|
Jacob Of Chinon
Rabbi Jacob of Chinon also known as Rav Tam of Chinon (Hebrew: רב יעקב מקינון; -1260) was a 13th-century French Tosafist from Chinon. He was a pupil of Isaac ben Abraham of Dampierre and a teacher of Perez of Corbeil. Mordechai ben Hillel mentions that Jacob wrote "Shitṭah", a commentary on the Talmudic tractate, Sanhedrin The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Middle Aramaic , a loanword from , 'assembly,' 'sitting together,' hence ' assembly' or 'council') was a Jewish legislative and judicial assembly of either 23 or 70 elders, existing at both a local and central level i .... Besides that Rabbi Jacob is known for several of his tosafot. References 13th-century French rabbis Tosafists 1190 births 1260 deaths {{France-rabbi-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Language
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language until after 200 CE and as the liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. The language was revived as a spoken language in the 19th century, and is the only successful large-scale example of linguistic revival. It is the only Canaanite language, as well as one of only two Northwest Semitic languages, with the other being Aramaic, still spoken today. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosafist
The Tosafot, Tosafos or Tosfot () are medieval commentaries on the Talmud. They take the form of critical and explanatory glosses, printed, in almost all Talmud editions, on the outer margin and opposite Rashi's notes. The authors of the Tosafot are known as Tosafists; for a listing (see List of Tosafists.) Meaning of name The word ''tosafot'' literally means "additions". The reason for the title is a matter of dispute among modern scholars. Many of them, including Heinrich Graetz, think the glosses are so-called as additions to Rashi's commentary on the Talmud. In fact, the period of the Tosafot began immediately after Rashi had written his commentary; the first tosafists were Rashi's sons-in-law and grandsons, and the Tosafot consist mainly of strictures on Rashi's commentary. Others, especially Isaac Hirsch Weiss, object that many tosafot — particularly those of Isaiah di Trani — have no reference to Rashi. Weiss, followed by other scholars, asserts that ''tosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinon
Chinon () is a Communes of France, commune in the Indre-et-Loire Departments of France, department, Centre-Val de Loire, France. The traditional province around Chinon, Touraine, became a favorite resort of French kings and their nobles beginning in the late 15th and early 16th centuries. The Renaissance châteaux which they built new or erected on the foundations of old fortresses earned this part of the Loire Valley the nickname "The Garden of France." Chinon played an important and strategic role during the Middle Ages, serving both French and English kings. Chinon is known for Chinon AOC, its wine, Château de Chinon, castle, and historic town. Its part of the Loire Valley has been registered as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2000. History The historic town of Chinon is on the banks of the river Vienne (river), Vienne about from where it joins the Loire. Settlement in Chinon dates from prehistoric times, with a pronounced importance for both French and English histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Ben Abraham Of Dampierre
Isaac ben Abraham (יצחק בן אברהם), also called Rabbi Isaac ha-Baḥur (Hebrew: ר"י הבחור or רבי יצחק הבחור, which translates to "Rabbi Isaac the Younger") and by its Hebrew acronym RIBA (ריב"א) or RIẒBA (ריצב"א), was a tosafist of the late twelfth and early thirteenth centuries. He succeeded his teacher Isaac ben Samuel as head of the school of Dampierre, after which place he is often called, as well as by the epithet Isaac ha-Baḥur ("the younger"), to distinguish him from his teacher, Isaac ben Samuel ha-Zaḳen ("the elder") (ר"י הזקן). Life Together with his brother, Samson ben Abraham of Sens, Isaac lived as a youth at Troyes, where he attended the lectures of Jacob Tam, and afterward at Sens, before the two studied together at Dampierre. Isaac died at Dampierre prior to 1210, not long before his brother Samson emigrated to Palestine. Isaac was one of the French rabbis to whom Meïr ben Todros Abulafia addressed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peretz Ben Elijah
Perez ben Elijah of Corbeil (died about 1295) was a French tosafist, son of the Talmudist Elijah of Tours. In Talmudic literature he is designated by the abbreviations RaP (= Rabbeinu Perez), RaPaSh (= Rabbeinu Perez, may he live), and MaHaRPaSh (= our master Rabbeinu Perez, may he live). Perez had four masters Jehiel of Paris, Jacob of Chinon and Samuel of Evreux. He traveled throughout Brabant, and sojourned for a time in Germany and France, where he made the acquaintance of Meir of Rothenburg. On his return home he delivered lectures on Talmudical subjects, which were attended by the most celebrated rabbis of the fourteenth century. His fame as a Talmudical authority eventually became universal, his commentaries being studied in France, Germany, and Spain. He died before 1298, probably in 1295. Perez was the author of the following works: # Glosses on the ''Ammude ha-Golah'' of Isaac of Corbeil, published together with the text, Cremona, 1556. #Commentaries on the greater par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mordechai Ben Hillel
Mordechai ben Hillel HaKohen (; c. 1250–1298), also known as The Mordechai or, by some Sephardic scholars, as The Mordechie, was a 13th-century German rabbi and posek. His chief legal commentary on the Talmud, referred to as ''The Mordechai'', is one of the sources of the ''Shulchan Aruch''. He was killed in the Rintfleisch massacres in 1298. Biography Little is known of Mordechai's early life. He belonged to one of the most prominent families of scholars in Germany: his grandfather Hillel, on his mother's side, was a grandson of Eliezer ben Joel ha-Levi, who was in turn a grandson of Eliezer ben Nathan. Mordechai was also a relative of Rabbi Asher ben Jehiel. He was a son-in-law of R' Yechiel of Paris. He was married to Zelda, with whom he had five children. His principal teacher was Meir ben Baruch of Rothenburg; he was also taught by Perez ben Elijah of Corbeil, Ephraim ben Nathan, Abraham ben Baruch (Meir of Rothenburg's brother), and Dan Ashkenazi. In addition to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmud
The Talmud (; ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of Haskalah#Effects, modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish culture, Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The Talmud includes the teachings and opinions of thousands of rabbis on a variety of subjects, including halakha, Jewish ethics, Jewish philosophy, philosophy, Jewish customs, customs, Jewish history, history, and Jewish folklore, folklore, and many other topics. The Talmud is a commentary on the Mishnah. This text is made up of 63 Masekhet, tractates, each covering one subject area. The language of the Talmud is Jewish Babylonian Aramaic. Talmudic tradition emerged and was compiled between the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE and the Arab conquest in the early seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
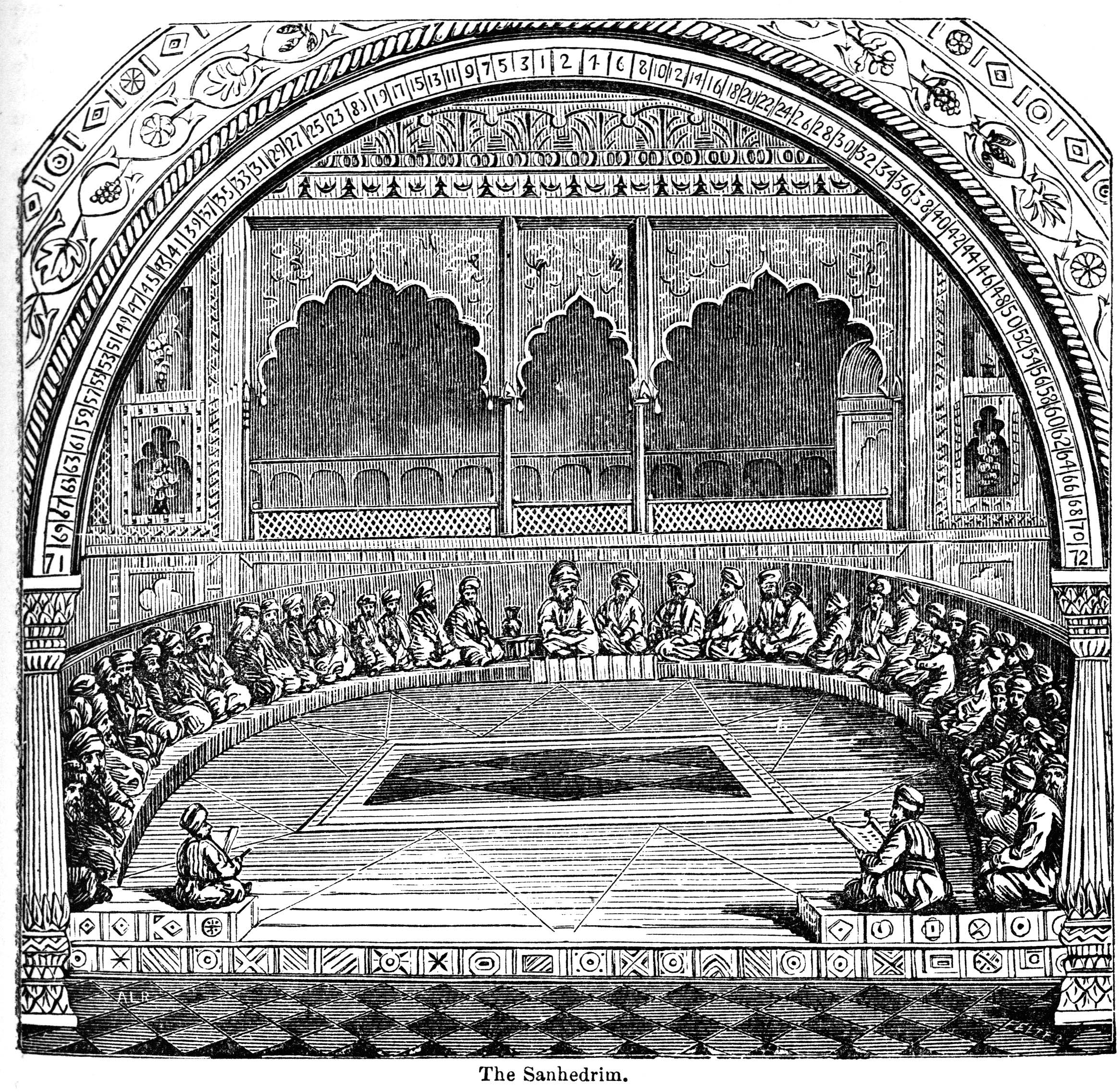
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Middle Aramaic , a loanword from , 'assembly,' 'sitting together,' hence ' assembly' or 'council') was a Jewish legislative and judicial assembly of either 23 or 70 elders, existing at both a local and central level in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite courts called sanhedrins: Greater and Lesser. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city. There was only one Great Sanhedrin of 70 judges, which, among other roles, acted as a supreme court, taking appeals from cases that lesser courts decided. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier usually refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the Nasi, who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the Av Beit Din or the chief of the court, who was second to the Nasi and 69 general members. In the Second Temple period, the Great Sanhedrin met in the Temple in Jerusalem, in a bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century French Rabbis
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 (represented by the Roman numerals MCCI) through December 31, 1300 (MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258) and the destruction of the House of Wisdom. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The earliest Islamic states in Southeast Asia formed during this century, most notably Samudera Pasai. The Kingdoms of Sukhothai and Hanthawaddy would emerge and go on to dominate their surrounding territories. Europe entered the apex of the High Middle Ages, characterized by rapid legal, cultural, and religious evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosafists
Tosafists were rabbis of France, Germany, Bohemia and Austria, who lived from the 12th to the mid-15th centuries, in the period of Rishonim. The Tosafists composed critical and explanatory glosses (questions, notes, interpretations, rulings and sources) on the Talmud, which are collectively called Tosafot ("additions"). The Tosafot are important to the practical application of Jewish law, because the law depends on how the Talmud is understood and interpreted. Alphabetical list of Tosafists Not all of the many tosafists are known by name. The following is an alphabetical list of them; many, however, are known only through citations. A (HaRA) Quoted in the edited Tosafot to Mo'ed Katan 14b, 19a, 20b, 21a etc. Avigdor Cohen of Vienna Also known as Avigdor ben Elijah ha-Kohen. Flourished in the middle of the 13th century and an early Talmudists of Austria; his tosafot are mentioned in the edited tosafot to Ketuvot 63b. Abraham ben Joseph of Orleans French Talmudist; liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1190 Births
Year 1190 (MCXC) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Spring – A German expeditionary force (some 15,000 men) led by Emperor Frederick I (Barbarossa) marches towards Constantinople, on the way to the Holy Land. Emperor Isaac II (Angelos), suspicious that Frederick is planning to conquer Constantinople, attempts to stop him by attacking the Crusaders. The German forces are too strong and they capture Adrianople. A peace treaty is signed by both Isaac and Frederick, that ensures the Germans are given supplies, and free passage through to Palestina. * Isaac II starts a campaign against the Bulgarians, who claim their independence. After passing the Balkan Mountains, Isaac marches westward to besiege Tarnovo, the new Bulgarian capital. Meanwhile, the Byzantine fleet reaches the Danube River in order to block the way of Cuman reinforcements from the North. The defense of Tarnovo is led by Ivan Asen I, emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |