands. Kyushu has a land area of and a population of 14,311,224 in 2018. In ancient times, there is a theory that Kyushu was home to its own independent dynasty, where a unique, southern-influenced culture and tradition distinct from that of Honshu flourished. In the 8th-century Taihō Code reforms, Dazaifu was established as a special administrative term for the region. Geography The island is mountainous, and Japan's most active volcano, Mount Aso at , is on Kyūshū. There are many other signs of tectonic activity, including numerous areas of hot springs. The most famous of these are in Beppu, on the east shore, and around Mt. Aso in central Kyūshū. The island is separated f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koryo-saram
Koryo-saram (; ) or Koryoin () are ethnic Koreans of the post-Soviet states, former Soviet Union, who descend from Koreans that were living in the Russian Far East. Koreans first began settling in the Russian Far East in the late 19th century. Their numbers increased as Koreans fled the Korea under Japanese rule, Japanese colonization of Korea beginning in 1910. A number of Koryo-saram became significant List of Korean independence activists, Korean independence activists, such as Hong Beom-do and Chŏng Sangjin. In 1937, Deportation of Koreans in the Soviet Union, they were all deported to Central Asia. They have since dispersed throughout the former Soviet Union, with significant populations in Siberia, Uzbekistan, and Kazakhstan. Approximately 500,000 Koryo-saram reside in the former Soviet Union, primarily in the now-independent states of Central Asia. There are also large Korean communities in Southern Russia (around Volgograd), the Russian Far East (around Vladivostok), th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karayuki
Prostitution in Japan has existed throughout the country's history. While the Prostitution Prevention Law of 1956 states that "No person may either do prostitution or become the customer of it", loopholes, liberal interpretations and a loose enforcement of the law have allowed the Japanese sex industry to prosper and earn an estimated 2.3 trillion yen ($24 billion) per year. Sex trade and sex services may be referred to as , which also means "manners", "customs" or "public morals". Since Japanese law defines prostitution as "intercourse with an unspecified person in exchange for payment", most services offer specifically non-coital services, such as conversation, dancing or bathing, sometimes accompanied by sexual acts that legally are not defined as "intercourse", in order to remain legal. History From the 15th century, Chinese, Koreans, and other East Asian visitors frequented brothels in Japan. This practice later continued among visitors from "the Western regions", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Tokugawa Shogunate
were the final years of the Edo period when the Tokugawa shogunate ended. Between 1853 and 1867, under foreign diplomatic and military pressure, Japan ended its isolationist foreign policy known as and changed from a feudal Tokugawa shogunate to the modern empire of the Meiji government. The major ideological-political divide during this period was between the pro-imperial nationalists called and the shogunate forces, which included the elite swordsmen. Although these two groups were the most visible powers, many other factions attempted to use the chaos of to seize personal power. Furthermore, there were two other main driving forces for dissent: first, growing resentment on the part of the (or outside lords), and second, growing anti-Western sentiment following the arrival of Matthew C. Perry. The first related to those lords whose predecessors had fought against Tokugawa forces at the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600, after which they had been permanently excluded from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty Legacy of the Qing dynasty, assembled the territoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
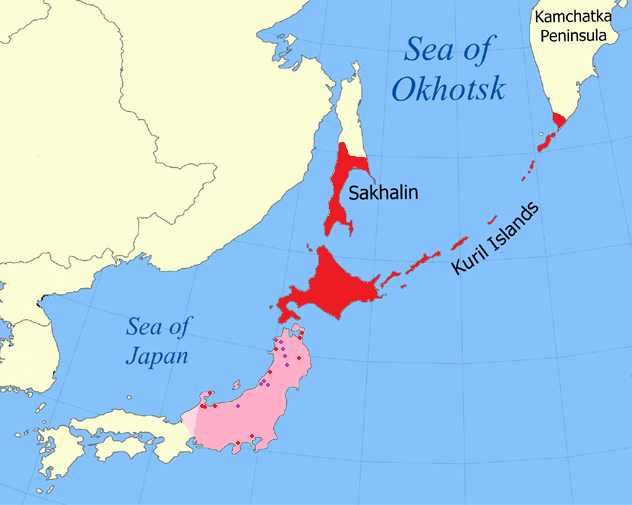
Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, p=səxɐˈlʲin) is an island in Northeast Asia. Its north coast lies off the southeastern coast of Khabarovsk Krai in Russia, while its southern tip lies north of the Japanese island of Hokkaido. An island of the West Pacific, Sakhalin divides the Sea of Okhotsk to its east from the Sea of Japan to its southwest. It is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast and is the largest island of Russia, with an area of . The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of whom are Russians. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers. The island's name is derived from the Manchu word ''Sahaliyan'' (), which was the name of the Qing dynasty city of Aigun. The Ainu people of Sakhalin paid tribute to the Yuan, Ming, and Qing dynasties and accepted official appointments from them. Sometimes the relationship was forced but control from dynasties in China was loose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Far East
The Russian Far East ( rus, Дальний Восток России, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asia, Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Eastern Federal District, which encompasses the area between Lake Baikal and the Pacific Ocean. The area's largest city is Khabarovsk, followed by Vladivostok. The region shares land borders with the countries of Mongolia, China, and North Korea to its south, as well as maritime boundary, maritime boundaries with Japan to its southeast, and with the United States along the Bering Strait to its northeast. Although the Russian Far East is often considered as a part of Siberia abroad, it has been historically categorized separately from Siberia in Russian regional schemes (and previously during the history of the Soviet Union, Soviet era when it was called the Soviet Far East). Terminology In Russia, the region is usually referred to as simply th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Language Education In Russia
Japanese language education in Russia formally dates back to December 1701 or January 1702, when Dembei, a shipwrecked Japanese merchant, was taken to Moscow and ordered to begin teaching the language as soon as possible. A 2006 survey by the Japan Foundation found 451 teachers teaching the language to 9,644 students at 143 institutions; the number of students had grown by 4.8% since the previous year. Aside from one Japanese-medium school serving Japanese people in Russia (the Japanese School in Moscow, founded in 1965), virtually all Japanese language education in Russia throughout history has been aimed at non-native speakers. As of 2021, according to the Japan Foundation, 12,426 people were learning Japanese in Russia. History Tsarist Russia Russian interest in Japan dated back to the early 17th century, when Flemish cartographer Gerardus Mercator's descriptions of Japan were translated into Russian. (The Russian ambassador to China at the time, Nikolai Spathari, also trie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |