|
Japanese Cultural House In Paris
The Japanese Culture House of Paris (French: La maison de la culture du Japon à Paris) ( Japanese: パリ日本文化会館) (also known as MCJP) is located at 101 bis, quai Jacques-Chirac, in the 15th arrondissement of Paris. Its purpose is to introduce Japanese culture to the French. It is managed by the Japan Foundation in France. Building The project for such an establishment was launched during a meeting in Japan between the President of the French Republic François Mitterrand and the Japanese Prime Minister Zenkō Suzuki. The building is the work of two architects, the British architect, Kenneth Armstrong and the Japanese architect, Masayuki Yamanaka. Started in 1994, the construction completed at the end of 1997. The MCJP was inaugurated on May 13, 1997, by the President of the French Republic at the time, Jacques Chirac, and by Princess Sayako. Description The building, built on a pre-existed building, from the Haussmann's renovation era of Paris, with a large mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Institution
A cultural institution or cultural organization is an organization within a culture/ subculture that works for the preservation or promotion of culture. The term is especially used of public and charitable organizations, but its range of meaning can be very broad. Examples of cultural institutions in modern society are museums, libraries, archives, churches, art galleries, theaters, concert halls and opera houses. See also * Art world * Confucius Institute Confucius Institutes (CI; ) are public educational and cultural promotion programs funded and arranged currently by the , a government-organized non-governmental organization (GONGO) under the Ministry of Education of the People's Republic of ... * GLAM (industry sector) * Institution References External links Social institutions * {{socio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haussmann's Renovation Of Paris
Haussmann's renovation of Paris was a vast public works programme commissioned by Emperor Napoleon III and directed by his prefect of Seine, Georges-Eugène Haussmann, between 1853 and 1870. It included the demolition of medieval neighbourhoods that were deemed overcrowded and unhealthy by officials at the time; the building of wide avenues; new parks and squares; the annexation of the suburbs surrounding Paris; and the construction of new sewers, fountains and aqueducts. Haussmann's work was met with fierce opposition, and he was finally dismissed by Napoleon III in 1870; but work on his projects continued until 1927. The street plan and distinctive appearance of the centre of Paris today are largely the result of Haussmann's renovation. Overcrowding, disease, crime and unrest in the centre of the old Paris In the middle of the 19th century, the centre of Paris was viewed as overcrowded, dark, dangerous, and unhealthy. In 1845, the French social reformer Victor Consideran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France–Japan Relations
The history of relations between France and Japan goes back to the early 17th century, when a Japanese samurai and ambassador on his way to Rome landed for a few days in Saint-Tropez and created a sensation. France and Japan have enjoyed a very robust and progressive relationship spanning centuries through various contacts in each other's countries by senior representatives, strategic efforts, and cultural exchanges. After nearly two centuries of seclusion by "Sakoku" in Japan, the two countries became very important partners from the second half of the 19th century in the military, economic, legal and artistic fields. The Tokugawa shogunate (''Bakufu'') modernized its army through the assistance of French military missions (Jules Brunet), and Japan later relied on France for several aspects of its modernization, particularly the development of a shipbuilding industry during the early years of the Imperial Japanese Navy (Léonce Verny, Émile Bertin), and the development of a Leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grenelle
Grenelle () is a neighbourhood in southwestern Paris, France. It is a part of the 15th arrondissement of the city. There is currently a Boulevard de Grenelle which runs along the North delimitation of the ''quartier'', and a Rue de Grenelle, a few kilometers North-East in the 7th arrondissement. History In 52 BC, ''Garanella'' plain was the site of the Battle of Lutetia between the troops of the Gaulish chief Camulogène and the Roman legion under General Labienus. Despite their courageous resistance, the Gauls were defeated. Towards the middle of the 13th century, Grenelle became a fiefdom of the Abbey of St Genevieve and became part of the village of Vaugirard. On May 15, 1824, two city councillors from Vaugirard, Jean-Léonard Violet and Alphonse Letellier, bought and divided up Grenelle plain. They did this rather quickly, and the new ''quartier'' '' Beaugrenelle'' was founded on June 27, 1824. Thenceforth, under the encouragement of a group of entrepreneurs (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le HuffPost
''HuffPost'' (formerly ''The Huffington Post'' until 2017 and sometimes abbreviated ''HuffPo'') is an American progressive news website, with localized and international editions. The site offers news, satire, blogs, and original content, and covers politics, business, entertainment, environment, technology, popular media, lifestyle, culture, comedy, healthy living, women's interests, and local news featuring columnists. It was created to provide a progressive alternative to the conservative news websites such as the Drudge Report. The site offers content posted directly on the site as well as user-generated content via video blogging, audio, and photo. In 2012, the website became the first commercially run United States digital media enterprise to win a Pulitzer Prize. Founded by Andrew Breitbart, Arianna Huffington, Kenneth Lerer, and Jonah Peretti, the site was launched on May 9, 2005 as a counterpart to the Drudge Report. In March 2011, it was acquired by AOL for US$315&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quai Branly Museum
A wharf, quay (, also ), staith, or staithe is a structure on the shore of a harbour or on the bank of a river or canal where ships may dock to load and unload cargo or passengers. Such a structure includes one or more berths (mooring locations), and may also include piers, warehouses, or other facilities necessary for handling the ships. Wharves are often considered to be a series of docks at which boats are stationed. Overview A wharf commonly comprises a fixed platform, often on pilings. Commercial ports may have warehouses that serve as interim storage: where it is sufficient a single wharf with a single berth constructed along the land adjacent to the water is normally used; where there is a need for more capacity multiple wharves, or perhaps a single large wharf with multiple berths, will instead be constructed, sometimes projecting over the water. A pier, raised over the water rather than within it, is commonly used for cases where the weight or volume of cargos will be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Paris
The Council of Paris (French: ''Conseil de Paris'') is the deliberative body responsible for governing Paris, the capital of France. It possesses both the powers of a municipal council (''conseil municipal'') and those of a departmental council (''conseil départemental'') for the ''département de Paris'', as defined by the so-called PLM Law (''Loi PLM'') of 1982 that redefined the governance of Paris, Lyon and Marseille (hence the PLM acronym). Paris is the only territorial collectivity in France to be both a ''commune'' and a ''département''. The Mayor of Paris presides over the Council of Paris and therefore holds the powers of mayor and of president of the departmental council. There are currently 163 councillors for Paris. History Although the history of Paris spans millennia, that of its municipal government, in its present form, is less than half a century old. Paris and its environs were always governed directly by the highest French polity of the time: the Crown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Batchelor (missionary)
Archdeacon John Batchelor D.D., OBE (20 March 1855 – 2 April 1944) was an Anglican English missionary to the Ainu people of Japan until 1941. First sent under the auspices of the Church Mission Society of the Church of England, Batchelor lived from 1877 to 1941 among the indigenous Ainu communities in the Northern Japanese island of Hokkaido. He was a charismatic and iconoclastic missionary for the Anglican Church in Japan and published highly regarded work on the language and culture of the Ainu people. Batchelor only reluctantly left Japan at the outbreak of the Second World War in 1941. Early life and missionary career John Batchelor was born in Uckfield, East Sussex son of William Batchelor, a local tailor and parish clerk. Batchelor attended Uckfield Grammar School and with the support of the Rev. E.T. Cardale was accepted as a candidate for study at the Church Missionary Society College, Islington. On 22 September 1875, Batchelor set out with a group of Church ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ainu People
The Ainu are the indigenous people of the lands surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, including Hokkaido Island, Northeast Honshu Island, Sakhalin Island, the Kuril Islands, the Kamchatka Peninsula and Khabarovsk Krai, before the arrival of the Yamato Japanese and Russians. These regions are referred to as in historical Japanese texts. Official estimates place the total Ainu population of Japan at 25,000. Unofficial estimates place the total population at 200,000 or higher, as the near-total assimilation of the Ainu into Japanese society has resulted in many individuals of Ainu descent having no knowledge of their ancestry. As of 2000, the number of "pure" Ainu was estimated at about 300 people. In 1966, there were about 300 native Ainu speakers; in 2008, however, there were about 100. Names This people's most widely known ethnonym, "Ainu" ( ain, ; ja, アイヌ; russian: Айны) means "human" in the Ainu language, particularly as opposed to , divine beings. Ainu also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Tea Ceremony
The Japanese tea ceremony (known as or ) is a Japanese cultural activity involving the ceremonial preparation and presentation of , powdered green tea, the procedure of which is called . While in the West it is known as "tea ceremony", it is seldom ceremonial in practice. Most often tea is served to family, friends, and associates; religious and ceremonial connotations are overstated in western spaces. While in the West it is known as a form of tea ceremony, in Japan the art and philosophy of tea can be more accurately described as "Teaism" as opposed to focusing on the ceremonial aspect. Zen Buddhism was a primary influence in the development of the culture of Japanese tea. Much less commonly, Japanese tea practice uses leaf tea, primarily , a practice known as . Tea gatherings are classified as either an informal tea gathering () or a formal tea gathering (). A is a relatively simple course of hospitality that includes confections, thin tea, and perhaps a light meal. A is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
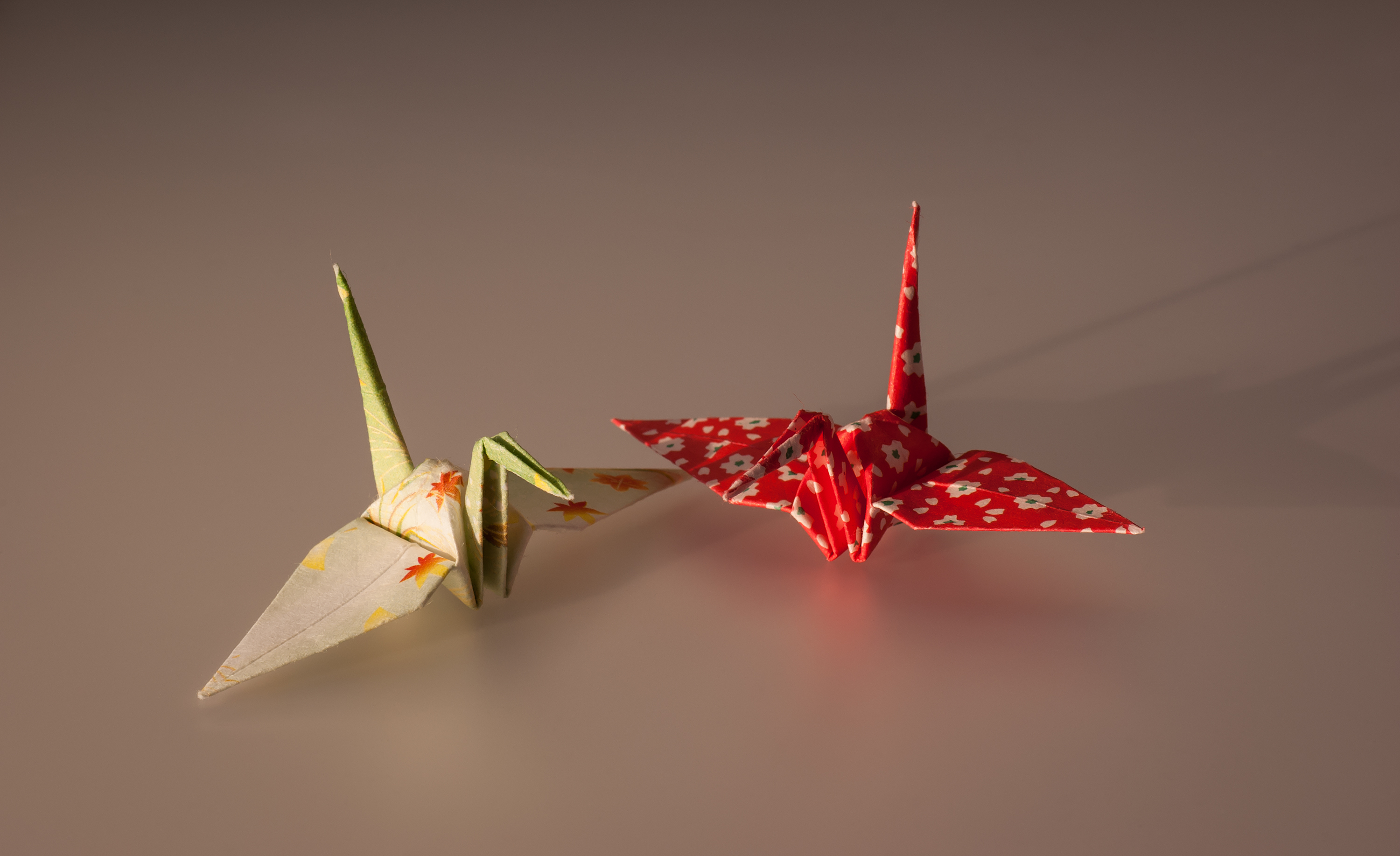
Origami
) is the Japanese art of paper folding. In modern usage, the word "origami" is often used as an inclusive term for all folding practices, regardless of their culture of origin. The goal is to transform a flat square sheet of paper into a finished sculpture through folding and sculpting techniques. Modern origami practitioners generally discourage the use of cuts, glue, or markings on the paper. Origami folders often use the Japanese word ' to refer to designs which use cuts. On the other hand, in the detailed Japanese classification, origami is divided into stylized ceremonial origami (儀礼折り紙, ''girei origami'') and recreational origami (遊戯折り紙, ''yūgi origami''), and only recreational origami is generally recognized as origami. In Japan, ceremonial origami is generally called "origata" ( :ja:折形) to distinguish it from recreational origami. The term "origata" is one of the old terms for origami. The small number of basic origami folds can be combin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manga
Manga ( Japanese: 漫画 ) are comics or graphic novels originating from Japan. Most manga conform to a style developed in Japan in the late 19th century, and the form has a long prehistory in earlier Japanese art. The term ''manga'' is used in Japan to refer to both comics and cartooning. Outside of Japan, the word is typically used to refer to comics originally published in the country. In Japan, people of all ages and walks of life read manga. The medium includes works in a broad range of genres: action, adventure, business and commerce, comedy, detective, drama, historical, horror, mystery, romance, science fiction and fantasy, erotica (''hentai'' and '' ecchi''), sports and games, and suspense, among others. Many manga are translated into other languages. Since the 1950s, manga has become an increasingly major part of the Japanese publishing industry. By 1995, the manga market in Japan was valued at (), with annual sales of 1.9billion manga books and mang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |